Intro
Maintain healthy blood pressure during pregnancy with 5 essential tips, managing normal pregnancy BP through lifestyle changes, nutrition, and stress reduction, ensuring a safe and healthy gestation period, and minimizing risks of hypertension and preeclampsia.
Normal pregnancy blood pressure is a crucial aspect of a healthy pregnancy. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of arteries as the heart pumps blood. During pregnancy, blood pressure is closely monitored because it can affect the health of both the mother and the baby. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. On the other hand, low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, can cause dizziness, fainting, and decreased blood flow to the baby.
Maintaining a normal blood pressure during pregnancy is essential to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. A normal blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg, but it can vary slightly from person to person. During pregnancy, blood pressure tends to decrease in the first trimester due to the relaxation of blood vessels, and then it returns to pre-pregnancy levels in the second and third trimesters. It is essential to monitor blood pressure regularly during pregnancy to detect any changes or abnormalities early on.
Blood pressure monitoring during pregnancy is a critical aspect of prenatal care. Healthcare providers use a blood pressure cuff to measure blood pressure at each prenatal visit. The cuff is wrapped around the upper arm, and it inflates to constrict the artery, then deflates to release the pressure. The healthcare provider listens to the heartbeat with a stethoscope to determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings. Systolic blood pressure is the top number, which measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, while diastolic blood pressure is the bottom number, which measures the pressure in the arteries between beats.
Understanding Normal Pregnancy Blood Pressure
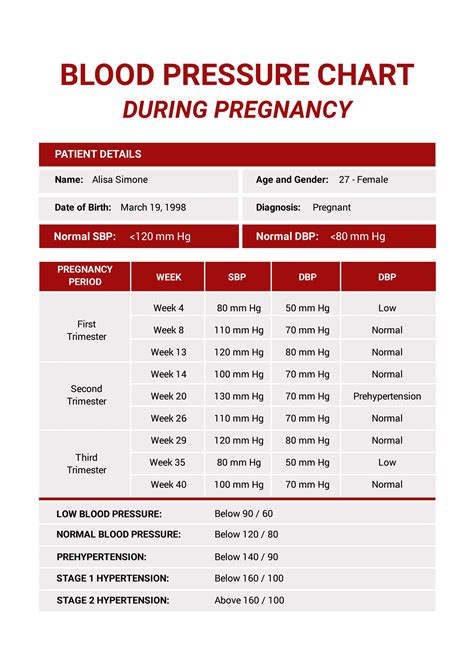
Understanding normal pregnancy blood pressure is vital to maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Normal blood pressure during pregnancy is typically defined as a systolic reading of less than 120 mmHg and a diastolic reading of less than 80 mmHg. However, some women may have a slightly higher or lower blood pressure reading due to various factors such as age, weight, and pre-existing medical conditions. It is essential to discuss any concerns or questions about blood pressure with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Several factors can affect blood pressure during pregnancy, including: * Age: Women over 35 years old are more likely to experience high blood pressure during pregnancy. * Weight: Women who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop high blood pressure during pregnancy. * Pre-existing medical conditions: Women with pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, or heart disease are more likely to experience high blood pressure during pregnancy. * Family history: Women with a family history of high blood pressure are more likely to develop high blood pressure during pregnancy. * Lifestyle factors: Women who smoke, consume excessive caffeine, or have a poor diet are more likely to experience high blood pressure during pregnancy.5 Tips for Maintaining Normal Pregnancy Blood Pressure

Maintaining normal pregnancy blood pressure requires a combination of lifestyle changes and regular monitoring. Here are 5 tips to help maintain normal pregnancy blood pressure:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help regulate blood pressure and prevent dehydration.
- Eat a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help maintain healthy blood pressure.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help lower blood pressure and improve overall health.
- Manage stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help lower blood pressure and improve overall well-being.
- Get enough sleep: Getting adequate sleep, typically 7-9 hours per night, can help regulate blood pressure and improve overall health.
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Pregnancy Blood Pressure
Maintaining normal pregnancy blood pressure has numerous benefits for both the mother and the baby. Some of the benefits include: * Reduced risk of preeclampsia and other pregnancy complications * Improved fetal growth and development * Reduced risk of low birth weight and preterm birth * Improved maternal health and well-being * Reduced risk of long-term health problems, such as heart disease and kidney diseaseMonitoring Blood Pressure During Pregnancy

Monitoring blood pressure during pregnancy is crucial to detecting any changes or abnormalities early on. Healthcare providers typically monitor blood pressure at each prenatal visit, which can range from every 4-6 weeks in the first trimester to every 1-2 weeks in the third trimester. Women with a history of high blood pressure or other medical conditions may need to monitor their blood pressure more frequently.
What to Expect During Blood Pressure Monitoring
During blood pressure monitoring, a healthcare provider will typically: * Use a blood pressure cuff to measure blood pressure * Take multiple readings to ensure accuracy * Compare readings to previous measurements to detect any changes * Discuss any concerns or questions about blood pressure with the patientManaging High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy

Managing high blood pressure during pregnancy requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Some ways to manage high blood pressure during pregnancy include:
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes to diet, exercise, and stress management can help lower blood pressure.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to lower blood pressure.
- Regular monitoring: Regular blood pressure monitoring can help detect any changes or abnormalities early on.
- Bed rest: In severe cases, bed rest may be recommended to reduce blood pressure and prevent complications.
Risks of Unmanaged High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Unmanaged high blood pressure during pregnancy can lead to serious complications, including: * Preeclampsia * Placental abruption * Premature birth * Low birth weight * Fetal growth restrictionConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal pregnancy blood pressure is crucial to ensuring a healthy pregnancy and preventing complications. By following the 5 tips outlined in this article and working closely with a healthcare provider, women can reduce their risk of high blood pressure and related complications. It is essential to stay informed and take an active role in managing blood pressure during pregnancy.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with normal pregnancy blood pressure in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with friends and family members who may be interested in learning more about normal pregnancy blood pressure.
What is normal blood pressure during pregnancy?
+Normal blood pressure during pregnancy is typically defined as a systolic reading of less than 120 mmHg and a diastolic reading of less than 80 mmHg.
How often should I monitor my blood pressure during pregnancy?
+Blood pressure should be monitored at each prenatal visit, which can range from every 4-6 weeks in the first trimester to every 1-2 weeks in the third trimester.
What are the risks of unmanaged high blood pressure during pregnancy?
+Unmanaged high blood pressure during pregnancy can lead to serious complications, including preeclampsia, placental abruption, premature birth, low birth weight, and fetal growth restriction.
