Intro
Discover the ultimate Prenatal Glucose Test Guide, covering gestational diabetes screening, glucose tolerance tests, and pregnancy blood sugar monitoring for a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Prenatal care is a crucial aspect of pregnancy, ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. One of the key tests performed during pregnancy is the prenatal glucose test, also known as the glucose screening test or gestational diabetes screening. This test is designed to detect gestational diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that can develop during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can have significant implications for both the mother's health and the baby's development, making early detection and management essential.
The importance of the prenatal glucose test cannot be overstated. Gestational diabetes affects a significant number of pregnancies worldwide and can lead to complications such as high birth weight, premature birth, and increased risk of cesarean delivery. Moreover, gestational diabetes can also have long-term health implications for both the mother and the child, including an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Therefore, understanding the prenatal glucose test, its purpose, and its implications is vital for expectant mothers.
As pregnancy progresses, the body undergoes numerous changes to support the growing fetus. One of these changes involves the way the body processes glucose, which can sometimes lead to gestational diabetes. The prenatal glucose test is a simple, non-invasive screening that helps identify women at risk of gestational diabetes. The test typically involves drinking a glucose solution and then having blood drawn after a certain period to measure glucose levels. This process allows healthcare providers to assess how well the body is regulating blood sugar levels, providing valuable insights into the risk of gestational diabetes.
Purpose of the Prenatal Glucose Test

Benefits of Early Detection
The benefits of early detection of gestational diabetes through the prenatal glucose test are multifaceted. It enables healthcare providers to implement a management plan that includes dietary changes, exercise, and, if necessary, medication to control blood sugar levels. This proactive approach can help prevent complications associated with gestational diabetes, such as high birth weight and premature birth. Furthermore, early detection and management of gestational diabetes can also reduce the risk of long-term health issues for both the mother and the child, including the development of type 2 diabetes.How the Prenatal Glucose Test Works
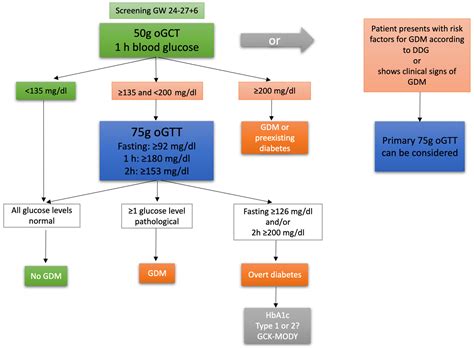
Preparing for the Test
Preparing for the prenatal glucose test is crucial to ensure accurate results. Women are usually advised to fast for a certain period before the test, although specific instructions may vary depending on the healthcare provider. It's also important to follow a normal diet for a few days leading up to the test to ensure that the results reflect typical glucose processing. On the day of the test, the glucose solution is consumed, and blood is drawn after a specified time, usually an hour, to measure glucose levels.Understanding the Results

Follow-Up Testing
The glucose tolerance test is a more detailed assessment that involves fasting, consuming a glucose solution, and then having blood drawn at multiple intervals to measure glucose levels. This test provides a comprehensive view of how the body regulates blood sugar levels over time, helping to confirm or rule out gestational diabetes. If gestational diabetes is diagnosed, healthcare providers will work with the expectant mother to develop a personalized management plan to ensure the best possible outcomes for both the mother and the baby.Managing Gestational Diabetes

Dietary Changes
Dietary changes are a cornerstone of managing gestational diabetes. This typically involves eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, and high in fiber and nutrients. Portion control is also important, as eating large meals can cause blood sugar levels to spike. Additionally, spreading meals throughout the day can help keep blood sugar levels more stable.Risks and Complications

Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of gestational diabetes are significant. Women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as well as heart disease. Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may also have an increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. Therefore, early detection and management of gestational diabetes, facilitated by the prenatal glucose test, are crucial for preventing these long-term health issues.Conclusion and Next Steps

What is the purpose of the prenatal glucose test?
+The purpose of the prenatal glucose test is to detect gestational diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that can develop during pregnancy.
How is the prenatal glucose test performed?
+The test involves consuming a glucose solution and then having blood drawn after a certain period to measure glucose levels, assessing how well the body regulates blood sugar.
What are the risks of gestational diabetes if left unmanaged?
+Unmanaged gestational diabetes can lead to complications such as high birth weight, premature birth, and an increased risk of cesarean delivery, as well as long-term health issues like type 2 diabetes for both the mother and the child.
We hope this comprehensive guide to the prenatal glucose test has provided you with valuable insights and information. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Sharing this article with others can also help spread awareness about the importance of prenatal care and the role of the glucose test in ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Thank you for reading, and we wish you all the best on your pregnancy journey.
