Intro
Discover the Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty procedure, a minimally invasive vascular treatment using balloon angioplasty and stenting to improve blood flow, reduce plaque buildup, and prevent artery blockages, promoting cardiovascular health and relieving symptoms of peripheral artery disease.
The Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) procedure has revolutionized the treatment of vascular diseases, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods. This innovative technique has been widely adopted in medical practices worldwide, providing patients with a safer, more efficient, and less painful solution for managing conditions such as atherosclerosis, peripheral artery disease, and renal artery stenosis. As medical technology continues to advance, the importance of understanding the PTA procedure cannot be overstated, particularly for individuals seeking to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
The significance of PTA lies in its ability to restore blood flow to affected areas, alleviating symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness. By inflating a small balloon within the narrowed or blocked artery, medical professionals can effectively widen the vessel, improving circulation and reducing the risk of complications. This procedure has been instrumental in enhancing the quality of life for countless individuals, enabling them to resume their daily activities with renewed vitality and confidence. Furthermore, the PTA procedure has also been shown to be an effective treatment option for patients who are at high risk for surgical complications or have undergone previous failed interventions.
The PTA procedure is typically performed in a hospital or outpatient setting, under local anesthesia and mild sedation. During the procedure, a small incision is made in the skin, and a guidewire is inserted through the femoral artery, navigating it to the affected area. A catheter is then advanced over the guidewire, and a balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed or blocked section of the artery. In some cases, a stent may be placed to keep the artery open, ensuring long-term patency and preventing restenosis. The entire process usually takes between 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the complexity of the case and the number of lesions being treated.
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty Procedure Overview
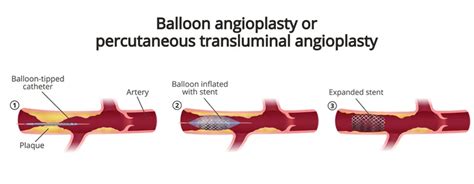
The PTA procedure offers numerous benefits, including reduced recovery time, minimal scarring, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional surgical methods. Additionally, the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day, thereby reducing hospitalization costs and minimizing the risk of hospital-acquired infections. The PTA procedure has also been shown to be highly effective in treating a wide range of vascular conditions, including iliac artery disease, femoral artery disease, and popliteal artery disease.
Indications and Contraindications
The PTA procedure is typically indicated for patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease, renal artery stenosis, or other vascular conditions that have not responded to medical therapy or lifestyle modifications. However, there are certain contraindications to the procedure, including severe vascular disease, presence of a prosthetic graft, or active bleeding disorders. Patients with severe kidney disease or those who are taking anticoagulant medications may also require special consideration before undergoing the PTA procedure.Preparation and Procedure

Before the PTA procedure, patients typically undergo a series of diagnostic tests, including angiography, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance angiography, to evaluate the extent and location of the vascular disease. Patients are also required to provide a complete medical history, including any allergies, medications, or previous surgeries. On the day of the procedure, patients are usually asked to arrive at the hospital or outpatient facility several hours in advance to allow for preparation and anesthesia administration.
The PTA procedure itself involves several key steps, including:
- Insertion of the guidewire and catheter
- Advancement of the catheter to the affected area
- Inflation of the balloon to widen the narrowed or blocked section of the artery
- Placement of a stent, if necessary
- Removal of the catheter and guidewire
- Application of pressure to the access site to prevent bleeding
Post-Procedure Care and Follow-Up
After the PTA procedure, patients are typically monitored in the recovery room for several hours to ensure that there are no complications. Patients may experience some discomfort, bruising, or swelling at the access site, but these symptoms usually resolve on their own within a few days. Patients are also advised to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for several weeks to allow the access site to heal properly.Follow-up appointments are usually scheduled several weeks after the procedure to evaluate the patient's progress and assess the patency of the treated artery. Patients may also be required to undergo additional diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound or angiography, to monitor the treated area and detect any potential complications.
Risks and Complications

While the PTA procedure is generally considered safe and effective, there are certain risks and complications that patients should be aware of. These include:
- Bleeding or hematoma at the access site
- Infection or abscess formation
- Restenosis or re-narrowing of the treated artery
- Dissection or tearing of the artery
- Embolism or blockage of a distant artery
- Contrast-induced nephropathy or kidney damage
To minimize the risk of complications, patients should carefully follow their doctor's instructions and attend all scheduled follow-up appointments.
Advantages and Limitations
The PTA procedure offers several advantages over traditional surgical methods, including reduced recovery time, minimal scarring, and lower risk of complications. Additionally, the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. However, the PTA procedure also has some limitations, including the potential for restenosis or re-narrowing of the treated artery, and the risk of complications such as bleeding or infection.Current Research and Developments

Current research and developments in the field of PTA are focused on improving the safety and efficacy of the procedure, as well as expanding its indications to include a wider range of vascular conditions. Some of the latest advancements include the development of new balloon and stent technologies, such as drug-eluting balloons and bioabsorbable stents, which are designed to reduce the risk of restenosis and improve long-term patency.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of novel imaging modalities, such as intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography, to improve the accuracy and precision of the PTA procedure. These advances have the potential to further enhance the safety and efficacy of the procedure, and to expand its indications to include a wider range of vascular conditions.
Future Directions
The future of PTA is exciting and rapidly evolving, with ongoing research and developments aimed at improving the safety, efficacy, and accessibility of the procedure. Some potential future directions include the development of new technologies, such as robotic-assisted PTA, and the expansion of the procedure to include new indications, such as treatment of cerebral vasculature and coronary artery disease.As medical technology continues to advance, it is likely that the PTA procedure will become even safer, more effective, and more widely available, offering new hope and improved outcomes for patients with vascular disease.
Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, the PTA procedure is a safe and effective treatment option for patients with vascular disease, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods. While the procedure has its risks and limitations, the benefits of PTA, including reduced recovery time, minimal scarring, and lower risk of complications, make it an attractive option for many patients.
Based on the current evidence, we recommend that patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease, renal artery stenosis, or other vascular conditions consider the PTA procedure as a potential treatment option. Additionally, we recommend that medical professionals stay up-to-date with the latest research and developments in the field of PTA, and that they carefully evaluate each patient's individual needs and circumstances before recommending the procedure.
What is the Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty procedure?
+The Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) procedure is a minimally invasive treatment option for patients with vascular disease, in which a small balloon is inflated within the narrowed or blocked artery to widen it and improve blood flow.
What are the benefits of the PTA procedure?
+The benefits of the PTA procedure include reduced recovery time, minimal scarring, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional surgical methods. Additionally, the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
What are the risks and complications of the PTA procedure?
+The risks and complications of the PTA procedure include bleeding or hematoma at the access site, infection or abscess formation, restenosis or re-narrowing of the treated artery, dissection or tearing of the artery, and embolism or blockage of a distant artery.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the PTA procedure, and to ask any questions you may have about this innovative treatment option. By working together, we can improve our understanding of the PTA procedure and its potential benefits and limitations, and provide better care and outcomes for patients with vascular disease.
