Intro
Explore private health insurance plans options, including individual, family, and group plans, with varying coverage levels, deductibles, and premiums, to find the best fit for your healthcare needs and budget.
The world of private health insurance plans can be complex and overwhelming, with numerous options available to individuals, families, and businesses. Understanding the different types of plans, their benefits, and drawbacks is crucial for making informed decisions about healthcare coverage. In this article, we will delve into the various private health insurance plans options, exploring their features, advantages, and limitations.
Private health insurance plans are designed to provide financial protection against medical expenses, offering a range of benefits, including access to healthcare services, prescription medication, and hospitalization coverage. With the rising costs of healthcare, having a private health insurance plan can help individuals and families avoid financial hardship in the event of unexpected medical expenses. Moreover, private health insurance plans often provide more comprehensive coverage than public health insurance programs, including access to specialized care, alternative therapies, and preventive services.
The importance of private health insurance plans cannot be overstated, particularly in countries with underfunded public healthcare systems. In these countries, private health insurance plans can provide a vital safety net, ensuring that individuals and families have access to quality healthcare services, regardless of their income level or social status. Furthermore, private health insurance plans can offer more flexibility and choice, allowing individuals to select from a range of providers, hospitals, and treatments, rather than being limited to a specific network or facility.
Types of Private Health Insurance Plans
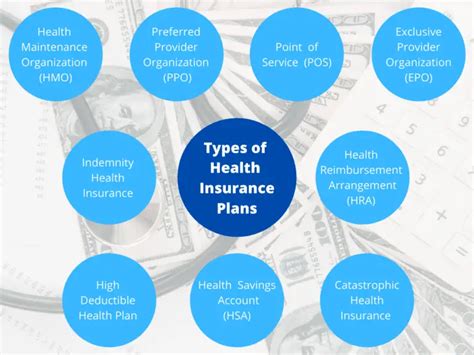
Private health insurance plans can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its unique features and benefits. The most common types of private health insurance plans include:
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans: These plans offer a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to provide discounted services to plan members. PPO plans typically require a deductible, copayment, or coinsurance for services received from in-network providers.
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans: HMO plans provide a network of healthcare providers who offer comprehensive care to plan members. HMO plans often require a referral from a primary care physician to see a specialist.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) plans: EPO plans are similar to PPO plans but do not cover services received from out-of-network providers, except in emergency situations.
- Point of Service (POS) plans: POS plans combine features of HMO and PPO plans, allowing plan members to choose between receiving care from in-network or out-of-network providers.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance Plans
Private health insurance plans offer numerous benefits, including:- Access to quality healthcare services: Private health insurance plans provide access to a network of healthcare providers, hospitals, and facilities, ensuring that plan members receive high-quality care.
- Financial protection: Private health insurance plans help protect individuals and families from financial hardship in the event of unexpected medical expenses.
- Preventive care: Many private health insurance plans cover preventive services, such as routine check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations, which can help prevent illnesses and detect health problems early.
- Choice and flexibility: Private health insurance plans often offer more flexibility and choice than public health insurance programs, allowing plan members to select from a range of providers, hospitals, and treatments.
How Private Health Insurance Plans Work

Private health insurance plans typically involve a premium, deductible, copayment, or coinsurance for services received. The premium is the monthly or annual payment made by the plan member to maintain coverage. The deductible is the amount that plan members must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance plan begins to cover expenses. Copayments and coinsurance are payments made by plan members for specific services or treatments.
The process of using a private health insurance plan typically involves the following steps:
- Selecting a plan: Plan members choose a private health insurance plan that meets their needs and budget.
- Paying premiums: Plan members pay monthly or annual premiums to maintain coverage.
- Receiving care: Plan members receive healthcare services from in-network or out-of-network providers, depending on the plan.
- Submitting claims: Plan members or healthcare providers submit claims to the insurance company for reimbursement.
- Receiving reimbursement: The insurance company reimburses plan members or healthcare providers for covered expenses.
Private Health Insurance Plan Networks
Private health insurance plan networks refer to the group of healthcare providers, hospitals, and facilities that have agreed to provide discounted services to plan members. Networks can be categorized into several types, including:- In-network providers: Healthcare providers who have agreed to participate in the plan's network, offering discounted services to plan members.
- Out-of-network providers: Healthcare providers who do not participate in the plan's network, but may still provide services to plan members at a higher cost.
- Referral networks: Networks that require plan members to obtain a referral from a primary care physician to see a specialist.
Private Health Insurance Plan Costs
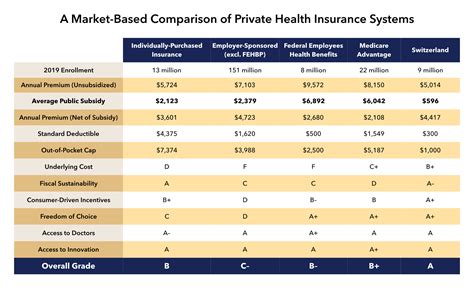
The cost of private health insurance plans can vary widely, depending on factors such as age, health status, location, and plan type. The main costs associated with private health insurance plans include:
- Premiums: Monthly or annual payments made by plan members to maintain coverage.
- Deductibles: Amounts that plan members must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance plan begins to cover expenses.
- Copayments: Payments made by plan members for specific services or treatments.
- Coinsurance: Payments made by plan members for a percentage of covered expenses.
Factors Affecting Private Health Insurance Plan Costs
Several factors can affect the cost of private health insurance plans, including:- Age: Older individuals may pay higher premiums due to increased health risks.
- Health status: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions may pay higher premiums or face coverage limitations.
- Location: Premiums can vary depending on the state or region, with urban areas often having higher costs than rural areas.
- Plan type: Different plan types, such as PPO or HMO plans, can have varying costs and benefits.
Private Health Insurance Plan Enrollment

Enrolling in a private health insurance plan typically involves the following steps:
- Researching plans: Individuals or families research and compare different private health insurance plans to find the best option for their needs and budget.
- Submitting an application: Individuals or families submit an application to the insurance company, providing required documentation and information.
- Undergoing underwriting: The insurance company reviews the application and may require additional information or medical examinations to determine eligibility and premium rates.
- Receiving approval: The insurance company approves or denies the application, and plan members receive notification of their coverage and premium rates.
Private Health Insurance Plan Eligibility
Eligibility for private health insurance plans can vary depending on the insurance company and plan type. Generally, eligibility is based on factors such as:- Age: Most private health insurance plans are available to individuals and families of all ages.
- Health status: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions may face coverage limitations or higher premiums.
- Income: Some private health insurance plans may have income limits or restrictions.
- Employment: Some private health insurance plans may be available only to employees or members of certain organizations.
Private Health Insurance Plan Benefits and Limitations
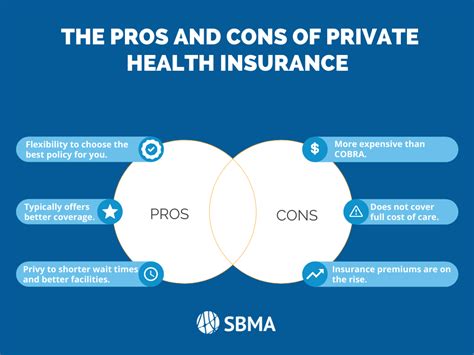
Private health insurance plans offer numerous benefits, including access to quality healthcare services, financial protection, and preventive care. However, private health insurance plans also have limitations, such as:
- Cost: Private health insurance plans can be expensive, with high premiums, deductibles, and copayments.
- Network restrictions: Plan members may face restrictions on accessing care from out-of-network providers.
- Coverage limitations: Private health insurance plans may have coverage limitations or exclusions for certain services or treatments.
Private Health Insurance Plan Alternatives
Individuals or families who are unable to afford private health insurance plans or face coverage limitations may consider alternative options, such as:- Public health insurance programs: Government-sponsored health insurance programs, such as Medicaid or the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace plans.
- Short-term health insurance plans: Temporary health insurance plans that provide limited coverage for a specific period.
- Health sharing ministries: Non-profit organizations that provide healthcare coverage to members through shared contributions.
What are the main types of private health insurance plans?
+The main types of private health insurance plans include Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans, Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans, Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) plans, and Point of Service (POS) plans.
How do private health insurance plans work?
+Private health insurance plans typically involve a premium, deductible, copayment, or coinsurance for services received. Plan members pay premiums, receive care from in-network or out-of-network providers, submit claims, and receive reimbursement for covered expenses.
What are the benefits of private health insurance plans?
+Private health insurance plans offer numerous benefits, including access to quality healthcare services, financial protection, preventive care, and choice and flexibility in selecting healthcare providers and treatments.
In summary, private health insurance plans offer a range of benefits and options for individuals, families, and businesses. By understanding the different types of plans, their benefits, and limitations, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage. Whether you are looking for comprehensive coverage, flexibility, or affordability, there is a private health insurance plan that can meet your needs. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with private health insurance plans in the comments below and to explore the various options available to find the best plan for your unique situation.
