Intro
Understand low albumin blood test results, causes, and symptoms. Learn about hypoalbuminemia, liver and kidney issues, and nutritional deficiencies affecting albumin levels, and discover treatment options for optimal health.
Albumin is a type of protein found in the blood, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions. A low albumin blood test result can indicate a range of health issues, from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the world of albumin, exploring its importance, the reasons behind low albumin levels, and what it means for your overall health.
Albumin is produced by the liver and secreted into the bloodstream, where it accounts for approximately 50-60% of the total protein content. This protein is essential for maintaining blood volume, transporting hormones, vitamins, and other nutrients throughout the body, and regulating blood pressure. A decrease in albumin levels can disrupt these functions, leading to a range of symptoms and health complications. Understanding the causes and consequences of low albumin levels is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
The importance of albumin in the body cannot be overstated. It helps to maintain blood volume, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs. Albumin also binds to various substances, such as calcium, hormones, and vitamins, facilitating their transport to target cells. Additionally, albumin plays a role in regulating blood pressure and preventing fluid buildup in the body. With so many critical functions, it is no wonder that low albumin levels can have far-reaching consequences for overall health and well-being.
What is a Low Albumin Blood Test Result?

A low albumin blood test result is typically defined as a level below 3.4 grams per deciliter (g/dL) of blood. However, the normal range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the significance of your test results and to discuss any concerns or questions you may have.
Causes of Low Albumin Levels

There are several reasons why albumin levels may be low, including liver disease, kidney disease, malnutrition, and inflammation. Liver disease, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, can impair the liver's ability to produce albumin. Kidney disease, particularly nephrotic syndrome, can lead to excessive loss of albumin in the urine. Malnutrition, either due to inadequate dietary intake or malabsorption, can also contribute to low albumin levels. Inflammation, whether chronic or acute, can cause the liver to produce less albumin.
Other potential causes of low albumin levels include:
- Gastrointestinal disorders, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease
- Cancer, particularly liver or pancreatic cancer
- Heart failure
- Severe burns or trauma
- Certain medications, such as steroids or diuretics
Liver Disease and Low Albumin Levels
Liver disease is a common cause of low albumin levels. The liver is responsible for producing albumin, and any condition that impairs liver function can lead to decreased albumin production. Cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer are all potential causes of low albumin levels.Kidney Disease and Low Albumin Levels
Kidney disease, particularly nephrotic syndrome, can cause excessive loss of albumin in the urine. This can lead to low albumin levels in the blood, as the kidneys are unable to reabsorb the protein.Symptoms of Low Albumin Levels
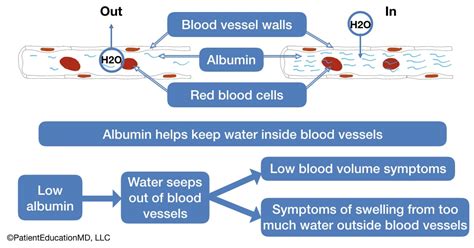
The symptoms of low albumin levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Edema, or swelling, particularly in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain or tenderness
- Shortness of breath
In severe cases, low albumin levels can lead to more serious complications, such as:
- Respiratory failure
- Cardiac failure
- Sepsis
- Malnutrition
Treatment Options for Low Albumin Levels
Treatment for low albumin levels depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, albumin infusions may be necessary to rapidly increase albumin levels. However, this is typically reserved for severe cases or those with significant symptoms.Other treatment options may include:
- Dietary changes, such as increasing protein intake
- Medications to manage underlying conditions, such as liver or kidney disease
- Addressing underlying inflammation or infection
- Surgery, in some cases, to repair or remove damaged tissues or organs
Diagnosing Low Albumin Levels
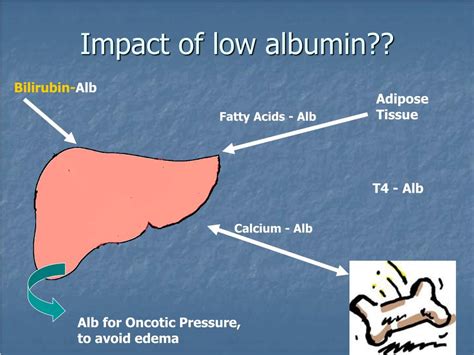
Diagnosing low albumin levels typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional may perform a physical examination to look for signs of edema, weight loss, or other symptoms. They will also take a thorough medical history to identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to low albumin levels.
Laboratory tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and liver function tests, may be ordered to evaluate liver and kidney function. A serum albumin test, which measures the level of albumin in the blood, is typically the primary diagnostic tool for low albumin levels.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting test results requires careful consideration of various factors, including the individual's age, sex, and medical history. A healthcare professional will evaluate the results in the context of the individual's overall health and medical history.Complications of Low Albumin Levels

Low albumin levels can lead to a range of complications, from mild to severe. Some potential complications include:
- Edema, or swelling, particularly in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Malnutrition, due to inadequate dietary intake or malabsorption
- Infection, particularly in those with compromised immune systems
- Respiratory failure
- Cardiac failure
In severe cases, low albumin levels can lead to life-threatening complications, such as sepsis or organ failure.
Preventing Low Albumin Levels
Preventing low albumin levels requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical management. Some strategies for preventing low albumin levels include:- Maintaining a healthy diet, rich in protein and essential nutrients
- Staying hydrated, particularly in hot weather or during exercise
- Managing underlying medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting regular exercise, to maintain overall health and well-being
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, low albumin blood test results can indicate a range of health issues, from mild to severe. Understanding the causes and consequences of low albumin levels is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By incorporating lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical management, individuals can reduce their risk of developing low albumin levels and related complications.
If you have concerns about your albumin levels or overall health, consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your individual situation, provide personalized guidance, and develop a comprehensive treatment plan to address any underlying conditions.
What is the normal range for albumin levels in the blood?
+The normal range for albumin levels in the blood is typically between 3.4 and 5.4 grams per deciliter (g/dL), although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and individual factors.
What are the symptoms of low albumin levels?
+The symptoms of low albumin levels can vary, but may include edema, fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite, nausea, and abdominal pain.
How are low albumin levels treated?
+Treatment for low albumin levels depends on the underlying cause, but may include dietary changes, medications, and albumin infusions in severe cases.
Can low albumin levels be prevented?
+Yes, low albumin levels can be prevented by maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
What are the potential complications of low albumin levels?
+The potential complications of low albumin levels include edema, malnutrition, infection, respiratory failure, and cardiac failure.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of low albumin blood test results and their implications for your health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Share this article with friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of albumin and its role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
