Intro
Learn about foot pronation, its causes, and effects on running. Understand overpronation, underpronation, and neutral pronation to improve foot health and prevent injuries like plantar fasciitis.
The human foot is a complex and fascinating structure, comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. One of the key aspects of foot function is pronation, a term that refers to the natural movement of the foot as it rolls inward and outward during walking or running. Understanding foot pronation is essential for maintaining proper foot health, preventing injuries, and improving overall mobility. In this article, we will delve into the world of foot pronation, exploring its mechanisms, types, and significance for our overall well-being.
Foot pronation is a vital component of the gait cycle, which is the sequence of events that occurs when we walk or run. As we strike the ground with our heel, the foot begins to pronate, allowing the arch to collapse and the foot to roll inward. This movement helps to absorb shock, distribute pressure, and facilitate the transfer of weight from the heel to the toe. Pronation also enables the foot to adapt to different surfaces and terrain, ensuring stability and balance. However, excessive or abnormal pronation can lead to a range of problems, including foot pain, ankle injuries, and even lower back strain.
The importance of foot pronation cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining proper foot mechanics and preventing injuries. When the foot pronates excessively or abnormally, it can lead to a range of issues, including flat feet, plantar fasciitis, and Achilles tendonitis. Furthermore, improper foot pronation can also affect the entire lower limb, leading to problems such as knee pain, hip strain, and lower back discomfort. By understanding the mechanisms and types of foot pronation, we can take steps to prevent these issues and maintain optimal foot health.
What is Foot Pronation?
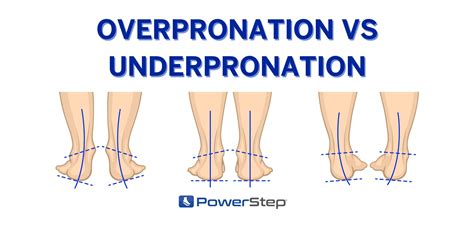
Types of Foot Pronation
There are three main types of foot pronation: neutral, overpronation, and underpronation. Neutral pronation refers to the normal, healthy movement of the foot, where the arch collapses and the foot rolls inward to a moderate degree. Overpronation, on the other hand, occurs when the foot pronates excessively, leading to a flat foot or low arch. Underpronation, also known as supination, occurs when the foot pronates too little, resulting in a high arch or rigid foot.Causes of Abnormal Foot Pronation
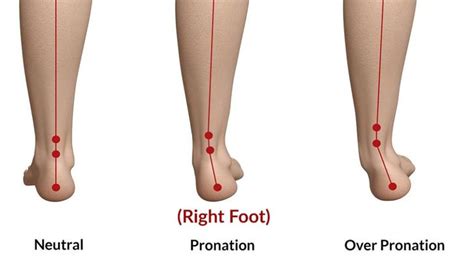
Biomechanical Factors
Biomechanical factors play a significant role in foot pronation, as they can affect the way the foot moves and functions. For example, a leg length discrepancy can cause the foot to pronate abnormally, leading to issues such as hip or knee pain. Similarly, muscle imbalances in the lower limb can affect the way the foot pronates, leading to problems such as Achilles tendonitis or plantar fasciitis. By addressing these biomechanical factors, we can help to prevent abnormal foot pronation and maintain optimal foot health.Effects of Abnormal Foot Pronation
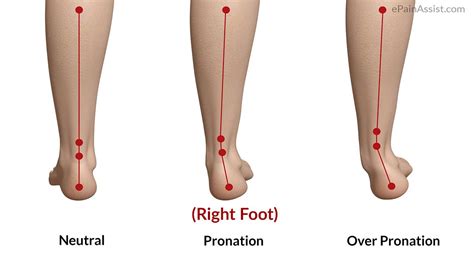
Treatments and Prevention
Fortunately, there are a range of treatments and prevention strategies available for abnormal foot pronation. These include orthotics and shoe inserts, physical therapy and exercise, and footwear modifications. Orthotics and shoe inserts can help to support the arch and reduce pronation, while physical therapy and exercise can help to strengthen the muscles and improve foot mechanics. Footwear modifications, such as using shoes with good arch support and cushioning, can also help to prevent abnormal pronation.Footwear and Foot Pronation
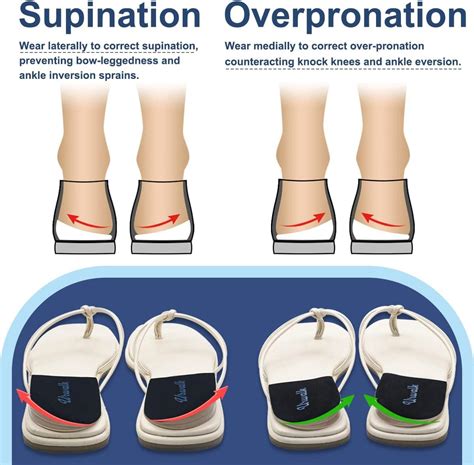
Orthotics and Shoe Inserts
Orthotics and shoe inserts can be highly effective in treating abnormal foot pronation. These devices can help to support the arch, reduce pronation, and alleviate pain and discomfort. There are a range of orthotics and shoe inserts available, from custom-made devices to over-the-counter products. By using orthotics and shoe inserts, individuals can help to prevent abnormal foot pronation and maintain optimal foot health.Exercises and Stretches

Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can also be highly effective in treating abnormal foot pronation. A physical therapist can help to identify the underlying causes of abnormal pronation and develop a personalized treatment plan. This may include exercises and stretches, as well as orthotics and shoe inserts. By working with a physical therapist, individuals can help to prevent abnormal foot pronation and maintain optimal foot health.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As we reflect on the importance of foot pronation, it's clear that this topic deserves our attention and consideration. By prioritizing foot health and taking steps to prevent abnormal pronation, we can help to maintain optimal foot mechanics and reduce the risk of injury and disease. Whether you're an athlete, a healthcare professional, or simply someone who wants to maintain optimal foot health, we hope that this article has provided you with valuable insights and information. Remember to take care of your feet, and they will take care of you.What is foot pronation?
+Foot pronation refers to the natural movement of the foot as it rolls inward and outward during walking or running.
What are the types of foot pronation?
+There are three main types of foot pronation: neutral, overpronation, and underpronation.
How can I prevent abnormal foot pronation?
+You can prevent abnormal foot pronation by using orthotics and shoe inserts, exercising and stretching, and wearing proper footwear.
What are the effects of abnormal foot pronation?
+Abnormal foot pronation can lead to a range of issues, including foot pain, ankle injuries, and lower back strain.
How can I treat abnormal foot pronation?
+You can treat abnormal foot pronation by using orthotics and shoe inserts, exercising and stretching, and seeking physical therapy.
