Intro
Discover radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment, leveraging advanced techniques like IMRT and SBRT to target tumors, minimizing side effects and promoting survival rates.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting men worldwide, and its treatment has evolved significantly over the years. Radiation therapy is a highly effective treatment option for prostate cancer, offering a high success rate in curing the disease or managing its symptoms. The importance of radiation therapy in prostate cancer treatment cannot be overstated, as it provides an alternative to surgery and can be used in conjunction with other treatments to achieve optimal results. In this article, we will delve into the world of radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information that patients need to know.
Radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. It is a local treatment, meaning it targets the tumor directly, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. For prostate cancer, radiation therapy can be used as a primary treatment, especially for early-stage cancers, or as an adjunct treatment to surgery or hormone therapy. The goal of radiation therapy is to eradicate the cancer cells, preventing the disease from progressing and improving the patient's quality of life.
The role of radiation therapy in prostate cancer treatment is multifaceted. It can be used to treat the cancer itself, reduce symptoms, and prevent the disease from recurring. Radiation therapy can also be used to alleviate pain and other symptoms associated with advanced prostate cancer. With advancements in technology, radiation therapy has become more precise, allowing for higher doses of radiation to be delivered directly to the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding tissues. This precision has led to improved outcomes and reduced side effects, making radiation therapy an attractive option for many patients.
Radiation Therapy Types
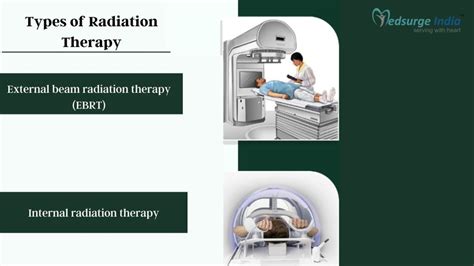
There are several types of radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is the most common type, where a machine outside the body delivers radiation to the tumor. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) are advanced forms of EBRT that allow for more precise targeting of the tumor. Brachytherapy, on the other hand, involves placing small radioactive seeds directly into the prostate gland, where they emit radiation to kill cancer cells. Proton therapy is another type of radiation therapy that uses protons instead of X-rays to kill cancer cells, offering potentially fewer side effects.
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
EBRT is a non-invasive treatment that uses a machine to deliver radiation to the prostate gland from outside the body. This type of radiation therapy is typically given in fractions, with the patient receiving treatment over several weeks. EBRT can be used to treat prostate cancer at any stage, from early-stage to advanced disease. The benefits of EBRT include its non-invasive nature, relatively low risk of side effects, and high success rate in controlling the disease.Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
IMRT is an advanced form of EBRT that allows for more precise targeting of the tumor. This type of radiation therapy uses sophisticated computer software to modulate the intensity of the radiation beams, delivering a higher dose to the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding tissues. IMRT has been shown to reduce the risk of side effects, such as urinary and bowel problems, and improve treatment outcomes.Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
SBRT is a highly precise form of radiation therapy that delivers high doses of radiation to the tumor in a few fractions. This type of radiation therapy is typically used to treat small, localized tumors, and has been shown to be highly effective in controlling the disease. SBRT offers several benefits, including a shorter treatment duration, reduced risk of side effects, and improved treatment outcomes.Benefits of Radiation Therapy
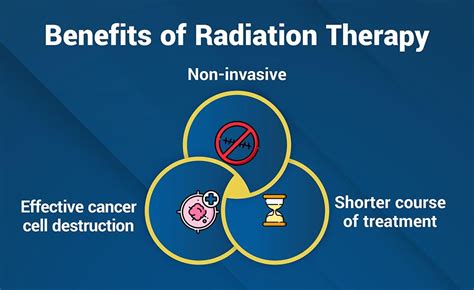
Radiation therapy offers several benefits for patients with prostate cancer. These benefits include:
- High success rate in curing the disease or controlling its symptoms
- Non-invasive nature, reducing the risk of complications and side effects
- Can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as hormone therapy or surgery
- Relatively low risk of side effects, especially with advanced technologies like IMRT and SBRT
- Improved quality of life, reducing symptoms and improving functional outcomes
Reduced Risk of Side Effects
Advances in radiation therapy have led to a reduced risk of side effects, making it a more attractive option for patients. The use of sophisticated technologies like IMRT and SBRT allows for more precise targeting of the tumor, minimizing exposure to surrounding tissues. This reduced risk of side effects has improved treatment outcomes and enhanced the quality of life for patients with prostate cancer.Improved Treatment Outcomes
Radiation therapy has been shown to improve treatment outcomes for patients with prostate cancer. By delivering high doses of radiation directly to the tumor, radiation therapy can eradicate cancer cells, preventing the disease from progressing. The use of advanced technologies like IMRT and SBRT has further improved treatment outcomes, reducing the risk of recurrence and improving survival rates.Working Mechanism of Radiation Therapy

Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing. When radiation is delivered to the tumor, it causes damage to the DNA of cancer cells, leading to cell death. The goal of radiation therapy is to deliver a high enough dose of radiation to kill cancer cells, while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Cell Death and Tumor Shrinkage
The damage caused by radiation therapy leads to cell death and tumor shrinkage. As cancer cells die, the tumor begins to shrink, reducing symptoms and improving functional outcomes. The rate of cell death and tumor shrinkage can vary depending on the type of radiation therapy used and the individual patient's response to treatment.Immune System Stimulation
Radiation therapy can also stimulate the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight cancer. The damage caused by radiation therapy can release tumor antigens, stimulating the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. This immune system stimulation can lead to a systemic response, reducing the risk of recurrence and improving treatment outcomes.Steps Involved in Radiation Therapy
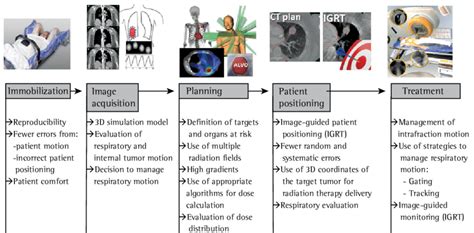
The steps involved in radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment include:
- Consultation with a radiation oncologist to determine the best course of treatment
- Simulation, where the patient is positioned and the radiation beams are aligned with the tumor
- Treatment planning, where the radiation dose and delivery schedule are determined
- Radiation therapy delivery, where the patient receives treatment according to the planned schedule
- Follow-up care, where the patient is monitored for side effects and treatment response
Simulation and Treatment Planning
The simulation and treatment planning process is critical in radiation therapy. During simulation, the patient is positioned and the radiation beams are aligned with the tumor. This process ensures that the radiation is delivered accurately and safely. Treatment planning involves determining the radiation dose and delivery schedule, taking into account the patient's individual needs and the characteristics of the tumor.Radiation Therapy Delivery
Radiation therapy delivery is typically done on an outpatient basis, with the patient receiving treatment over several weeks. The radiation therapy machine delivers the radiation beams to the tumor, according to the planned schedule. The patient may experience some side effects during treatment, which can be managed with medication and supportive care.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that radiation therapy is highly effective in treating prostate cancer. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that radiation therapy improved survival rates for patients with localized prostate cancer. Another study published in the Journal of Urology found that radiation therapy reduced the risk of recurrence and improved treatment outcomes for patients with high-risk prostate cancer.
Some statistical data on radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment includes:
- 85-90% of patients with localized prostate cancer can be cured with radiation therapy
- 70-80% of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer can be cured with radiation therapy
- 50-60% of patients with high-risk prostate cancer can be cured with radiation therapy
Success Rates and Treatment Outcomes
The success rates and treatment outcomes for radiation therapy in prostate cancer treatment are highly dependent on the individual patient's characteristics and the stage of the disease. Generally, radiation therapy is highly effective in treating localized and intermediate-risk prostate cancer, with high cure rates and improved treatment outcomes.Side Effects and Complications
While radiation therapy is generally well-tolerated, there are some potential side effects and complications to consider. These can include urinary and bowel problems, fatigue, and skin irritation. However, with advanced technologies like IMRT and SBRT, the risk of side effects has been significantly reduced.What is radiation therapy and how does it work?
+Radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing.
What are the benefits of radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment?
+The benefits of radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment include a high success rate in curing the disease or controlling its symptoms, non-invasive nature, and reduced risk of side effects.
What are the different types of radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer?
+The different types of radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer include external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), and brachytherapy.
In summary, radiation therapy is a highly effective treatment option for prostate cancer, offering a high success rate in curing the disease or controlling its symptoms. With its non-invasive nature, reduced risk of side effects, and improved treatment outcomes, radiation therapy has become a popular choice for patients with prostate cancer. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with radiation therapy for prostate cancer treatment in the comments below. If you or a loved one is considering radiation therapy, we invite you to consult with a radiation oncologist to determine the best course of treatment. Together, we can raise awareness about the benefits of radiation therapy and improve treatment outcomes for patients with prostate cancer.
