Intro
Discover Radiation Treatment For Cancer, including types like external beam therapy, brachytherapy, and stereotactic body radiotherapy, to combat tumors and cancer cells, improving survival rates and quality of life.
Radiation treatment for cancer is a complex and highly effective method of combating the disease. The importance of radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer cannot be overstated, as it has been used for decades to help patients achieve remission and improve their quality of life. With the advancement of technology, radiation therapy has become more precise and targeted, allowing for better outcomes and fewer side effects. In this article, we will delve into the world of radiation treatment for cancer, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and the various types of radiation therapy available.
The use of radiation to treat cancer is based on the principle that cancer cells are more sensitive to radiation than healthy cells. By targeting the cancer cells with high-energy rays, radiation therapy can kill or slow the growth of the cancer, reducing the risk of recurrence and improving survival rates. Radiation therapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy, to achieve the best possible outcome. With the help of radiation therapy, many patients are able to overcome their cancer and go on to lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Radiation treatment for cancer is a highly specialized field that requires a deep understanding of the disease and the latest technologies. Radiation oncologists, who are doctors that specialize in radiation therapy, work closely with other healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans for each patient. These plans take into account the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health and medical history. By working together, the healthcare team can ensure that the patient receives the most effective treatment possible, with the fewest side effects.
How Radiation Therapy Works
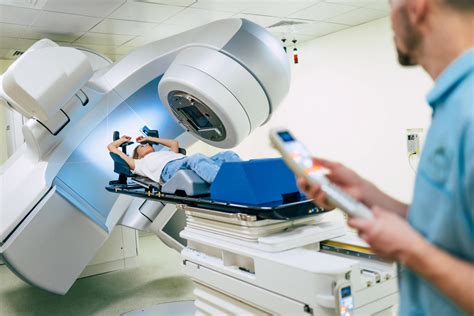
Radiation therapy works by using high-energy rays to damage the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing. There are several types of radiation therapy, including external beam radiation therapy, internal radiation therapy, and systemic radiation therapy. External beam radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to deliver the radiation, while internal radiation therapy uses a small implant or injection to deliver the radiation directly to the tumor. Systemic radiation therapy uses radioactive drugs that are given orally or intravenously to target cancer cells throughout the body.
Types of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy can be classified into several types, including: * External beam radiation therapy: This is the most common type of radiation therapy, where a machine outside the body delivers the radiation. * Internal radiation therapy: This type of radiation therapy uses a small implant or injection to deliver the radiation directly to the tumor. * Systemic radiation therapy: This type of radiation therapy uses radioactive drugs that are given orally or intravenously to target cancer cells throughout the body. * Stereotactic body radiation therapy: This type of radiation therapy uses high doses of radiation to target small tumors in a few sessions. * Total body irradiation: This type of radiation therapy uses high doses of radiation to target the entire body, often used to prepare patients for bone marrow transplants.Benefits of Radiation Therapy
The benefits of radiation therapy are numerous, including:
- High success rates: Radiation therapy has been shown to be effective in treating many types of cancer, with high success rates and improved survival rates.
- Reduced side effects: With the advancement of technology, radiation therapy has become more targeted and precise, reducing the risk of side effects and improving the quality of life for patients.
- Non-invasive: Radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment, which means that it does not require surgery or other invasive procedures.
- Cost-effective: Radiation therapy can be a cost-effective treatment option, especially when compared to other treatments such as surgery or chemotherapy.
Radiation Therapy Side Effects
While radiation therapy is generally well-tolerated, there are some potential side effects to be aware of, including: * Fatigue: Radiation therapy can cause fatigue, which can range from mild to severe. * Skin changes: Radiation therapy can cause skin changes, such as redness, itching, and dryness. * Hair loss: Radiation therapy can cause hair loss, especially in the area being treated. * Nausea and vomiting: Radiation therapy can cause nausea and vomiting, especially when used in combination with chemotherapy. * Diarrhea: Radiation therapy can cause diarrhea, especially when used to treat cancers in the abdominal area.Radiation Therapy for Specific Cancers
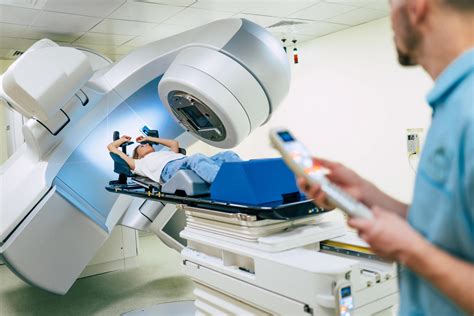
Radiation therapy can be used to treat a wide range of cancers, including:
- Breast cancer: Radiation therapy is often used to treat breast cancer, especially after surgery to remove the tumor.
- Prostate cancer: Radiation therapy is often used to treat prostate cancer, especially in the early stages.
- Lung cancer: Radiation therapy is often used to treat lung cancer, especially in combination with chemotherapy.
- Brain cancer: Radiation therapy is often used to treat brain cancer, especially in combination with surgery and chemotherapy.
- Cervical cancer: Radiation therapy is often used to treat cervical cancer, especially in combination with chemotherapy.
Future of Radiation Therapy
The future of radiation therapy is exciting, with new technologies and treatments being developed all the time. Some of the latest advancements in radiation therapy include: * Proton therapy: Proton therapy uses protons instead of X-rays to target cancer cells, which can reduce side effects and improve outcomes. * Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy uses the body's immune system to fight cancer, and can be used in combination with radiation therapy to improve outcomes. * Personalized medicine: Personalized medicine uses genetic testing and other technologies to tailor treatment to the individual patient, which can improve outcomes and reduce side effects.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, radiation therapy is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer. With its high success rates, reduced side effects, and cost-effectiveness, radiation therapy is an attractive treatment option for many patients. Whether used alone or in combination with other treatments, radiation therapy can help patients achieve remission and improve their quality of life. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the field of radiation therapy, which will help to improve outcomes and save lives.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with radiation therapy in the comments below. If you or a loved one has undergone radiation therapy, we would love to hear about your journey and any tips or advice you may have for others. By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can help to raise awareness and support for cancer patients and their families.
What is radiation therapy and how does it work?
+Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to damage the DNA of cancer cells, preventing them from growing and dividing. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy.
What are the benefits of radiation therapy?
+The benefits of radiation therapy include high success rates, reduced side effects, and cost-effectiveness. It is also a non-invasive treatment, which means that it does not require surgery or other invasive procedures.
What are the potential side effects of radiation therapy?
+Potential side effects of radiation therapy include fatigue, skin changes, hair loss, nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea. However, these side effects can often be managed with medication and other treatments.
