Intro
Discover Raynauds Syndrome symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Learn about vasospasm, blood flow, and cold stress triggers, to manage this autoimmune disorder and alleviate finger, toe, and circulation issues.
Raynaud's syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon or Raynaud's disease, is a condition that affects blood flow to the fingers and toes, and sometimes the ears, nose, and lips. It is characterized by a sudden and temporary narrowing of the blood vessels in response to cold temperatures or stress, resulting in a range of symptoms. Understanding the symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and management of the condition.
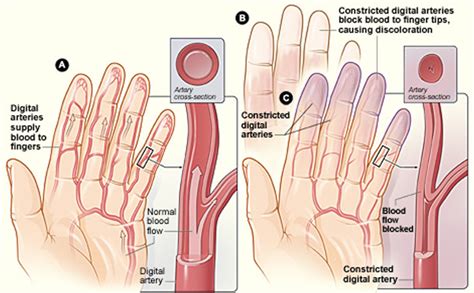
The symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome can vary in severity and frequency, but they often follow a predictable pattern. When an individual with Raynaud's syndrome is exposed to cold temperatures or experiences stress, the blood vessels in the affected areas constrict or narrow, reducing blood flow. This can cause the skin to turn white or pale, as the blood is unable to reach the surface. As the blood vessels constrict, the affected areas may also feel cold, numb, or tingling.
In addition to the initial symptoms, Raynaud's syndrome can also cause a range of other symptoms, including pain, swelling, and discoloration of the affected areas. In some cases, the condition can also cause ulcers or sores to develop on the fingers or toes, which can be painful and take time to heal. Understanding the symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome is essential for seeking medical attention and receiving proper treatment.
What are the Symptoms of Raynaud's Syndrome?
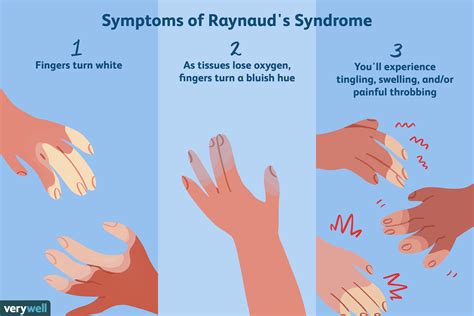
Primary Symptoms
The primary symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome include: * Discoloration of the skin, typically turning white or pale * Numbness or tingling in the affected areas * Cold hands or feet * Pain or discomfort in the affected areas * Swelling or inflammation of the affected areasCauses and Triggers of Raynaud's Syndrome
Secondary Symptoms
In addition to the primary symptoms, Raynaud's syndrome can also cause a range of secondary symptoms, including: * Ulcers or sores on the fingers or toes * Gangrene or tissue death in severe cases * Increased risk of infection in the affected areas * Decreased mobility or dexterity in the affected areasTreatment and Management of Raynaud's Syndrome

Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help to manage the symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome and prevent complications. These include: * Quitting smoking: Smoking can reduce blood flow and worsen symptoms * Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help to improve blood flow and reduce stress * Avoiding cold temperatures: Avoiding cold temperatures can help to reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms * Managing stress: Managing stress through techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help to reduce the frequency and severity of symptomsComplications of Raynaud's Syndrome
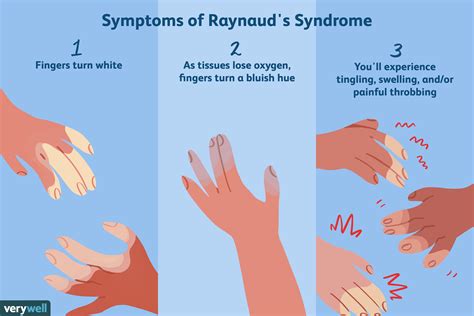
Prevention
Preventing Raynaud's syndrome is not always possible, but there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include: * Avoiding cold temperatures * Quitting smoking * Exercising regularly * Managing stressDiagnosis of Raynaud's Syndrome

Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for Raynaud's syndrome include: * A history of symptoms triggered by cold temperatures or stress * A physical examination revealing discoloration, numbness, or tingling in the affected areas * A cold stimulation test that triggers symptoms * Imaging tests that reveal narrowing or blockages in the blood vesselsLiving with Raynaud's Syndrome

Coping Strategies
Coping with Raynaud's syndrome can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help. These include: * Joining a support group: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and connect individuals with others who are experiencing similar symptoms * Practicing stress-reducing techniques: Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help to reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms * Staying active: Staying active and exercising regularly can help to improve blood flow and reduce symptomsWhat is Raynaud's syndrome?
+Raynaud's syndrome is a condition that affects blood flow to the fingers and toes, and sometimes the ears, nose, and lips. It is characterized by a sudden and temporary narrowing of the blood vessels in response to cold temperatures or stress.
What are the symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome?
+The symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome include discoloration, numbness, or tingling in the affected areas, as well as pain, swelling, and decreased mobility or dexterity.
How is Raynaud's syndrome diagnosed?
+Diagnosing Raynaud's syndrome typically involves a physical examination and a review of medical history, as well as several tests such as blood tests, imaging tests, and a cold stimulation test.
Can Raynaud's syndrome be treated?
+While there is no cure for Raynaud's syndrome, there are several treatment options available to manage symptoms and prevent complications. These include medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
How can I manage my Raynaud's syndrome symptoms?
+Managing Raynaud's syndrome symptoms requires making several lifestyle changes, such as avoiding cold temperatures, quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and managing stress. It is also important to take medications as prescribed and to seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or if complications develop.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Raynaud's syndrome, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Additionally, we invite you to share your experiences and tips for managing Raynaud's syndrome in the comments below. By working together, we can raise awareness and support for this condition, and help individuals affected by Raynaud's syndrome to live full and active lives.
