Intro
The Rhogam shot is a crucial medical intervention that has been a cornerstone in preventing a specific type of immune reaction in pregnant women. Understanding its importance, mechanism, and implications is vital for expectant mothers and healthcare providers alike. The Rhogam shot has been instrumental in saving countless lives and preventing complications that could arise from Rh incompatibility between a mother and her fetus. This article delves into the intricacies of the Rhogam shot, exploring its significance, how it works, and key facts that every pregnant woman should know.
The significance of the Rhogam shot cannot be overstated. It is administered to pregnant women who have an Rh-negative blood type, to prevent their immune system from reacting to an Rh-positive fetus. This reaction can lead to the production of antibodies that can cross the placenta in future pregnancies, attacking the red blood cells of an Rh-positive fetus. The consequences can be severe, including anemia, jaundice, and even death of the fetus. The introduction of the Rhogam shot has dramatically reduced the incidence of such complications, making it a pivotal component of prenatal care for Rh-negative women.
The mechanism behind the Rhogam shot is fascinating and underscores its efficacy. Essentially, the shot contains antibodies that are directed against the Rh factor on red blood cells. When an Rh-negative mother is exposed to Rh-positive blood (as might happen during childbirth or certain prenatal tests), her body might start producing its own antibodies against the Rh factor. The Rhogam shot prevents this by introducing antibodies that neutralize any Rh-positive red blood cells that might have entered the mother's bloodstream, thereby preventing her immune system from recognizing them as foreign and mounting an immune response. This preventive measure ensures that in any future pregnancies with an Rh-positive fetus, the mother's immune system will not attack the fetus's red blood cells.
Rhogam Shot Administration
Benefits of the Rhogam Shot
The benefits of the Rhogam shot are multifaceted, primarily revolving around the prevention of Rh incompatibility issues in future pregnancies. By preventing the formation of antibodies against the Rh factor, the Rhogam shot ensures that an Rh-negative mother can safely carry an Rh-positive fetus in subsequent pregnancies without the risk of her immune system attacking the fetus. This has significantly reduced the incidence of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), a condition that can lead to severe anemia and other complications in newborns.Rhogam Shot Side Effects
Who Needs the Rhogam Shot?
Not all pregnant women require the Rhogam shot. It is specifically indicated for those who are Rh-negative and are pregnant with an Rh-positive fetus, or if the fetus's Rh status is unknown. The shot is also recommended in situations where there might be exposure to Rh-positive blood, such as during prenatal diagnostic procedures or after a miscarriage, abortion, or ectopic pregnancy if the woman is Rh-negative.Rhogam Shot and Pregnancy

Pregnancy Complications Prevented by Rhogam
The Rhogam shot prevents a range of potential complications that could arise from Rh incompatibility. One of the most significant conditions it prevents is hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), where the mother's immune system produces antibodies that attack the fetus's red blood cells. This can lead to severe anemia, heart failure, and even death in the fetus. By preventing the formation of these antibodies, the Rhogam shot ensures a safer pregnancy for both the mother and the baby.Rhogam Shot Dosage and Schedule
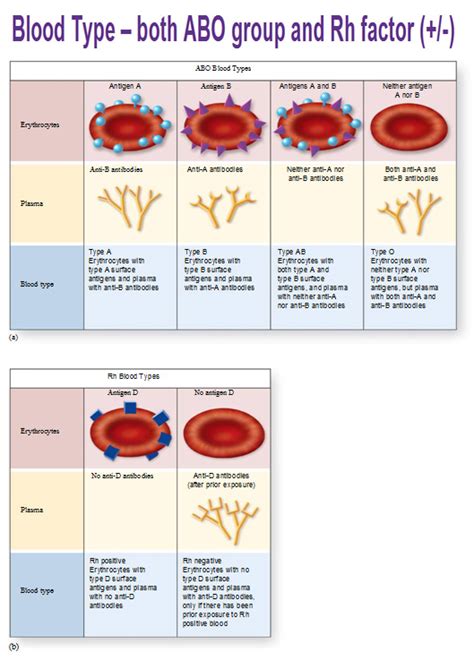
Importance of Following the Rhogam Shot Schedule
Following the recommended schedule for the Rhogam shot is crucial for its effectiveness. Missing a dose or not receiving the shot at the appropriate time can leave a window of vulnerability, where the mother's immune system could start producing antibodies against the Rh factor. This underscores the importance of close communication between pregnant women and their healthcare providers to ensure that all necessary prenatal care, including the Rhogam shot, is received as scheduled.Rhogam Shot and Breastfeeding
Common Misconceptions About the Rhogam Shot
There are several misconceptions about the Rhogam shot that need to be addressed. One common myth is that the Rhogam shot is only for first-time mothers, which is not true. Any Rh-negative woman who is pregnant and has not been sensitized to the Rh factor should receive the Rhogam shot. Another misconception is that the shot is not needed if the father of the baby is Rh-negative, but this is also incorrect. The Rh status of the father is not a determining factor in whether the mother needs the Rhogam shot.Rhogam Shot Alternatives

Future Directions in Rh Incompatibility Prevention
Research into Rh incompatibility and its prevention continues to evolve. While the Rhogam shot has been highly effective, there is ongoing work to develop even safer and more effective methods of preventing immune reactions in Rh-negative mothers. This includes the development of new antibodies and the exploration of genetic factors that influence Rh incompatibility. As medical science advances, it is likely that even more effective strategies for managing Rh incompatibility will emerge.Rhogam Shot and Insurance Coverage

Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the Rhogam shot is a vital component of prenatal care for Rh-negative women, offering protection against Rh incompatibility and ensuring safer pregnancies. By understanding the importance of the Rhogam shot, its mechanism, and its benefits, pregnant women can make informed decisions about their care. If you're an Rh-negative pregnant woman or are considering becoming pregnant, discussing the Rhogam shot with your healthcare provider is a crucial step in ensuring the best possible outcome for both you and your baby.What is the Rhogam shot used for?
+The Rhogam shot is used to prevent the immune system of an Rh-negative mother from reacting against an Rh-positive fetus, thereby preventing complications that could arise from Rh incompatibility.
Who needs the Rhogam shot?
+Rh-negative pregnant women who are carrying an Rh-positive fetus, or whose fetus's Rh status is unknown, need the Rhogam shot. It is also recommended in situations where there might be exposure to Rh-positive blood.
Are there any side effects of the Rhogam shot?
+While generally safe, the Rhogam shot can cause mild side effects such as redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site, as well as mild fever or headache. Severe reactions are rare.
Can I breastfeed after receiving the Rhogam shot?
+Yes, the Rhogam shot is safe for breastfeeding mothers. The antibodies in the shot do not affect milk production or the safety of the breast milk for the baby.
Is the Rhogam shot covered by insurance?
+Typically, the Rhogam shot is covered by health insurance as part of standard prenatal care. However, coverage details can vary, so it's best to check with your insurance provider.
We hope this comprehensive guide to the Rhogam shot has been informative and helpful. Whether you're an expectant mother or simply looking to understand more about prenatal care, the Rhogam shot plays a critical role in ensuring the health and safety of both mothers and babies. Feel free to share your thoughts, ask questions, or seek further clarification on any aspects of the Rhogam shot in the comments below. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the best possible information and support.
