Intro
Discover 5 effective ways to treat keratosis, a skin condition causing rough patches. Learn natural remedies, removal methods, and preventive measures for keratosis pilaris, seborrheic keratosis, and actinic keratosis, promoting smoother skin and reducing symptoms.
Keratosis is a skin condition characterized by the growth of small, rough, and scaly patches on the skin, often caused by excessive exposure to the sun. It can be unsightly and, in some cases, may develop into skin cancer if left untreated. Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for managing keratosis effectively. The importance of treating keratosis lies not only in improving the appearance of the skin but also in preventing potential complications. With the advancements in dermatology, there are several methods to treat keratosis, each with its benefits and considerations.
The treatment of keratosis depends on the severity of the condition, the location of the lesions, and the patient's overall health. While some cases may require medical intervention, others can be managed with topical treatments or preventive measures. The key to successful treatment is early detection and intervention. By understanding the different treatment options and their implications, individuals can make informed decisions about their skin health. Moreover, awareness about keratosis and its treatment can encourage people to adopt preventive measures, such as using sunscreen and protective clothing, to reduce the risk of developing the condition.
The management of keratosis involves a range of approaches, from topical creams and gels to more invasive procedures like surgery. Each method has its advantages and may be recommended based on the specific characteristics of the keratosis lesions and the patient's preferences. The decision to choose one treatment over another should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering factors such as the potential for scarring, the risk of recurrence, and the cost of treatment. By exploring the different treatment options available, individuals can find the most suitable approach for their condition, leading to improved skin health and reduced risk of complications.
Understanding Keratosis
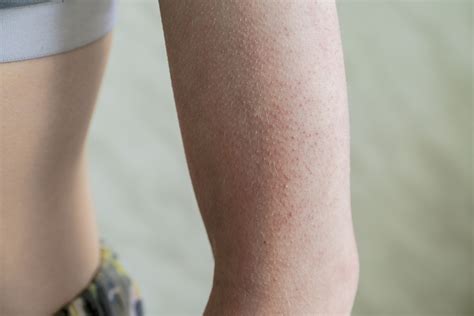
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of keratosis are primarily linked to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. UV radiation damages the skin cells' DNA, leading to abnormal growth and the formation of keratosis lesions. Other risk factors include fair skin, aging, a history of significant sun exposure, and a weakened immune system. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures, such as avoiding excessive sun exposure, using sunscreen regularly, and wearing protective clothing.Treatment Options for Keratosis

Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of treatment for keratosis, especially for mild cases. These treatments can help soften the scaly patches, reduce their appearance, and prevent further growth. Common topical treatments include: - Urea creams to moisturize and soften the skin - Salicylic acid to help remove the top layers of the skin - Fluorouracil to prevent the growth of abnormal cells These treatments are generally well-tolerated but may cause skin irritation, redness, or dryness in some individuals.Cryotherapy for Keratosis
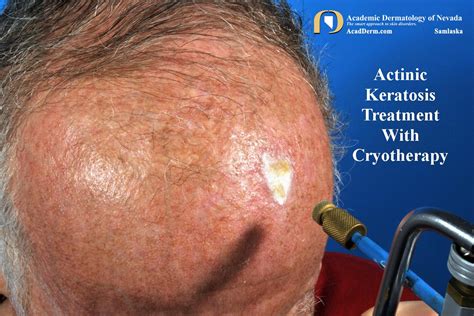
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is another treatment option for keratosis, especially for lesions that are sensitive or in areas where other treatments may not be suitable. PDT involves applying a light-sensitive medication to the affected area and then exposing it to a specific wavelength of light. This treatment can be effective in removing keratosis lesions with minimal scarring but may cause temporary redness, swelling, or sensitivity to light.Surgical Removal of Keratosis
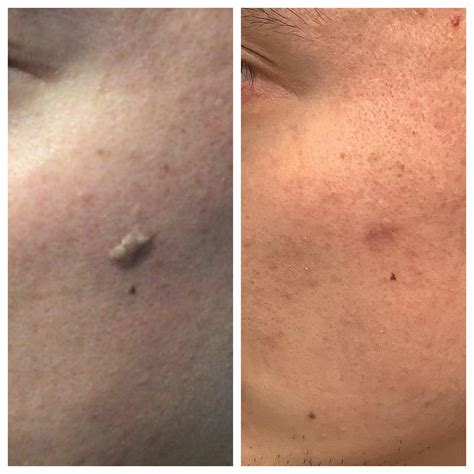
Preventive Measures
Prevention is key in managing keratosis. By taking simple preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing keratosis and its complications. These measures include: - Using sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 30 daily - Wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, when spending time outdoors - Avoiding excessive sun exposure, especially during peak hours - Conducting regular skin self-exams to identify any new or changing lesions earlyLiving with Keratosis
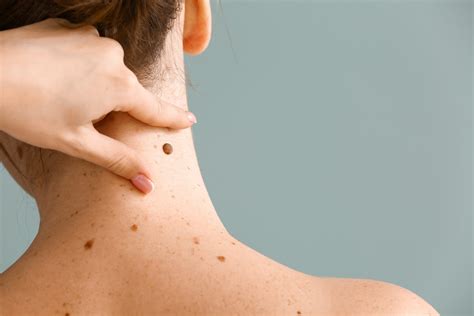
Support and Resources
For individuals living with keratosis, accessing support and resources can be invaluable. This includes consulting with dermatologists, joining support groups, and staying informed about the latest treatments and research. By connecting with others who have similar experiences, individuals can find emotional support, share knowledge, and learn about new approaches to managing keratosis.Future Directions in Keratosis Treatment
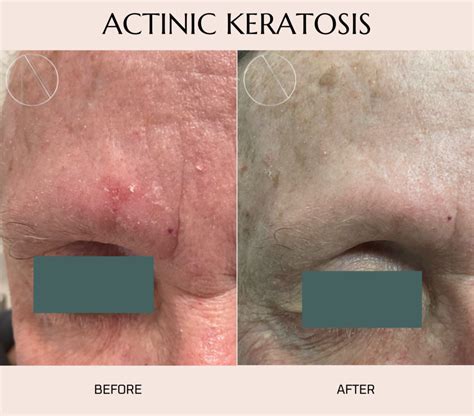
Advancements in Technology
Advancements in technology are playing a significant role in the treatment of keratosis. For example, the development of more precise laser technologies allows for the selective removal of keratosis lesions with minimal damage to surrounding skin. Additionally, improvements in topical treatments and the development of new medications are providing individuals with more options for managing their keratosis.What are the symptoms of keratosis?
+The symptoms of keratosis typically include small, hard, or scaly patches on the skin that can be flesh-colored, pink, red, or brown and may feel rough to the touch.
How is keratosis diagnosed?
+Keratosis is diagnosed through a physical examination of the skin and, in some cases, a biopsy to rule out other conditions or to check for signs of skin cancer.
Can keratosis be prevented?
+Yes, keratosis can be prevented or its risk reduced by avoiding excessive sun exposure, using sunscreen regularly, and wearing protective clothing.
In conclusion, keratosis is a manageable condition with various treatment options available, ranging from topical treatments to surgical removal. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about their skin health. It is crucial to adopt preventive measures and seek medical advice early to reduce the risk of complications. As research continues to advance, new and innovative treatments for keratosis will emerge, offering individuals more effective and less invasive options for managing their condition. We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, or seek advice on managing keratosis, and we look forward to your comments and feedback.
