Intro
Discover 5 metronidazole uses, including treating infections, parasites, and STDs, with this antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, effective against bacterial vaginosis, giardiasis, and trichomoniasis.
Metronidazole is a versatile antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various infections and conditions. Its effectiveness against a broad range of pathogens, including bacteria, protozoa, and anaerobic organisms, makes it a valuable tool in the medical field. The importance of understanding the uses of metronidazole cannot be overstated, as it can help healthcare professionals and patients alike make informed decisions about its application. In this article, we will delve into the uses of metronidazole, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and practical applications.
Metronidazole has been a cornerstone in the treatment of various infections, including those affecting the gastrointestinal tract, skin, and genital areas. Its ability to target and eliminate harmful microorganisms has made it an essential medication in many medical specialties. Moreover, metronidazole's relatively low cost and availability have contributed to its widespread use, especially in resource-limited settings. As we discuss the uses of metronidazole, it becomes clear that this medication plays a vital role in modern medicine, and its applications continue to expand as research uncovers new benefits.
The versatility of metronidazole is a significant factor in its popularity among healthcare professionals. With its broad spectrum of activity, metronidazole can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, from mild infections to life-threatening diseases. Additionally, its relatively low toxicity and side effect profile make it an attractive option for patients who may be sensitive to other medications. As we explore the uses of metronidazole in more detail, it becomes evident that this medication is a valuable asset in the fight against infectious diseases.
Introduction to Metronidazole
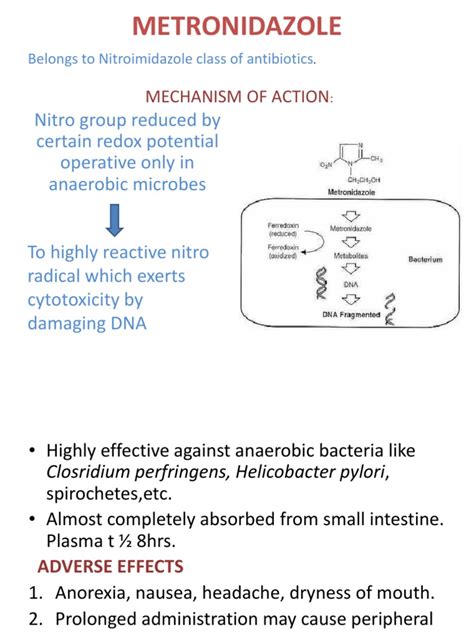
Pharmacology and Mechanism of Action
Metronidazole's pharmacology and mechanism of action are essential to understanding its uses. The medication is available in various formulations, including oral tablets, capsules, and suspensions, as well as topical creams and gels. When administered orally, metronidazole is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, where it reaches peak concentrations within 1-2 hours. The medication is then distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations achieved in the liver, kidneys, and other tissues.Uses of Metronidazole

Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis and Trichomoniasis
Metronidazole is commonly used to treat bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, two common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Bacterial vaginosis is a condition characterized by an imbalance of the normal vaginal flora, resulting in symptoms such as abnormal discharge and odor. Trichomoniasis, on the other hand, is a parasitic infection caused by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis. Metronidazole is effective against both conditions, with high cure rates reported in clinical trials.Benefits and Side Effects

Precautions and Contraindications
Metronidazole should be used with caution in certain patients, including those with a history of seizures, liver or kidney disease, and blood disorders. Additionally, metronidazole should not be used in patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding, as it may cause harm to the fetus or baby. Patients should also avoid consuming alcohol while taking metronidazole, as it may increase the risk of side effects.Practical Applications
Future Directions
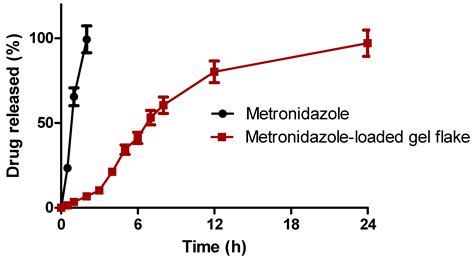
Research is ongoing to explore new uses for metronidazole, including its potential application in the treatment of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop new formulations and delivery systems for metronidazole, such as nanoparticles and liposomes, which may improve its efficacy and reduce its side effects.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Final Recommendations
Based on the information presented in this article, we recommend that healthcare professionals and patients alike consider metronidazole as a treatment option for various infections and conditions. Additionally, we encourage further research into the uses and applications of metronidazole, as well as the development of new formulations and delivery systems.What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections, including bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, and anaerobic infections.
How does metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by inhibiting DNA synthesis in microorganisms, ultimately leading to their death.
What are the side effects of metronidazole?
+The side effects of metronidazole include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and dizziness.
Can metronidazole be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+No, metronidazole should not be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it may cause harm to the fetus or baby.
What are the precautions and contraindications for metronidazole?
+Metronidazole should be used with caution in patients with a history of seizures, liver or kidney disease, and blood disorders. Additionally, metronidazole should not be used in patients who are allergic to the medication or have a history of allergic reactions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the uses of metronidazole. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with metronidazole, please comment below. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote the safe and effective use of metronidazole and improve patient outcomes.
