Intro
Discover the significance of a High Sed Rate Blood Test, revealing inflammation and infection through Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) results, aiding diagnosis of autoimmune disorders and chronic conditions.
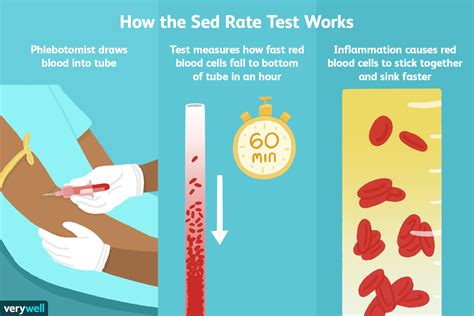
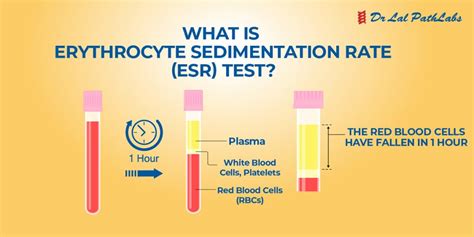
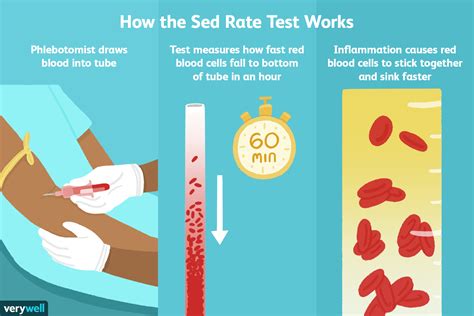
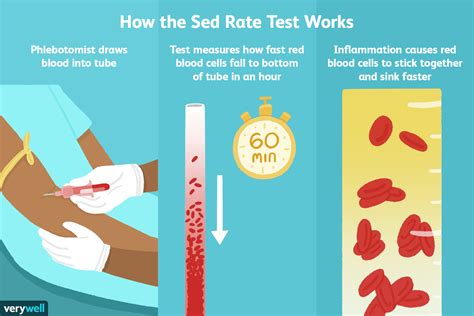
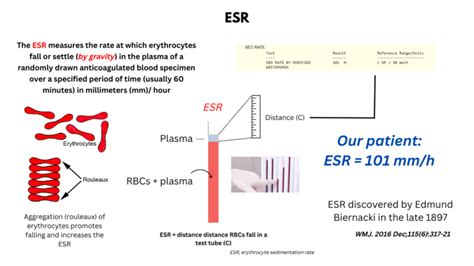
The sedimentation rate of red blood cells, also known as the sed rate or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. A high sed rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or autoimmune disorders, making it a crucial diagnostic tool in the medical field. Understanding the importance of the sed rate blood test can help individuals take proactive steps in managing their health and seeking medical attention when necessary.
The sed rate blood test is a simple, yet effective, method for detecting inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to injury or infection, and it can manifest in various ways, such as redness, swelling, pain, and warmth. When the body is injured or infected, it produces proteins that cause red blood cells to clump together, making them heavier and more likely to settle quickly. By measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle, healthcare professionals can determine the level of inflammation present in the body.
Inflammation can be acute or chronic, and it can affect various parts of the body, including the joints, organs, and tissues. A high sed rate can be an indicator of underlying conditions such as arthritis, lupus, or other autoimmune disorders. It can also be a sign of infection, cancer, or other diseases that cause inflammation. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes and consequences of a high sed rate and to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
What is a High Sed Rate?
Causes of a High Sed Rate
There are several causes of a high sed rate, including: * Inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis * Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, or endocarditis * Cancer, including lymphoma, multiple myeloma, or other types of cancer * Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis or type 1 diabetes * Pregnancy or postpartum period * Aging, as sed rates tend to increase with age * Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or hormonal therapiesHow is a High Sed Rate Diagnosed?
Interpreting Sed Rate Results
Interpreting sed rate results requires careful consideration of various factors, including the individual's age, sex, and medical history. A high sed rate may indicate inflammation or other underlying conditions, but it can also be influenced by other factors, such as: * Age: Sed rates tend to increase with age, so older adults may have higher sed rates than younger individuals. * Sex: Women tend to have higher sed rates than men, especially during pregnancy or postpartum period. * Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or hormonal therapies, can affect sed rate results. * Laboratory variations: Sed rate results can vary depending on the laboratory and the testing method used.Treatment and Management of a High Sed Rate
Complications and Risks
A high sed rate can be associated with various complications and risks, including: * Increased risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack or stroke * Increased risk of kidney disease or kidney failure * Increased risk of osteoporosis or bone fractures * Increased risk of infections or sepsis * Increased risk of cancer or cancer recurrencePrevention and Self-Care
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in reducing inflammation and preventing a high sed rate. Some examples include: * Eating an anti-inflammatory diet, such as the Mediterranean diet or a plant-based diet * Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking or yoga * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness or tai chi * Getting enough omega-3 fatty acids through fatty fish or supplements * Avoiding processed foods and added sugarsConclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with sed rate blood tests in the comments below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with a high sed rate? What steps have you taken to manage inflammation and prevent complications? Share your story and help others understand the importance of sed rate blood tests in maintaining overall health and well-being.
What is a normal sed rate range?
+A normal sed rate range is typically defined as 0-20 mm/h for adults, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and individual factors.
What causes a high sed rate?
+A high sed rate can be caused by various factors, including inflammatory diseases, infections, cancer, autoimmune disorders, pregnancy, or certain medications.
How is a high sed rate diagnosed?
+A high sed rate is typically diagnosed through a blood test, which involves collecting a blood sample from a vein in the arm and sending it to a laboratory for analysis.
What are the treatment options for a high sed rate?
+Treatment options for a high sed rate depend on the underlying cause of the inflammation and may include anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, cancer treatments, or lifestyle modifications.
Can a high sed rate be prevented?
+While a high sed rate cannot be completely prevented, reducing inflammation and managing underlying conditions through lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction, can help minimize the risk of developing a high sed rate.
