Intro
Discover the Coronary Calcium Scan Test, a non-invasive heart scan detecting calcium deposits, plaque buildup, and cardiovascular disease risks, using CT scans and imaging technology for early diagnosis and prevention of heart attacks and strokes.
The coronary calcium scan test, also known as a coronary artery calcium scan, is a non-invasive medical imaging test that helps diagnose and assess the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD is a condition where the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart, become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. This can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems. The coronary calcium scan test is an essential tool for detecting early signs of CAD, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further complications.
The test uses computed tomography (CT) technology to take detailed images of the heart and its blood vessels. It measures the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries, which is a marker of atherosclerosis, the underlying process that leads to CAD. The higher the calcium score, the greater the risk of CAD. The test is typically recommended for individuals with risk factors for CAD, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, or a family history of heart disease.
The importance of the coronary calcium scan test lies in its ability to identify individuals who are at high risk of CAD, even if they do not exhibit any symptoms. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes, improving overall cardiovascular health. Furthermore, the test can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track changes in the coronary arteries over time. With the increasing prevalence of CAD worldwide, the coronary calcium scan test has become a crucial diagnostic tool for preventing and managing this condition.
What is a Coronary Calcium Scan Test?
The test involves lying on a table that slides into a CT scanner, which takes X-ray images of the heart from different angles. The images are then reconstructed to create detailed pictures of the coronary arteries. The test is usually performed without contrast dye, but in some cases, a small amount of contrast may be used to enhance the images.
How Does the Test Work?
The coronary calcium scan test works by detecting the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries. Calcium is a marker of atherosclerosis, which is the underlying process that leads to CAD. The test uses a special type of CT scanner that can detect very small amounts of calcium in the arteries.The test produces a calcium score, which is a measure of the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries. The score is calculated by measuring the amount of calcium in each artery and then adding up the scores. The higher the calcium score, the greater the risk of CAD.
Benefits of the Coronary Calcium Scan Test
- Early detection of CAD: The test can detect early signs of CAD, even if symptoms are not present.
- Risk assessment: The test can help assess an individual's risk of CAD and identify those who are at high risk.
- Monitoring treatment: The test can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track changes in the coronary arteries over time.
- Non-invasive: The test is non-invasive and painless, making it a convenient and comfortable option for patients.
- Quick results: The test produces quick results, which can help healthcare providers make prompt treatment decisions.
Who Should Get a Coronary Calcium Scan Test?
The coronary calcium scan test is typically recommended for individuals who are at high risk of CAD. This includes:- Individuals with a family history of heart disease
- Individuals with high blood pressure or high cholesterol
- Smokers
- Individuals who are overweight or obese
- Individuals with a history of diabetes
- Individuals who are physically inactive
How to Prepare for the Test
- Avoid eating or drinking anything that contains caffeine or nicotine for at least 2 hours before the test
- Wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing jewelry or metal objects that may interfere with the test
- Remove any clothing or accessories that may contain metal, such as underwire bras or jeans with metal buttons
- Inform the healthcare provider of any medical conditions or allergies
- Inform the healthcare provider of any medications being taken
What to Expect During the Test
During the test, individuals can expect:- To lie on a table that slides into a CT scanner
- To wear a gown or comfortable clothing
- To have electrocardiogram (ECG) leads attached to the chest to monitor heart activity
- To hold their breath for a few seconds during the scan
- To hear a loud knocking or whirring noise during the scan
- To feel a slight sensation of warmth or pressure during the scan
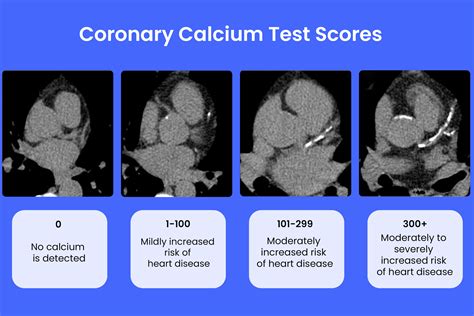
Understanding the Results
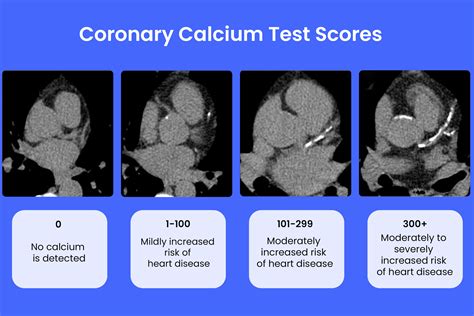
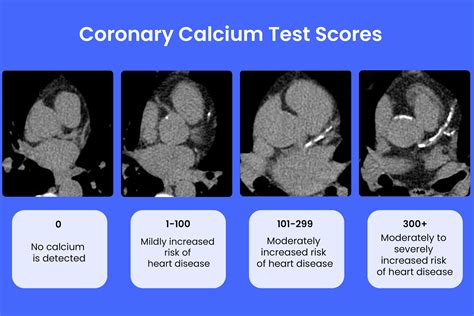
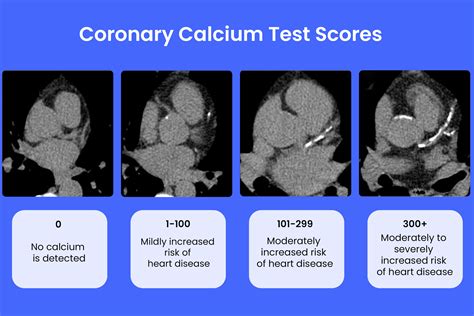
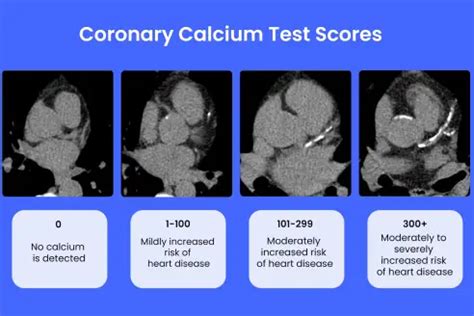
The following are the typical categories of calcium scores:
- 0: No calcium detected, indicating a low risk of CAD
- 1-10: Minimal calcium detected, indicating a low risk of CAD
- 11-100: Mild calcium detected, indicating a moderate risk of CAD
- 101-400: Moderate calcium detected, indicating a high risk of CAD
- Over 400: Extensive calcium detected, indicating a very high risk of CAD
What Do the Results Mean?
The results of the coronary calcium scan test can help healthcare providers:- Assess an individual's risk of CAD
- Identify individuals who are at high risk of CAD
- Monitor the effectiveness of treatment
- Track changes in the coronary arteries over time
Individuals with a high calcium score may need to undergo further testing or treatment to reduce their risk of CAD. This may include lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking or exercising regularly, or medication to lower cholesterol or blood pressure.
Limitations and Risks
- Radiation exposure: The test uses X-rays, which can expose individuals to radiation.
- Cost: The test can be expensive, especially for individuals without health insurance.
- False positives: The test can produce false positive results, which can lead to unnecessary further testing or treatment.
- False negatives: The test can produce false negative results, which can lead to a false sense of security.
Alternatives to the Coronary Calcium Scan Test
There are several alternatives to the coronary calcium scan test, including:- Stress test: A test that measures the heart's ability to function during physical activity.
- Echocardiogram: A test that uses sound waves to produce images of the heart.
- Cardiac catheterization: A test that uses a catheter to inject dye into the coronary arteries and produce images of the heart.
- MRI: A test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the heart.
What is the purpose of a coronary calcium scan test?
+The purpose of a coronary calcium scan test is to detect early signs of coronary artery disease (CAD) and assess an individual's risk of CAD.
How is the test performed?
+The test is performed using a CT scanner, which takes X-ray images of the heart from different angles. The images are then reconstructed to create detailed pictures of the coronary arteries.
What do the results of the test mean?
+The results of the test are reported as a calcium score, which is a measure of the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries. The score can range from 0 to over 400, with higher scores indicating a greater risk of CAD.
In conclusion, the coronary calcium scan test is a valuable diagnostic tool for detecting early signs of coronary artery disease and assessing an individual's risk of CAD. While the test has some limitations and risks, it can help healthcare providers make prompt treatment decisions and improve overall cardiovascular health. If you have any questions or concerns about the coronary calcium scan test, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others. Additionally, if you are at risk of CAD, we recommend speaking with your healthcare provider about undergoing a coronary calcium scan test to assess your risk and develop a treatment plan.
