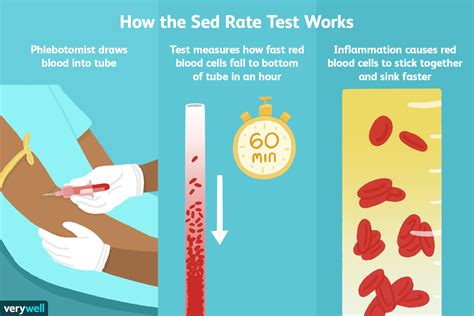
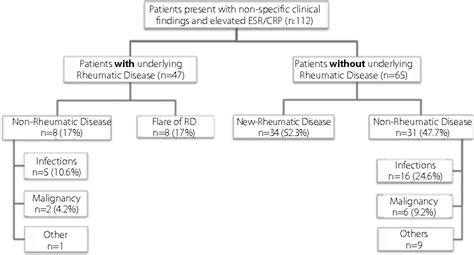
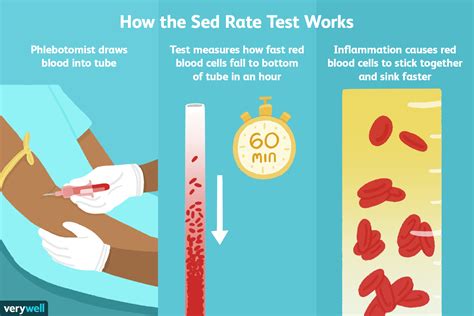
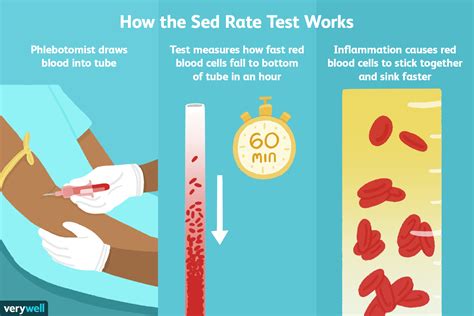
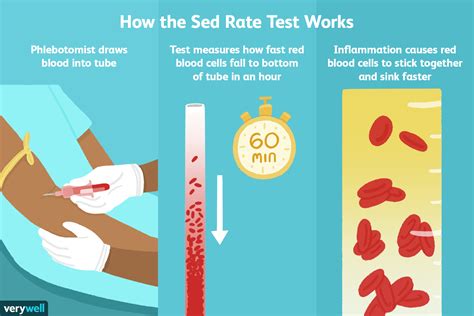
The sed rate blood test, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, is a widely used medical test that measures the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. This test is used to detect inflammation in the body, which can be a sign of various medical conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. In this article, we will delve into the details of the sed rate blood test, its uses, and what the results mean.
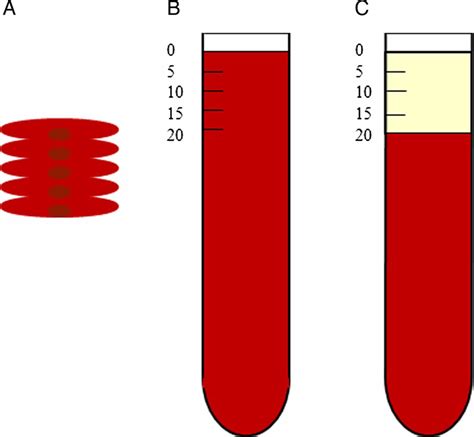
The sed rate blood test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that requires a blood sample to be drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant, which prevents the blood from clotting. The test tube is then left to stand for a specified period, usually one hour, and the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is measured. The result is expressed in millimeters per hour (mm/h).
The sed rate blood test is a useful diagnostic tool because it can detect inflammation in the body, which can be a sign of various medical conditions. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection, and it can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, swelling, and redness. By measuring the sed rate, doctors can determine the level of inflammation in the body and use this information to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
What is a Normal Sed Rate?
A normal sed rate varies depending on age and sex. In general, a sed rate of 0-20 mm/h is considered normal for adults. However, this range can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific test used. For example, some laboratories may consider a sed rate of 0-15 mm/h to be normal, while others may consider a sed rate of 0-25 mm/h to be normal. It's essential to note that a normal sed rate does not necessarily mean that there is no inflammation in the body, as some medical conditions can cause inflammation without affecting the sed rate.
What is an Elevated Sed Rate?
An elevated sed rate is a sed rate that is higher than the normal range. This can be a sign of inflammation in the body, which can be caused by various medical conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. An elevated sed rate can also be a sign of other medical conditions, such as anemia, kidney disease, and thyroid disease. In some cases, an elevated sed rate can be a sign of a life-threatening medical condition, such as sepsis or meningitis.
Causes of an Elevated Sed Rate
There are many possible causes of an elevated sed rate, including:
* Infections, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and urinary tract infections
* Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis
* Cancers, such as lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and prostate cancer
* Anemia, including iron deficiency anemia and vitamin deficiency anemia
* Kidney disease, including chronic kidney disease and kidney failure
* Thyroid disease, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
* Inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
What to Expect During a Sed Rate Blood Test
During a sed rate blood test, a healthcare professional will draw a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The blood sample will be placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant, which prevents the blood from clotting. The test tube will then be left to stand for a specified period, usually one hour, and the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube will be measured. The result will be expressed in millimeters per hour (mm/h).
How to Prepare for a Sed Rate Blood Test
To prepare for a sed rate blood test, it's essential to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional or laboratory. In general, there is no special preparation required for a sed rate blood test, but it's essential to:
* Avoid eating or drinking anything that may affect the test results, such as fatty foods or caffeine
* Avoid taking any medications that may affect the test results, such as aspirin or ibuprofen
* Wear loose and comfortable clothing to make it easier to draw the blood sample
* Arrive at the laboratory or healthcare professional's office at least 15 minutes before the scheduled appointment time
Interpreting Sed Rate Blood Test Results
Interpreting sed rate blood test results requires a thorough understanding of the test and its limitations. A sed rate result can be influenced by various factors, including age, sex, and medical conditions. It's essential to consider the sed rate result in conjunction with other medical test results and clinical findings to make an accurate diagnosis. In general, a sed rate result can be interpreted as follows:
* A normal sed rate result indicates that there is no significant inflammation in the body.
* An elevated sed rate result indicates that there is inflammation in the body, which can be caused by various medical conditions.
* A very high sed rate result can indicate a life-threatening medical condition, such as sepsis or meningitis.
Factors that Can Affect Sed Rate Blood Test Results
There are several factors that can affect sed rate blood test results, including:
* Age: Sed rate increases with age, so older adults may have a higher sed rate than younger adults.
* Sex: Women tend to have a higher sed rate than men, especially during pregnancy and menstruation.
* Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as anemia, kidney disease, and thyroid disease, can affect sed rate results.
* Medications: Certain medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, can affect sed rate results.
* Laboratory variations: Sed rate results can vary between laboratories, so it's essential to use the same laboratory for repeat tests.
Limitations of the Sed Rate Blood Test
The sed rate blood test has several limitations, including:
* It's not specific: A sed rate result can be elevated in various medical conditions, making it difficult to diagnose a specific condition.
* It's not sensitive: A sed rate result can be normal in some medical conditions, even if there is significant inflammation in the body.
* It can be influenced by various factors: Sed rate results can be affected by age, sex, medical conditions, medications, and laboratory variations.
Alternatives to the Sed Rate Blood Test
There are several alternatives to the sed rate blood test, including:
* C-reactive protein (CRP) test: This test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which is a protein that increases in response to inflammation.
* Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test: This test measures the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample.
* Complete blood count (CBC) test: This test measures the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What is the normal range for a sed rate blood test?
+
A normal sed rate varies depending on age and sex, but in general, a sed rate of 0-20 mm/h is considered normal for adults.
What can cause an elevated sed rate?
+
An elevated sed rate can be caused by various medical conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers.
How is a sed rate blood test performed?
+
A sed rate blood test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm and measuring the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube.
In conclusion, the sed rate blood test is a useful diagnostic tool that can detect inflammation in the body. By understanding the sed rate blood test results and their limitations, healthcare professionals can make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans. If you have any questions or concerns about the sed rate blood test, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional. Share your thoughts and experiences with the sed rate blood test in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may find it helpful.