Intro
Stay protected with our Tetanus Immunization Schedule Guide, covering vaccination timelines, booster shots, and prevention methods to avoid tetanus infection and lockjaw, ensuring a healthy immune system through proper immunization and disease prevention strategies.
Tetanus is a serious bacterial infection that can lead to severe muscle stiffness, spasms, and even death. The good news is that tetanus can be prevented through immunization. In this article, we will delve into the world of tetanus immunization, exploring the importance of vaccination, the recommended schedule, and the benefits of staying protected against this deadly disease. Whether you're a parent, a healthcare professional, or simply someone looking to stay informed, this guide is for you.
The importance of tetanus immunization cannot be overstated. Tetanus bacteria are ubiquitous in the environment, and infection can occur through even minor wounds or cuts. The consequences of tetanus infection are severe, with symptoms ranging from muscle stiffness and spasms to respiratory failure and even death. Fortunately, tetanus immunization is highly effective in preventing infection, and widespread vaccination has led to a significant decline in tetanus cases worldwide.
As we explore the world of tetanus immunization, it's essential to understand the different types of vaccines available, including DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis) and Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis). We'll also examine the recommended immunization schedule, including booster shots and special considerations for certain populations, such as pregnant women and individuals with compromised immune systems. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of tetanus immunization and the importance of staying protected against this serious disease.
Tetanus Immunization Overview

The benefits of tetanus immunization are numerous, including:
- Prevention of severe muscle stiffness and spasms
- Reduction in respiratory failure and other complications
- Protection against tetanus infection in wounds and cuts
- Boosting of immune system function to prevent infection
Types of Tetanus Vaccines
There are several types of tetanus vaccines available, including: * DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis) * Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis) * Td (tetanus and diphtheria) Each vaccine has its own unique characteristics and recommendations for use, and healthcare professionals can help determine the best vaccine for individual needs.Tetanus Immunization Schedule
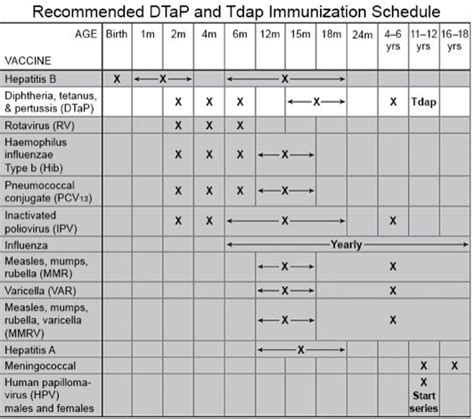
It's essential to follow the recommended immunization schedule to ensure optimal protection against tetanus infection. Booster shots are also crucial to maintain immunity and prevent waning protection over time.
Special Considerations
Certain populations may require special considerations when it comes to tetanus immunization, including: * Pregnant women: Tdap vaccine during pregnancy to protect against pertussis and tetanus * Individuals with compromised immune systems: Tdap or Td vaccine as recommended by healthcare professionals * Travelers: Tdap or Td vaccine before travel to areas with high tetanus riskHealthcare professionals can help determine the best immunization schedule and recommendations for individual needs and circumstances.
Tetanus Immunization Benefits

In addition to these benefits, tetanus immunization also plays a critical role in public health efforts to prevent infectious disease. Widespread vaccination has led to a significant decline in tetanus cases worldwide, and continued immunization efforts are essential to maintaining this progress.
Common Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions about tetanus immunization, including: * The idea that tetanus vaccine is only necessary for individuals who work with soil or animals * The belief that tetanus vaccine is not effective or is associated with serious side effects * The notion that tetanus infection is not a significant risk in developed countriesIt's essential to separate fact from fiction and understand the importance of tetanus immunization for all individuals, regardless of age, occupation, or health status.
Tetanus Immunization Side Effects

Serious side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions or neurological complications. Healthcare professionals can help determine the best course of action and provide guidance on managing side effects.
Managing Side Effects
To manage side effects and minimize discomfort, individuals can: * Apply a cold compress to the injection site to reduce pain and swelling * Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen * Rest and avoid strenuous activity * Stay hydrated and drink plenty of fluidsIt's essential to follow the recommended immunization schedule and consult with healthcare professionals if side effects persist or worsen over time.
Tetanus Immunization and Pregnancy

Pregnant women should consult with healthcare professionals to determine the best immunization schedule and recommendations for their individual needs.
Pregnancy and Tetanus Immunization
Pregnancy is a critical time for tetanus immunization, as it provides protection against pertussis and tetanus for both mother and baby. The benefits of tetanus immunization during pregnancy include: * Prevention of pertussis infection in newborns * Reduction in the risk of tetanus infection in mothers and babies * Boosting of immune system function to prevent infectionHealthcare professionals can help determine the best immunization schedule and recommendations for pregnant women, taking into account individual needs and health status.
Tetanus Immunization FAQs

What is tetanus immunization, and why is it important?
+Tetanus immunization is a critical component of public health efforts to prevent infectious disease. The tetanus vaccine provides protection against tetanus infection, which can lead to severe muscle stiffness, spasms, and even death.
Who should receive tetanus immunization, and what is the recommended schedule?
+The CDC recommends tetanus immunization for all individuals, regardless of age or health status. The recommended schedule varies depending on age, health status, and other factors, but generally includes DTaP vaccine for infants and young children, Tdap vaccine for preteens and teens, and Td vaccine for adults.
What are the benefits of tetanus immunization, and how does it work?
+The benefits of tetanus immunization include prevention of severe muscle stiffness and spasms, reduction in respiratory failure and other complications, and protection against tetanus infection in wounds and cuts. The tetanus vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that recognize and attack the tetanus bacteria, preventing infection and disease.
In conclusion, tetanus immunization is a critical component of public health efforts to prevent infectious disease. By understanding the importance of tetanus immunization, the recommended schedule, and the benefits of staying protected, individuals can take control of their health and well-being. We encourage readers to share this article with friends and family, and to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the best immunization schedule and recommendations for their individual needs. Together, we can work towards a healthier and more informed community, where tetanus infection is a rarity rather than a reality.
