Intro
Discover the implications of a high sed rate, including inflammation, infection, and autoimmune disorders, and learn 5 ways to address elevated sedimentation rates for improved health outcomes and reduced disease risk.
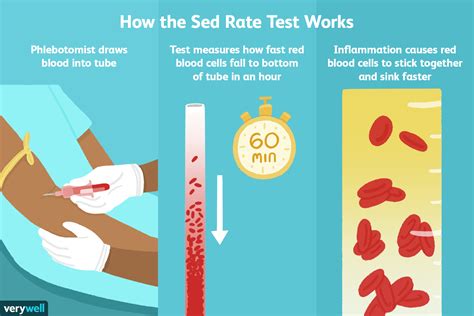
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, or sed rate, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. A high sed rate indicates the presence of inflammation, which can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. Understanding the causes and implications of a high sed rate is crucial for diagnosing and managing underlying health issues.
The sed rate test is a simple, yet effective tool for assessing the level of inflammation in the body. It works by measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle in a test tube. In the presence of inflammation, red blood cells tend to clump together, causing them to settle more quickly than normal. This results in a higher sed rate. The test is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as blood tests and imaging studies, to help identify the underlying cause of inflammation.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system, designed to protect against harm caused by injury, infection, or disease. While acute inflammation is a necessary and beneficial response, chronic inflammation can lead to a range of health problems, including tissue damage, organ dysfunction, and increased risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A high sed rate can indicate the presence of chronic inflammation, highlighting the need for further investigation and treatment to prevent long-term complications.
Understanding Sed Rate
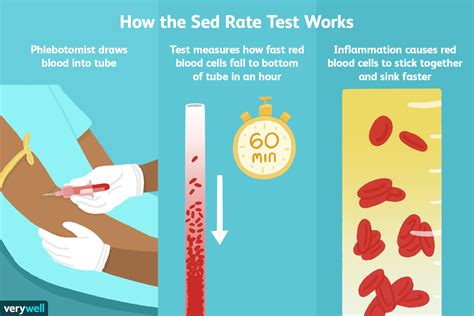
The sed rate is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/hr) and is typically categorized as follows: 0-20 mm/hr for men and 0-30 mm/hr for women. A high sed rate is generally considered to be above 40 mm/hr, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health. It's essential to note that a high sed rate is not a diagnosis in itself but rather an indicator of inflammation that requires further investigation to determine the underlying cause.
Factors Influencing Sed Rate
Several factors can influence sed rate, including age, sex, and the presence of certain medical conditions. For example, sed rate tends to increase with age, and women generally have higher sed rates than men. Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can also affect sed rate, making it essential to consider these factors when interpreting test results.Causes of High Sed Rate
A high sed rate can be caused by a range of conditions, including:
- Infections, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, or sepsis
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Cancers, such as lymphoma, multiple myeloma, or prostate cancer
- Chronic inflammatory diseases, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
- Vasculitis, or inflammation of the blood vessels
It's crucial to identify the underlying cause of a high sed rate to provide appropriate treatment and management. This may involve further diagnostic testing, such as blood work, imaging studies, or biopsies, to determine the presence and extent of inflammation.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a high sed rate depends on the underlying cause of inflammation. For example, if the cause is an infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. If the cause is an autoimmune disorder, treatment may involve immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids or biologics. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or stress management, may also be recommended to help reduce inflammation.5 Ways to Address High Sed Rate

While a high sed rate is not a condition that can be treated directly, addressing the underlying cause of inflammation can help reduce sed rate and alleviate symptoms. Here are five ways to address high sed rate:
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, medications such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress, can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
- Alternative Therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or mind-body therapies, may also be beneficial in reducing inflammation and promoting relaxation.
- Dietary Changes: Eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on inflammation.
Prevention Strategies
While it's not possible to prevent all cases of high sed rate, adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing chronic conditions can help reduce the risk of inflammation and related health problems. This includes: * Maintaining a healthy weight * Engaging in regular physical activity * Eating a balanced diet * Managing stress * Getting enough sleep * Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumptionConclusion and Next Steps

A high sed rate is a significant indicator of inflammation that requires further investigation to determine the underlying cause. By understanding the causes and implications of a high sed rate, individuals can take proactive steps to address inflammation and promote overall health. If you're concerned about your sed rate or are experiencing symptoms of inflammation, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the best course of action.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with sed rate and inflammation in the comments below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with a high sed rate? What steps have you taken to address inflammation and promote healing? Your insights and stories can help others better understand the importance of managing inflammation and maintaining overall health.
What is a normal sed rate range?
+A normal sed rate range is typically considered to be 0-20 mm/hr for men and 0-30 mm/hr for women.
What are the common causes of a high sed rate?
+Common causes of a high sed rate include infections, autoimmune disorders, cancers, chronic inflammatory diseases, and vasculitis.
How can I reduce inflammation and lower my sed rate?
+Reducing inflammation and lowering sed rate can be achieved through a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, dietary changes, and stress management.
