Intro
Discover the significance of a high sediment rate blood test, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) results, inflammation indicators, and related conditions like anemia, infection, and autoimmune disorders.
The presence of sediment in the blood can be an indicator of various health issues, ranging from minor to severe conditions. A high sediment rate blood test, also known as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a diagnostic tool used to measure the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. This rate can provide valuable insights into the body's inflammatory response and help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor a range of conditions.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection, and it can manifest in various ways, including redness, swelling, pain, and fever. While some level of inflammation is necessary for the body to heal and protect itself, excessive or chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. A high sediment rate blood test can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing these conditions or monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
The ESR test is a simple, non-invasive procedure that involves collecting a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then placed in a test tube containing an anticoagulant to prevent clotting, and the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is measured over a period of time, usually one hour. The results are expressed in millimeters per hour (mm/h), and the normal range varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. In general, a high sediment rate is considered to be above 20-30 mm/h, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used.
Understanding ESR Results
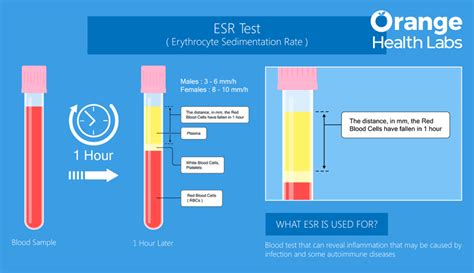
To interpret the results of a high sediment rate blood test, it's essential to consider the individual's overall health status, medical history, and other diagnostic findings. A high ESR can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or other conditions that affect the blood or immune system. Some common causes of a high sediment rate include:
- Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, or urinary tract infections
- Inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or Crohn's disease
- Cancer, particularly multiple myeloma or lymphoma
- Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis or type 1 diabetes
- Chronic diseases such as kidney disease or heart disease
Factors That Influence ESR Results

Several factors can influence the results of a high sediment rate blood test, including:
- Age: ESR tends to increase with age, so older adults may have higher ESR results than younger individuals.
- Sex: Women tend to have higher ESR results than men, particularly during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy.
- Pregnancy: ESR can increase during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can affect ESR results.
- Laboratory variations: Different laboratories may use different testing methods or equipment, which can affect ESR results.
Conditions Associated with High ESR

A high sediment rate blood test can be associated with various conditions, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: A chronic autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and pain in the joints.
- Lupus: A systemic autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause a high ESR, particularly if they are severe or chronic.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as multiple myeloma or lymphoma, can cause a high ESR.
- Kidney disease: Chronic kidney disease or kidney failure can cause a high ESR due to inflammation and immune system activation.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of a high sediment rate blood test depend on the underlying cause of the elevated ESR. In some cases, no treatment may be necessary, and the ESR may return to normal on its own. However, if the high ESR is associated with an underlying condition, treatment may involve:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If the high ESR is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the underlying infection.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of ESR results and other diagnostic tests can help healthcare professionals track the effectiveness of treatment and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Limitations and Potential Risks

While a high sediment rate blood test can provide valuable information about the body's inflammatory response, there are some limitations and potential risks to consider:
- False positives: A high ESR can be caused by non-inflammatory conditions, such as pregnancy or aging, which can lead to false positives.
- False negatives: A normal ESR does not necessarily rule out inflammation or underlying conditions, which can lead to false negatives.
- Laboratory errors: Errors in laboratory testing or equipment can affect ESR results, leading to inaccurate diagnoses or treatments.
- Over-reliance on ESR: Relying too heavily on ESR results can lead to over-treatment or under-treatment of underlying conditions.
Future Directions

Research is ongoing to improve the accuracy and reliability of high sediment rate blood tests. Some potential future directions include:
- Developing more sensitive and specific testing methods to reduce false positives and false negatives.
- Investigating the use of ESR in combination with other diagnostic tests to improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Exploring the potential of ESR as a biomarker for chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes.
What is a high sediment rate blood test?
+A high sediment rate blood test, also known as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a diagnostic tool used to measure the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample.
What are the common causes of a high sediment rate?
+Common causes of a high sediment rate include infections, inflammatory diseases, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic diseases such as kidney disease or heart disease.
How is a high sediment rate blood test performed?
+The test involves collecting a blood sample from a vein in the arm, placing it in a test tube containing an anticoagulant, and measuring the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube over a period of time, usually one hour.
What are the limitations and potential risks of a high sediment rate blood test?
+Limitations and potential risks include false positives and false negatives, laboratory errors, and over-reliance on ESR results, which can lead to inaccurate diagnoses or treatments.
What are the future directions for high sediment rate blood tests?
+Future directions include developing more sensitive and specific testing methods, investigating the use of ESR in combination with other diagnostic tests, and exploring the potential of ESR as a biomarker for chronic diseases.
In conclusion, a high sediment rate blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide insights into the body's inflammatory response and help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor a range of conditions. While there are limitations and potential risks to consider, ongoing research and development are aimed at improving the accuracy and reliability of ESR tests. If you have any questions or concerns about high sediment rate blood tests, we encourage you to consult with a healthcare professional or share your thoughts in the comments below.
