Intro
The sedimentation rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sedimentation rate is a widely used laboratory test to help diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. In this article, we will delve into the meaning and significance of the sedimentation rate, its working mechanism, and the steps involved in the test.
The sedimentation rate is an important indicator of the body's inflammatory response. When the body is inflamed, the liver produces more proteins, which cause red blood cells to clump together, making them heavier and more likely to settle quickly. The sedimentation rate is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h) and is calculated by measuring the distance the red blood cells have settled after a specified period, usually one hour. A higher sedimentation rate indicates greater inflammation in the body.
The sedimentation rate has been a cornerstone of laboratory testing for many decades, providing valuable information about the body's inflammatory status. It is often used in conjunction with other laboratory tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to confirm or rule out certain conditions. The sedimentation rate is particularly useful in monitoring the progression of diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other inflammatory conditions. It is also used to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to detect any potential complications.
How Sedimentation Rate Works
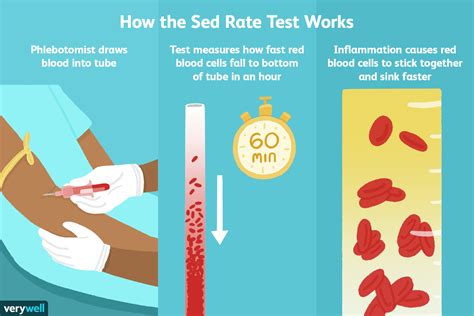
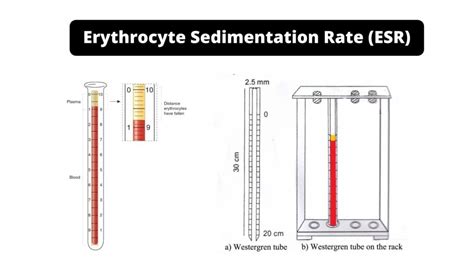
The sedimentation rate works by measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube. The test involves adding an anticoagulant to a blood sample to prevent the blood from clotting. The blood sample is then placed in a test tube, and the red blood cells are allowed to settle for a specified period. The distance the red blood cells have settled is then measured, and the result is calculated in mm/h. The sedimentation rate is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of fibrinogen and other proteins in the blood, the size and shape of the red blood cells, and the presence of any inflammatory conditions.
Factors Affecting Sedimentation Rate
Several factors can affect the sedimentation rate, including age, sex, and the presence of certain medical conditions. For example, women tend to have a higher sedimentation rate than men, and the rate tends to increase with age. Certain medical conditions, such as pregnancy, anemia, and inflammatory disorders, can also affect the sedimentation rate. It is essential to consider these factors when interpreting the results of the sedimentation rate test.Steps Involved in Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test involves several steps, including:
- Collecting a blood sample from the patient
- Adding an anticoagulant to the blood sample to prevent clotting
- Placing the blood sample in a test tube
- Allowing the red blood cells to settle for a specified period
- Measuring the distance the red blood cells have settled
- Calculating the sedimentation rate in mm/h
The test is usually performed in a laboratory setting, and the results are available within a few hours. The sedimentation rate test is a relatively simple and inexpensive test, making it a widely used diagnostic tool.
Interpreting Sedimentation Rate Results
Interpreting the results of the sedimentation rate test requires careful consideration of several factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results. A high sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of an inflammatory condition, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. However, a high sedimentation rate can also be caused by other factors, such as pregnancy or anemia. A low sedimentation rate can indicate the absence of inflammation or the effectiveness of treatment.Benefits of Sedimentation Rate Test

The sedimentation rate test has several benefits, including:
- Helping to diagnose and monitor inflammatory and autoimmune disorders
- Assessing the effectiveness of treatment
- Detecting potential complications
- Providing valuable information about the body's inflammatory status
- Being a relatively simple and inexpensive test
The sedimentation rate test is a widely used diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the body's inflammatory status. It is essential to consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results when interpreting the results of the sedimentation rate test.
Limitations of Sedimentation Rate Test
While the sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. For example, the test is not specific to any particular condition and can be affected by several factors, including age, sex, and the presence of certain medical conditions. The test is also not sensitive enough to detect mild inflammation. Additionally, the test requires careful handling and processing of the blood sample to ensure accurate results.Common Conditions Diagnosed with Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor several conditions, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Cancer
- Infections
- Pregnancy complications
The sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the body's inflammatory status. It is essential to consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results when interpreting the results of the sedimentation rate test.
Other Laboratory Tests Used in Conjunction with Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test is often used in conjunction with other laboratory tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to confirm or rule out certain conditions. The CRP test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which is a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation. Other laboratory tests, such as the complete blood count (CBC) and the blood chemistry test, may also be used to provide a comprehensive picture of the patient's condition.Monitoring Sedimentation Rate Over Time
Monitoring the sedimentation rate over time is essential to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to detect any potential complications. The sedimentation rate test can be repeated at regular intervals to monitor the patient's condition and adjust treatment as needed. It is essential to consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results when interpreting the results of the sedimentation rate test.
Importance of Sedimentation Rate in Clinical Practice
The sedimentation rate is an essential tool in clinical practice, providing valuable information about the body's inflammatory status. It is widely used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, assess the effectiveness of treatment, and detect potential complications. The sedimentation rate test is a relatively simple and inexpensive test, making it a widely used diagnostic tool.Future Directions of Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test is a widely used diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the body's inflammatory status. Future research directions may include the development of more sensitive and specific tests, the use of sedimentation rate in conjunction with other laboratory tests, and the exploration of new clinical applications for the sedimentation rate test.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, the sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the body's inflammatory status. It is essential to consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results when interpreting the results of the sedimentation rate test. We recommend the use of sedimentation rate test in conjunction with other laboratory tests to confirm or rule out certain conditions. Additionally, we recommend monitoring the sedimentation rate over time to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to detect any potential complications.What is the sedimentation rate test used for?
+The sedimentation rate test is used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, assess the effectiveness of treatment, and detect potential complications.
What are the benefits of the sedimentation rate test?
+The benefits of the sedimentation rate test include helping to diagnose and monitor inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, assessing the effectiveness of treatment, detecting potential complications, and providing valuable information about the body's inflammatory status.
What are the limitations of the sedimentation rate test?
+The limitations of the sedimentation rate test include being not specific to any particular condition, being affected by several factors, and not being sensitive enough to detect mild inflammation.
How is the sedimentation rate test performed?
+The sedimentation rate test involves collecting a blood sample, adding an anticoagulant, placing the blood sample in a test tube, allowing the red blood cells to settle, measuring the distance the red blood cells have settled, and calculating the sedimentation rate in mm/h.
What are the common conditions diagnosed with the sedimentation rate test?
+The common conditions diagnosed with the sedimentation rate test include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, infections, and pregnancy complications.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the sedimentation rate test and its significance in clinical practice. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
