Intro
Discover 5 key sedimentation rate facts, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) tests, blood sedimentation, and inflammation indicators, to understand its role in diagnosing medical conditions.
The sedimentation rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. This test has been used for over a century and remains a valuable tool in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions. Understanding the sedimentation rate is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as it provides insights into the body's inflammatory response and potential underlying health issues.
The importance of the sedimentation rate lies in its ability to indicate the presence of inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. By measuring the sedimentation rate, healthcare providers can assess the level of inflammation and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. Moreover, the sedimentation rate can help differentiate between conditions with similar symptoms, making it a valuable diagnostic tool.
The sedimentation rate has been extensively studied, and its clinical significance is well-established. Research has shown that elevated sedimentation rates are associated with increased morbidity and mortality in various patient populations. Furthermore, the sedimentation rate has been used to monitor disease activity and response to treatment in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease. With its wide range of applications and non-invasive nature, the sedimentation rate remains a widely used test in clinical practice.
Introduction to Sedimentation Rate
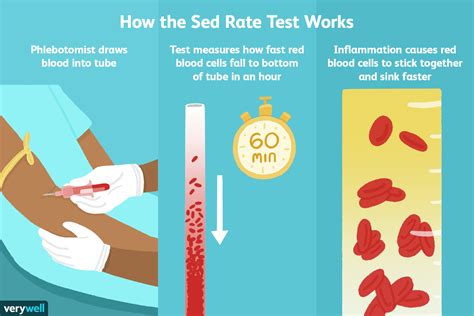
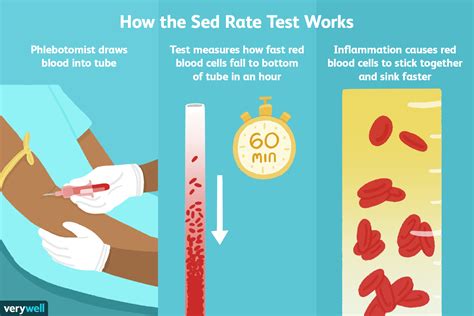
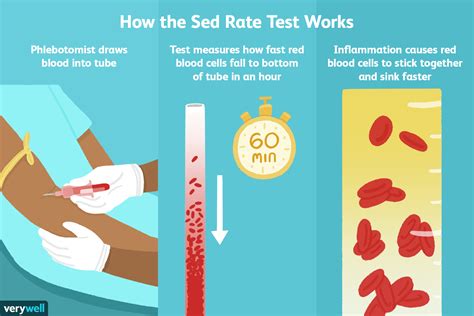
How the Sedimentation Rate Works
The sedimentation rate works by measuring the distance red blood cells travel in a test tube over a set period, usually one hour. The test tube contains a blood sample mixed with an anticoagulant to prevent clotting. The red blood cells settle at the bottom of the tube, and the distance they travel is measured. The sedimentation rate is calculated based on the distance the red blood cells have settled, with higher rates indicating greater inflammation.Benefits of the Sedimentation Rate Test
Common Applications of the Sedimentation Rate
The sedimentation rate has a wide range of applications, including: * Diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease * Identifying underlying infections, such as tuberculosis or pneumonia * Monitoring disease activity and response to treatment in conditions such as cancer or autoimmune disorders * Differentiating between conditions with similar symptoms, such as fever or fatigueInterpreting Sedimentation Rate Results
Factors that Influence the Sedimentation Rate
Several factors can influence the sedimentation rate, including: * Age: Sedimentation rates tend to increase with age * Sex: Women tend to have higher sedimentation rates than men * Pregnancy: Sedimentation rates can increase during pregnancy * Underlying medical conditions: Certain conditions, such as anemia or kidney disease, can affect the sedimentation rateLimitations of the Sedimentation Rate Test
Alternatives to the Sedimentation Rate Test
Several alternative tests can be used to measure inflammation, including: * C-reactive protein (CRP) test: Measures the level of CRP, a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation * Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test: Measures the rate at which red blood cells settle in a test tube * Plasma viscosity test: Measures the thickness and stickiness of blood plasmaConclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
The sedimentation rate is an important test that can help healthcare providers diagnose and monitor various conditions. By understanding the benefits, limitations, and alternatives to the sedimentation rate test, individuals can make informed decisions about their health. As research continues to advance our understanding of inflammation and its role in various diseases, the sedimentation rate will remain a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory conditions.What is the sedimentation rate test used for?
+The sedimentation rate test is used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory conditions, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
How is the sedimentation rate test performed?
+The sedimentation rate test is performed by measuring the distance red blood cells travel in a test tube over a set period, usually one hour.
What are the benefits of the sedimentation rate test?
+The benefits of the sedimentation rate test include its non-invasive nature, low cost, and wide availability, making it a valuable diagnostic tool.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the sedimentation rate and its importance in diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory conditions. If you have any further questions or would like to share your thoughts, please comment below. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
