Intro
Manage shoulder arthritis symptoms with exercises and treatments, alleviating joint pain and inflammation, improving mobility and reducing stiffness in shoulder joints affected by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other conditions.
The shoulder joint is one of the most mobile and complex joints in the human body, comprising multiple bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to facilitate a wide range of movements. However, this intricate structure also makes the shoulder joint prone to various types of arthritis, which can cause significant pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Arthritis in the shoulder can affect anyone, regardless of age or lifestyle, and it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to manage this condition effectively.
Arthritis in the shoulder can result from various factors, including wear and tear, injuries, infections, or autoimmune disorders. The most common types of arthritis that affect the shoulder joint are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and rotator cuff-related arthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears away, causing bone-on-bone contact and leading to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and damage to the joint lining, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Rotator cuff-related arthritis occurs when the tendons and muscles that surround the shoulder joint become inflamed or damaged, causing pain and weakness in the shoulder.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of shoulder arthritis is crucial for effective management and treatment. The symptoms of shoulder arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition but commonly include pain, stiffness, limited mobility, and weakness in the affected shoulder. In some cases, patients may also experience grinding or clicking sensations in the joint, as well as swelling and redness. If left untreated, shoulder arthritis can lead to significant disability and impaired quality of life, making it essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Understanding Shoulder Arthritis
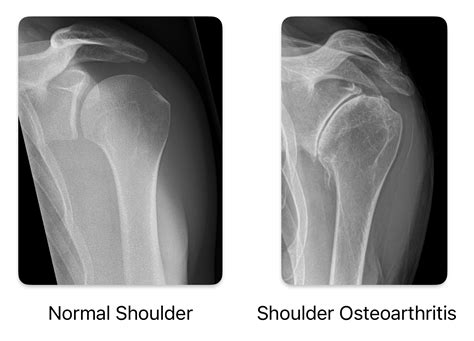
Shoulder arthritis can be diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. A thorough physical examination can help identify signs of joint inflammation, limited mobility, and muscle weakness, while imaging tests can confirm the presence of joint damage or degeneration. In some cases, a doctor may also order blood tests to rule out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.
Types of Shoulder Arthritis
There are several types of shoulder arthritis, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of shoulder arthritis, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is a less common but more aggressive form of arthritis that can cause significant joint damage and disability. Other types of shoulder arthritis include post-traumatic arthritis, which occurs after a shoulder injury, and rotator cuff-related arthritis, which affects the tendons and muscles surrounding the shoulder joint.Causes and Risk Factors

Several factors can increase the risk of developing shoulder arthritis, including age, genetics, obesity, and previous injuries or trauma. Age is a significant risk factor, as the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis increases significantly after the age of 50. Genetics can also play a role, as some people may be more prone to developing certain types of arthritis due to their genetic makeup. Obesity can put additional stress on the joints, increasing the risk of wear and tear, while previous injuries or trauma can cause joint damage and increase the risk of developing post-traumatic arthritis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of shoulder arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition but commonly include pain, stiffness, limited mobility, and weakness in the affected shoulder. In some cases, patients may also experience grinding or clicking sensations in the joint, as well as swelling and redness. A thorough physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests can help diagnose shoulder arthritis and rule out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.Treatment Options
Treatment for shoulder arthritis depends on the type and severity of the condition, as well as the patient's overall health and lifestyle. Conservative treatment options include physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and exercise. In some cases, medications such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid injections may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Surgical options, such as joint replacement or rotator cuff repair, may be necessary in more severe cases or when conservative treatment has failed to provide relief.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment options for shoulder arthritis include physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications. Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and reduce pain and stiffness. Pain management may involve the use of medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and exercise, can help reduce stress on the joints and improve overall health and well-being.Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for shoulder arthritis may be necessary in more severe cases or when conservative treatment has failed to provide relief. Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one, while rotator cuff repair surgery involves repairing or replacing the damaged tendons and muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Other surgical options, such as arthroscopy or joint resurfacing, may also be available, depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery and rehabilitation after shoulder arthritis surgery can take several months to a year or more, depending on the type of surgery and the individual's overall health and lifestyle. A thorough rehabilitation program, including physical therapy and exercise, can help improve joint mobility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and reduce pain and stiffness. It is essential to follow the doctor's instructions and attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.Prevention and Management

Preventing and managing shoulder arthritis requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, exercise, and medical treatment. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding repetitive movements or heavy lifting can help reduce stress on the joints and prevent wear and tear. Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help identify potential problems early on, while prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, exercise, and stress reduction, can help reduce stress on the joints and improve overall health and well-being. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the joints, while regular exercise can help improve joint mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.Conclusion and Next Steps
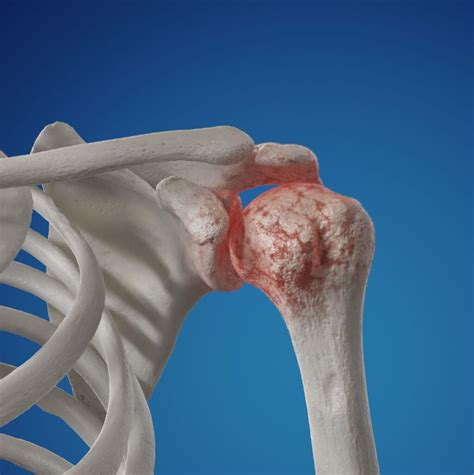
In conclusion, shoulder arthritis is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive treatment approach. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take the first step towards managing their condition and improving their overall health and well-being. If you are experiencing symptoms of shoulder arthritis, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment and develop a personalized plan to manage your condition.
We invite you to share your experiences and ask questions about shoulder arthritis in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help others better understand this condition and find the support they need to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may be affected by shoulder arthritis.
What are the most common symptoms of shoulder arthritis?
+The most common symptoms of shoulder arthritis include pain, stiffness, limited mobility, and weakness in the affected shoulder.
How is shoulder arthritis diagnosed?
+Shoulder arthritis can be diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans.
What are the treatment options for shoulder arthritis?
+Treatment options for shoulder arthritis include conservative treatment, such as physical therapy and pain management, as well as surgical options, such as joint replacement or rotator cuff repair.
Can shoulder arthritis be prevented?
+While shoulder arthritis cannot be completely prevented, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly, can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
What is the prognosis for shoulder arthritis?
+The prognosis for shoulder arthritis depends on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. With proper management and treatment, many individuals can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
