Intro
Glipizide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. As an oral sulfonylurea, glipizide works by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. While glipizide can be an effective treatment for managing blood sugar, it is not without its potential side effects. Understanding these side effects is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment plan and to recognize when they might need to seek medical attention.
The use of glipizide and other sulfonylureas has been a cornerstone in the management of type 2 diabetes for decades. However, the therapy's benefits must be weighed against its potential risks. Side effects can range from mild and temporary to severe and potentially life-threatening. Common side effects include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain, and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Less common but more serious side effects can include allergic reactions, liver damage, and an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Common Side Effects of Glipizide
Other common side effects include weight gain, which is a concern for many patients with diabetes, as excess weight can worsen the condition and increase the risk of other health problems. Gastrointestinal side effects like nausea and vomiting can also occur, potentially affecting the patient's ability to maintain adequate nutrition and hydration. These side effects can often be managed through dietary adjustments, taking the medication with food, or using anti-emetic drugs if necessary.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects

There is also evidence suggesting that sulfonylureas like glipizide may increase the risk of cardiovascular events, including heart attacks and strokes, especially in the early stages of treatment. This risk underscores the importance of careful patient selection and monitoring, particularly for those with pre-existing heart disease.
Managing and Preventing Side Effects
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for adjusting the dose of glipizide and for early detection of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Patients should also be aware of the symptoms of severe side effects and know when to seek medical help. Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers about any side effects or concerns can help in managing the treatment plan effectively.
Special Considerations and Interactions
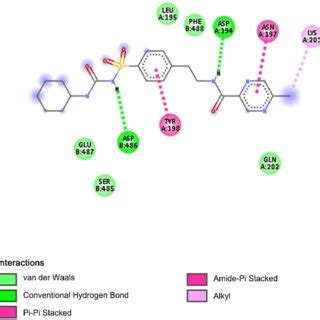
Patients should inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements, to minimize the risk of drug interactions. Alcohol consumption should also be limited, as it can affect blood sugar levels and increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Patient Education and Empowerment

By working closely with their healthcare team, patients can optimize their diabetes management plan, minimize the risk of side effects, and improve their overall quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for adjusting the treatment plan as needed and for addressing any concerns or questions patients may have.
Conclusion and Future Directions
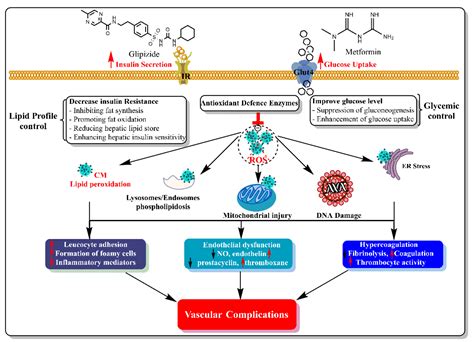
For now, glipizide remains a valuable option for many patients with type 2 diabetes, offering the potential for improved blood sugar control when used appropriately. By understanding the potential side effects of glipizide and taking proactive steps to manage them, patients can work towards achieving their health goals and reducing the risk of long-term diabetes complications.
What is the most common side effect of glipizide?
+The most common side effect of glipizide is hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, which can occur when the medication lowers blood glucose levels too much.
Can glipizide cause weight gain?
+Yes, weight gain is a potential side effect of glipizide, as the medication can increase insulin levels, leading to increased glucose uptake in cells and potentially resulting in weight gain.
How can I minimize the risk of side effects while taking glipizide?
+To minimize the risk of side effects, follow the prescribed dosage, monitor blood sugar levels regularly, maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine, and inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking.
We hope this comprehensive overview of glipizide's side effects has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with glipizide, please don't hesitate to comment below. Your input can help others better understand the potential benefits and risks of this medication. Additionally, consider sharing this article with anyone who might benefit from this information, as awareness and education are key to effective diabetes management.
