Intro
Discover common Levothyroxine side effects, including thyroid hormone imbalance, weight changes, and medication interactions, to manage hypothyroidism symptoms and minimize adverse reactions.
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4), which is used to treat hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. While levothyroxine is generally considered safe and effective, it can cause side effects, especially when not taken as directed or in excessive amounts. Understanding the potential side effects of levothyroxine is essential for individuals who are taking this medication to manage their hypothyroidism.
The importance of being aware of levothyroxine side effects cannot be overstated. Thyroid hormones have a broad impact on the body, and even small changes in hormone levels can lead to significant effects. For individuals with hypothyroidism, finding the right balance of thyroid hormone replacement is critical for managing their condition effectively and improving their quality of life. However, this balance can be delicate, and too much or too little thyroid hormone can lead to a range of adverse effects. By understanding these potential side effects, individuals can better navigate their treatment plan and work closely with their healthcare provider to optimize their thyroid hormone levels.
The management of hypothyroidism with levothyroxine requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. While levothyroxine is designed to replace the missing thyroid hormones in individuals with hypothyroidism, thereby alleviating symptoms such as fatigue, cold intolerance, and weight gain, it can also cause side effects, particularly if the dose is too high. These side effects can range from mild to severe and may include increased heart rate, anxiety, and changes in appetite, among others. It is crucial for patients to be vigilant about monitoring their symptoms and adjusting their medication as needed under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Introduction to Levothyroxine

Benefits of Levothyroxine

Common Side Effects of Levothyroxine

These side effects are often mild and temporary, resolving on their own once the body adjusts to the medication. However, in some cases, they can be more severe and may require a dose adjustment or other interventions.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
Less common but potentially serious side effects of levothyroxine include: - Allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing - Chest pain or irregular heartbeat - Seizures - Changes in vision or blurred vision - Severe headache or confusionIf any of these serious side effects occur, individuals should seek medical attention immediately.
Factors Influencing Levothyroxine Side Effects
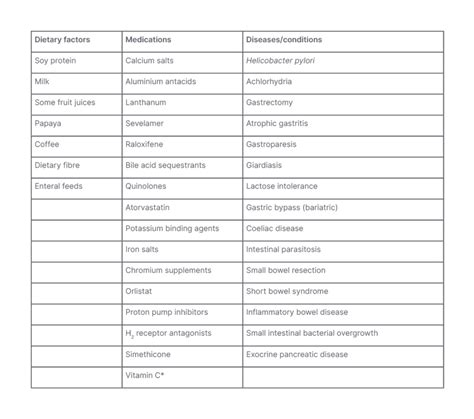
Understanding these factors can help individuals and their healthcare providers make informed decisions about levothyroxine treatment and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Managing Levothyroxine Side Effects
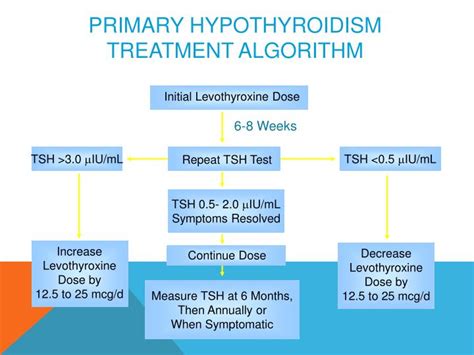
It is essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare provider to manage any side effects that occur and to find the right balance of thyroid hormone replacement for their specific needs.
Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite readers to share their experiences with levothyroxine and hypothyroidism in the comments below. Your insights can help others who are navigating similar challenges and contribute to a broader understanding of the complexities of thyroid health.
What is the most common side effect of levothyroxine?
+The most common side effects of levothyroxine include increased heart rate, nervousness, and changes in appetite.
Can levothyroxine cause weight loss?
+Yes, levothyroxine can cause weight loss, especially if the dose is too high. However, weight loss is often a desired effect for individuals with hypothyroidism who have experienced weight gain due to their condition.
How long does it take for levothyroxine to start working?
+The effects of levothyroxine can be seen within a few weeks, but it may take several months to achieve the full benefits of the medication.
