Intro
Discover Metoprolol side effects, interactions, and warnings. Learn about common symptoms, dosage, and long-term risks, including hypotension, bradycardia, and fatigue, to manage your health effectively.
Metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, chest pain, and heart failure. While it is effective in managing these conditions, metoprolol can cause a range of side effects, some of which can be mild and temporary, while others can be more severe and long-lasting. Understanding the potential side effects of metoprolol is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment and to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Metoprolol belongs to a class of medications known as beta-blockers, which work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and reducing the heart's workload. This can help to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart attack, and improve symptoms of heart failure. However, the same mechanism that makes metoprolol effective can also lead to side effects, particularly during the initial stages of treatment or when the dose is adjusted.
The importance of understanding metoprolol side effects cannot be overstated. Patients who are aware of the potential risks and benefits of their medication are more likely to adhere to their treatment plan, communicate effectively with their healthcare provider, and seek medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms. Moreover, recognizing the signs of metoprolol side effects can help patients to take proactive steps to manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life.
Common Metoprolol Side Effects

Some of the most common metoprolol side effects include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue. These symptoms can occur due to the medication's effect on blood pressure and heart rate, which can lead to a temporary decrease in blood flow to the brain and other organs. Other common side effects of metoprolol include headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These gastrointestinal symptoms can be mild and short-lived, but in some cases, they can be more severe and persistent.
Less Common Metoprolol Side Effects
In addition to the common side effects, metoprolol can also cause less common but more serious adverse reactions. These include shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing, which can be symptoms of bronchospasm or asthma. Metoprolol can also cause changes in blood sugar levels, which can be a concern for patients with diabetes. Other less common side effects of metoprolol include rash, itching, and hives, which can be signs of an allergic reaction.Severe Metoprolol Side Effects
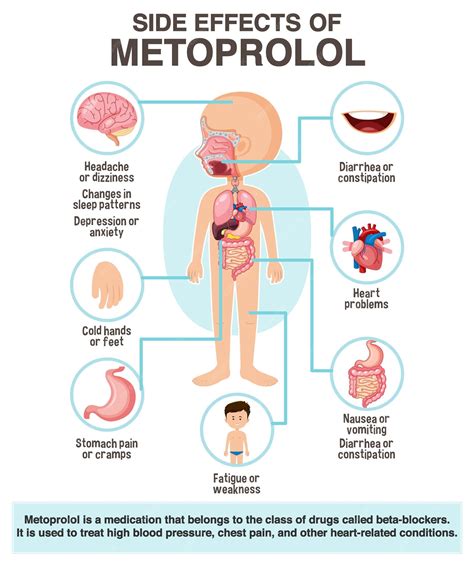
In rare cases, metoprolol can cause severe side effects that require immediate medical attention. These include symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain, tightness, or heaviness, as well as signs of stroke, such as weakness, numbness, or paralysis. Metoprolol can also cause abnormal heart rhythms, including bradycardia (slow heart rate) and tachycardia (fast heart rate). Other severe side effects of metoprolol include severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, and liver damage, which can cause jaundice, dark urine, and abdominal pain.
Metoprolol Interactions and Warnings
Metoprolol can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, which can increase the risk of side effects. Patients taking metoprolol should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking, including vitamins and herbal supplements. Metoprolol can also worsen certain medical conditions, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and peripheral artery disease. Patients with these conditions should be closely monitored while taking metoprolol.Managing Metoprolol Side Effects

While metoprolol side effects can be uncomfortable and concerning, there are steps that patients can take to manage them. For example, patients who experience dizziness or lightheadedness can try getting up slowly from a sitting or lying position, avoiding sudden changes in posture, and taking regular breaks to rest. Patients who experience gastrointestinal symptoms can try taking metoprolol with food, avoiding spicy or fatty foods, and staying hydrated.
Metoprolol Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of metoprolol can also play a role in managing side effects. Patients should take metoprolol exactly as prescribed by their healthcare provider, without skipping doses or taking more than the recommended amount. The medication should be taken at the same time every day, with or without food, depending on the patient's individual needs. Patients who experience side effects should not stop taking metoprolol without consulting their healthcare provider, as this can lead to a worsening of their condition.Metoprolol Alternatives and Substitutes

For patients who experience severe or persistent metoprolol side effects, there may be alternative medications or substitutes that can provide similar benefits with fewer adverse reactions. Some examples of metoprolol alternatives include other beta-blockers, such as atenolol, propranolol, and nadolol, as well as non-beta-blocker medications, such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), and calcium channel blockers. Patients who are considering switching to an alternative medication should consult their healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for their individual needs.
Metoprolol and Pregnancy
Metoprolol can be used during pregnancy, but it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks. Metoprolol can cross the placenta and affect the fetus, particularly during the first trimester. Patients who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should inform their healthcare provider, as they may need to adjust their medication or switch to a different treatment.Metoprolol and Breastfeeding

Metoprolol can also be used during breastfeeding, but it is crucial to monitor the infant for any signs of side effects, such as bradycardia, hypotension, or respiratory depression. Patients who are breastfeeding should inform their healthcare provider, as they may need to adjust their medication or switch to a different treatment.
Metoprolol and Geriatric Patients
Geriatric patients may be more susceptible to metoprolol side effects due to age-related changes in physiology, such as decreased renal function, reduced hepatic metabolism, and increased sensitivity to beta-blockers. Patients over 65 years old should be closely monitored while taking metoprolol, and their dosage should be adjusted accordingly.Metoprolol and Pediatric Patients

Metoprolol can be used in pediatric patients, but it is essential to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks. Children and adolescents may be more susceptible to metoprolol side effects, particularly during the initial stages of treatment. Patients under 18 years old should be closely monitored while taking metoprolol, and their dosage should be adjusted accordingly.
Metoprolol and Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for patients taking metoprolol, as it can help them to understand the potential benefits and risks of their medication, recognize the signs of side effects, and take proactive steps to manage their condition. Patients should be informed about the importance of adherence, the potential interactions with other medications, and the need for regular monitoring.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication that can be effective in managing various cardiovascular conditions. However, it can also cause a range of side effects, some of which can be mild and temporary, while others can be more severe and long-lasting. Patients who are taking metoprolol should be aware of the potential benefits and risks of their medication, recognize the signs of side effects, and take proactive steps to manage their condition. By working closely with their healthcare provider and following the recommended treatment plan, patients can minimize the risk of metoprolol side effects and improve their overall quality of life.
We encourage our readers to share their experiences with metoprolol, ask questions, and provide feedback. Your input is valuable to us, and we will do our best to address your concerns and provide accurate and helpful information.
What are the most common metoprolol side effects?
+The most common metoprolol side effects include dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
Can metoprolol cause severe side effects?
+Yes, metoprolol can cause severe side effects, including symptoms of a heart attack, stroke, abnormal heart rhythms, severe allergic reactions, and liver damage.
How can I manage metoprolol side effects?
+Patient can manage metoprolol side effects by getting up slowly from a sitting or lying position, avoiding sudden changes in posture, taking regular breaks to rest, and staying hydrated.
