Intro
Discover Ampicillin uses, a broad-spectrum antibiotic treating bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections, with effective dosage and side effects management.
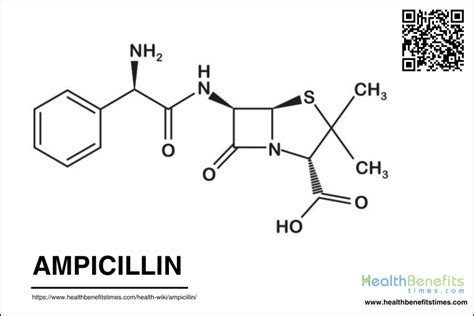
Ampicillin is a type of antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin group of medications. It has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections for several decades. The importance of ampicillin lies in its ability to combat infections caused by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile and effective treatment option. Understanding the uses of ampicillin is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it helps in making informed decisions about its application and ensures the most effective treatment outcomes.
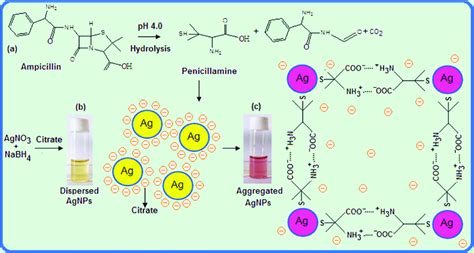
Ampicillin's mechanism of action involves inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cells. This process is critical in treating infections, as it prevents the bacteria from multiplying and spreading, thereby reducing the severity of the infection. The broad-spectrum activity of ampicillin means it can be used against a wide range of infections, from mild to severe. However, like all antibiotics, the misuse or overuse of ampicillin can lead to antibiotic resistance, a growing concern worldwide. Therefore, it is essential to use ampicillin judiciously and only under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
The use of ampicillin extends across various medical specialties, including pediatrics, internal medicine, and surgery. It is particularly useful in treating infections of the respiratory tract, urinary tract, and skin. Additionally, ampicillin is used in the treatment of certain types of meningitis and septicemia. Its application is not limited to these areas, as it can also be used to prevent infections in patients who are at high risk, such as those undergoing certain surgical procedures. The versatility of ampicillin in treating a broad range of infections makes it a valuable component of modern medicine.
Ampicillin Mechanism of Action
Types of Bacterial Infections Treated by Ampicillin
Ampicillin is effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including: - Respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis - Urinary tract infections such as cystitis and pyelonephritis - Skin and soft tissue infections - Meningitis caused by susceptible strains of bacteria - Septicemia or bacteremiaAmpicillin Uses in Medicine
Benefits of Using Ampicillin
The benefits of using ampicillin include: - Broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria - Effective in treating a wide range of infections - Can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection - Generally well-tolerated, with common side effects being mild and temporaryAmpicillin Administration and Dosage

Precautions and Side Effects
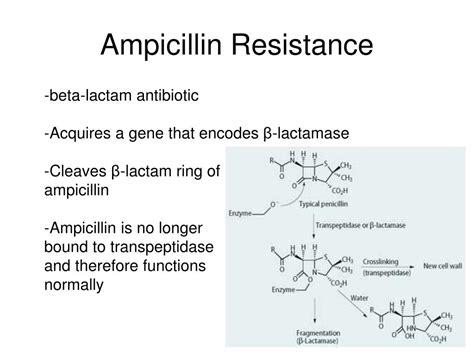
While ampicillin is generally safe, there are precautions and potential side effects to be aware of: - Allergic reactions, which can range from mild to severe - Gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting - Interactions with other medications, which can affect the efficacy or increase the risk of side effects - Use in pregnancy and lactation should be under the guidance of a healthcare professionalAmpicillin Resistance and Misuse
Strategies to Combat Resistance
Strategies to combat ampicillin resistance include: - Proper use of antibiotics, following guidelines and prescriptions - Monitoring and surveillance of antibiotic resistance patterns - Development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments - Public awareness and education on the appropriate use of antibioticsAmpicillin in Pediatric and Geriatric Populations

Special Considerations
Special considerations for the use of ampicillin in these populations include: - Dosage adjustment based on age, weight, and renal function - Monitoring for potential side effects and interactions - Use of ampicillin in pregnant and lactating women should be under the guidance of a healthcare professionalAmpicillin Interactions and Contraindications

Contraindications and Warnings
Contraindications and warnings for the use of ampicillin include: - History of allergic reactions to penicillins - Use in patients with a history of cephalosporin allergy, due to cross-reactivity - Caution in patients with renal impairment or hepatic dysfunctionAmpicillin and Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Considerations for the use of ampicillin during pregnancy include: - Use in the treatment of bacterial infections when benefits outweigh risks - Monitoring for potential side effects and interactions - Adjusting dosage based on renal function, as pregnancy can affect drug clearanceAmpicillin and Breastfeeding

Breastfeeding Considerations
Considerations for the use of ampicillin during breastfeeding include: - Monitoring the infant for signs of allergy or intolerance - Considering alternative treatments if possible - Weighing the benefits of treating the infection against the potential risks to the infantWhat is ampicillin used for?
+Ampicillin is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and certain types of meningitis and septicemia.
How does ampicillin work?
+Ampicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacterial cells. It binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, preventing the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains.
What are the common side effects of ampicillin?
+Common side effects of ampicillin include allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, and interactions with other medications. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage regimen and inform healthcare professionals about all medications being taken.
Can ampicillin be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Ampicillin can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it should be under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The benefits of treating the infection should be weighed against the potential risks to the fetus or infant.
How can antibiotic resistance to ampicillin be prevented?
+Antibiotic resistance to ampicillin can be prevented by using antibiotics judiciously, following guidelines and prescriptions, monitoring and surveillance of antibiotic resistance patterns, and developing new antibiotics and alternative treatments.
In summary, ampicillin is a valuable antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity against various bacterial infections. Its uses extend across different medical specialties, and it is effective in treating a wide range of infections. However, the misuse and overuse of ampicillin can lead to antibiotic resistance, emphasizing the need for judicious use and antimicrobial stewardship. By understanding the benefits, mechanisms, and precautions associated with ampicillin, healthcare professionals and patients can work together to ensure the most effective treatment outcomes while preserving the efficacy of this important antibiotic for future generations. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with ampicillin, and we encourage healthcare professionals to continue educating patients about the proper use of antibiotics to combat the growing concern of antibiotic resistance.
