Intro
Discover potential Rosuvastatin side effects, including muscle pain, liver damage, and diabetes risks, and learn how to manage them with proper dosage and medical supervision.
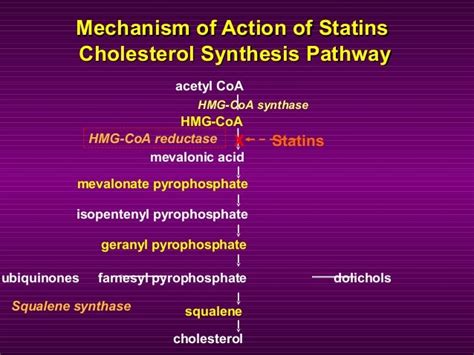
The importance of understanding the potential side effects of medications cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to statins like rosuvastatin. Rosuvastatin, known by its brand name Crestor among others, is a medication used to lower cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular disease. It works by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol in the liver. While rosuvastatin is effective in reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes, it can also cause a range of side effects, some of which can be serious. Understanding these side effects is crucial for patients who are considering or are already taking rosuvastatin.
Rosuvastatin, like other statins, is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause side effects in some people. Common side effects include muscle pain, liver enzyme abnormalities, and increased risk of diabetes. More severe but less common side effects can include muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), liver failure, and an increased risk of kidney problems. The risk of these side effects can be influenced by several factors, including the dose of rosuvastatin, the presence of other health conditions, and the use of other medications. It's essential for patients to discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider before starting rosuvastatin.
The management of cholesterol levels is a critical aspect of preventing cardiovascular diseases, and rosuvastatin has become a key player in this management due to its efficacy. However, the potential for side effects necessitates a careful consideration of the benefits and risks for each individual patient. This balance is what healthcare providers aim to achieve when prescribing rosuvastatin or any other medication. By understanding the full spectrum of rosuvastatin's effects, both beneficial and adverse, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its use.
Rosuvastatin Mechanism of Action
Common Side Effects of Rosuvastatin

Less Common but Serious Side Effects
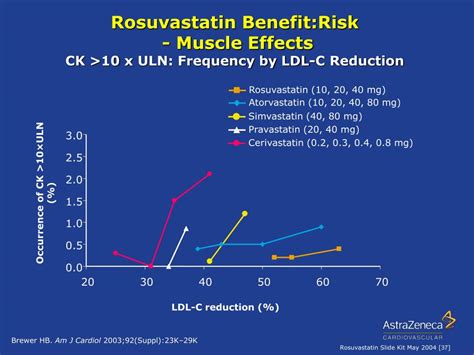
Less common but more serious side effects of rosuvastatin include liver enzyme elevations, which can indicate liver damage, and myopathy, a condition characterized by muscle tissue damage. Rhabdomyolysis, a severe form of myopathy, can lead to kidney failure and is considered a medical emergency. The risk of these side effects can be increased by high doses of rosuvastatin, interacting medications, and pre-existing medical conditions such as liver or kidney disease.Rosuvastatin Benefits and Risks
Monitoring and Management of Side Effects
To minimize the risk of side effects, patients taking rosuvastatin should undergo regular monitoring. This includes periodic checks of liver enzymes and creatine kinase (a marker of muscle damage) levels, as well as monitoring for signs of muscle pain or weakness. Patients should also be advised to report any unusual symptoms promptly. In cases where side effects do occur, management strategies may include dose reduction, temporary discontinuation of the medication, or, in severe cases, permanent discontinuation and consideration of alternative treatments.Alternatives to Rosuvastatin
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Rosuvastatin Efficacy
Lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the efficacy of rosuvastatin and contribute to overall cardiovascular health. A heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol, and high in soluble fiber, can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, can also improve lipid profiles and reduce cardiovascular risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding smoking are additional lifestyle modifications that can complement the effects of rosuvastatin and support overall health.Rosuvastatin in Special Populations

Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Considerations
Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus or baby. Statins are known to cross the placenta, and while there is limited data on the use of rosuvastatin in pregnancy, the potential for fetal harm cannot be ruled out. Similarly, statins are excreted in breast milk, and the use of rosuvastatin during breastfeeding is not recommended unless the benefits to the mother outweigh the potential risks to the infant.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with rosuvastatin and other cholesterol-lowering medications. Your insights can help others better understand the potential benefits and risks of these treatments and make informed decisions about their health. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful.
What are the most common side effects of rosuvastatin?
+The most common side effects of rosuvastatin include muscle pain, headache, dizziness, nausea, and constipation.
Can rosuvastatin cause liver damage?
+Yes, rosuvastatin can cause liver enzyme elevations, which can indicate liver damage. Regular monitoring of liver enzymes is recommended for patients taking rosuvastatin.
Is rosuvastatin safe to use during pregnancy?
+No, rosuvastatin is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus.
