Intro
Discover the hidden dangers of water pills, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and kidney strain, and learn how to minimize their side effects with proper usage and precautions.
The use of water pills, also known as diuretics, has become a common practice for individuals seeking to lose weight, alleviate bloating, or manage medical conditions such as high blood pressure and edema. While these medications can provide temporary relief and benefits, it is essential to understand the potential water pills side effects that can impact overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the world of diuretics, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and most importantly, the side effects that can arise from their use.
The importance of understanding water pills side effects cannot be overstated. Diuretics work by increasing urine production, which helps to remove excess fluids from the body. This can lead to a range of benefits, including weight loss, reduced blood pressure, and alleviated swelling. However, the removal of fluids and electrolytes can also have unintended consequences, affecting various bodily systems and potentially leading to serious health issues. As we explore the topic of water pills side effects, it is crucial to recognize the potential risks and take steps to mitigate them.
The use of diuretics is not limited to medical treatments; many individuals use water pills as a quick fix for weight loss or to reduce bloating before special events. While these motivations may seem harmless, they can lead to a pattern of misuse, increasing the risk of adverse side effects. Furthermore, the availability of diuretics over-the-counter and online has made it easier for individuals to self-medicate, often without proper guidance or understanding of the potential risks. As we navigate the complex world of water pills side effects, it is essential to approach the topic with a critical and informed perspective, recognizing both the benefits and drawbacks of diuretic use.
How Diuretics Work
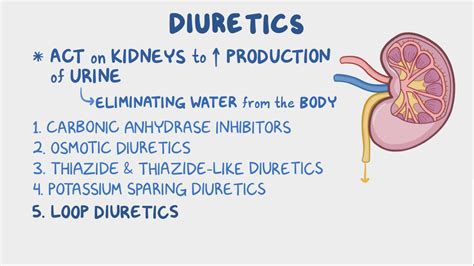
Types of Diuretics
The different types of diuretics are classified based on their mechanism of action and the part of the kidney they affect. Understanding the various types of diuretics is essential, as each can have distinct side effects and interactions. Loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, and potassium-sparing diuretics are the most commonly used types, each with its own set of benefits and risks.Benefits of Diuretics

Medical Uses of Diuretics
The medical uses of diuretics are diverse, and they are an essential part of treatment plans for various conditions. Diuretics can help to reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney damage, making them a crucial component of hypertension management. They can also be used to treat conditions such as hypercalcemia, where excess calcium in the blood can lead to kidney stones and other complications.Water Pills Side Effects
Common Side Effects of Diuretics
The common side effects of diuretics can be mild or severe, depending on the individual and the type of diuretic used. Increased urination is one of the most common side effects, as diuretics work by increasing urine production. Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can also occur, particularly if the individual is not drinking enough fluids or is taking other medications that affect electrolyte balance.Severe Side Effects of Diuretics
Interactions and Contraindications
Diuretics can interact with other medications, exacerbating side effects and reducing their effectiveness. Certain medications, such as NSAIDs and ACE inhibitors, can increase the risk of kidney damage and electrolyte imbalances. Diuretics can also interact with foods and supplements, such as licorice root and ginseng, which can affect blood pressure and electrolyte balance.Managing Water Pills Side Effects

Alternative Treatments and Lifestyle Changes
Alternative treatments and lifestyle changes can help to reduce the reliance on diuretics and minimize the risk of side effects. Dietary changes, such as reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium consumption, can help to manage blood pressure and alleviate edema. Regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and adequate sleep can also contribute to overall health and well-being, reducing the need for diuretics.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with water pills in the comments below. Have you used diuretics for medical or non-medical purposes? What side effects have you experienced, and how have you managed them? Your input can help to create a more comprehensive understanding of water pills and their effects on overall health and well-being.
What are the most common side effects of water pills?
+The most common side effects of water pills include increased urination, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances. Diuretics can also cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting, particularly when standing up quickly.
Can water pills be used for weight loss?
+While water pills can lead to weight loss, their use for this purpose is not recommended. Diuretics can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, which can lead to serious health issues. Additionally, weight loss achieved through diuretic use is often temporary and can lead to a cycle of dependence.
How can I minimize the risk of side effects when taking water pills?
+To minimize the risk of side effects when taking water pills, it is essential to drink plenty of fluids, eat a balanced diet, and monitor your blood pressure and electrolyte levels regularly. You should also follow the recommended dosage and consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any side effects or concerns.
