Intro
Recognize signs of dehydration, including fatigue, headaches, and dark urine, to prevent severe dehydration symptoms, heat exhaustion, and electrolyte imbalance, and learn how to stay hydrated.
Dehydration is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, and certain medical conditions. Despite its prevalence, dehydration often goes unrecognized, and its symptoms can be mistaken for other conditions. However, it is essential to be aware of the signs of dehydration to take prompt action and prevent complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of recognizing dehydration, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Dehydration can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It is particularly concerning for vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, young children, and people with underlying medical conditions. When dehydration is left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, including organ damage, seizures, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the signs of dehydration and take proactive measures to prevent it. By being informed, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from the adverse effects of dehydration.
The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, which plays a vital role in maintaining various bodily functions, such as regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, and removing waste products. When the body loses fluids, it disrupts the delicate balance of fluids and electrolytes, leading to dehydration. The signs of dehydration can be subtle, making it challenging to diagnose. However, by being aware of the common symptoms and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of dehydration and maintain optimal health.
Causes Of Dehydration
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in dehydration. High temperatures, humidity, and altitude can increase the risk of dehydration. When the temperature and humidity are high, the body loses more fluids through sweating, which can lead to dehydration if not adequately replenished. Similarly, high altitudes can cause dehydration due to the lower air pressure, which can lead to increased urine production and fluid loss.Physical Activities
Physical activities, especially those that involve strenuous exercise or outdoor work, can increase the risk of dehydration. When individuals engage in physical activities, they lose fluids through sweating, which can lead to dehydration if not adequately replenished. It is essential for individuals who engage in physical activities to drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.Symptoms Of Dehydration

Mild Dehydration
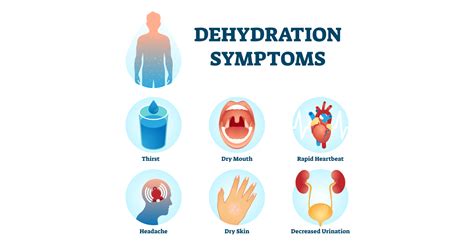
Mild dehydration may cause symptoms such as: * Dry mouth and throat * Fatigue and weakness * Headaches * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Dark yellow or brown urine * Decreased urine outputSevere Dehydration
Severe dehydration can lead to life-threatening complications, including: * Seizures * Organ damage * Low blood pressure * Rapid heartbeat * Sunken eyes * Decreased skin elasticityTreatment Options

Home Remedies
Home remedies can help treat mild dehydration, including: * Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks * Eating foods rich in electrolytes, such as bananas, avocados, and nuts * Avoiding caffeinated and carbonated beverages * Taking regular breaks to rest and hydrateMedical Treatment
Severe dehydration may require medical attention, including: * Intravenous fluids to replenish lost electrolytes and fluids * Medications to treat underlying conditions, such as diarrhea or vomiting * Hospitalization to monitor and manage complicationsPrevention

Hydration Tips
Hydration tips include: * Drinking at least eight glasses of water per day * Eating foods rich in electrolytes, such as bananas, avocados, and nuts * Avoiding caffeinated and carbonated beverages * Taking regular breaks to rest and hydrate * Monitoring urine output and color to ensure adequate hydrationConclusion And Next Steps

What are the common causes of dehydration?
+Dehydration can be caused by various factors, including environmental, physical, and medical conditions, such as excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and certain medications.
What are the symptoms of mild dehydration?
+Mild dehydration may cause symptoms such as dry mouth, fatigue, headaches, dizziness, and dark yellow or brown urine.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+Prevention is key to reducing the risk of dehydration. Individuals can take proactive measures to prevent dehydration, including drinking plenty of fluids, eating foods rich in electrolytes, and avoiding caffeinated and carbonated beverages.
What are the treatment options for dehydration?
+The treatment of dehydration depends on the severity of the condition. Mild dehydration can be treated by drinking plenty of fluids, while severe dehydration may require medical attention and intravenous fluids to replenish lost electrolytes and fluids.
How can I recognize the signs of severe dehydration?
+Severe dehydration can lead to life-threatening complications, including seizures, organ damage, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, sunken eyes, and decreased skin elasticity. It is essential to recognize these signs and seek medical attention immediately.
