Intro
Learn about wet cough no fever symptoms, causes, and treatments. Discover persistent cough remedies and relieve congested chest, mucus, and wheezing with natural expectorants and medications.
A persistent wet cough can be a frustrating and concerning symptom, especially when it's not accompanied by a fever. This type of cough is often characterized by the production of mucus or phlegm, which can be clear, yellow, or green in color. The absence of a fever can make it more challenging to determine the underlying cause of the cough, but there are several possible explanations. In this article, we'll delve into the potential causes of a wet cough with no fever, its symptoms, and what you can do to manage and treat it.
A wet cough can be a symptom of various respiratory conditions, ranging from mild to severe. It's essential to pay attention to other symptoms that may accompany the cough, such as chest tightness, wheezing, or shortness of breath. In some cases, a wet cough can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires medical attention. For instance, a chronic wet cough can be a symptom of bronchitis, pneumonia, or even lung cancer. On the other hand, a wet cough can also be caused by more benign conditions, such as a cold or allergies.
The importance of understanding the causes and symptoms of a wet cough cannot be overstated. By recognizing the potential underlying conditions, individuals can seek medical attention if necessary and take steps to manage their symptoms. In addition, being aware of the risk factors and preventive measures can help reduce the likelihood of developing a wet cough in the first place. With this knowledge, individuals can take control of their respiratory health and improve their overall well-being.
Causes of a Wet Cough with No Fever

A wet cough with no fever can be caused by a variety of factors, including respiratory infections, allergies, and environmental irritants. Some of the most common causes of a wet cough include:
- Bronchitis: This is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which can cause a persistent wet cough.
- Pneumonia: This is an infection of the lungs that can cause a wet cough, especially if it's caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
- Allergies: Allergies to dust, mold, or pet dander can cause a wet cough, especially if you have a history of allergies.
- Acid reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause stomach acid to flow up into the throat, leading to a wet cough.
- Environmental irritants: Exposure to pollutants, such as smoke or chemicals, can irritate the lungs and cause a wet cough.
Symptoms of a Wet Cough with No Fever
The symptoms of a wet cough with no fever can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include: * A persistent cough that produces mucus or phlegm * Chest tightness or wheezing * Shortness of breath * Fatigue * Sore throat * Runny nose or congestion * HeadachesDiagnosing a Wet Cough with No Fever
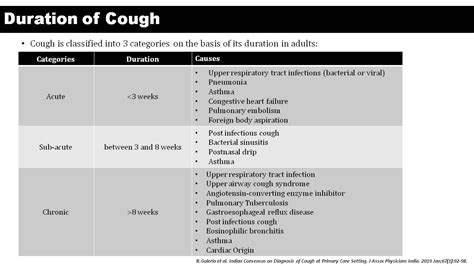
Diagnosing a wet cough with no fever can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. A doctor will typically perform a physical exam and take a medical history to determine the underlying cause of the cough. They may also order diagnostic tests, such as:
- Chest X-ray: This can help rule out pneumonia or other lung conditions.
- Pulmonary function tests: These tests can help assess lung function and determine if there's any obstruction or restriction.
- Allergy testing: This can help determine if allergies are contributing to the cough.
- Endoscopy: This can help visualize the throat and lungs to check for any abnormalities.
Treatment Options for a Wet Cough with No Fever
The treatment for a wet cough with no fever depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include: * Antibiotics: If the cough is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. * Antihistamines: If the cough is caused by allergies, antihistamines may be prescribed to help relieve symptoms. * Bronchodilators: If the cough is caused by bronchitis or asthma, bronchodilators may be prescribed to help open up the airways. * Cough suppressants: Over-the-counter cough suppressants can help relieve symptoms, but they should be used with caution and under the guidance of a doctor. * Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, avoiding environmental irritants, and staying hydrated can help manage symptoms and prevent future episodes.Managing a Wet Cough with No Fever at Home

While medical attention may be necessary to diagnose and treat the underlying cause of a wet cough, there are several steps you can take at home to manage symptoms and promote recovery. Some tips include:
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water or tea, can help thin out mucus and make it easier to cough up.
- Using a humidifier: Dry air can irritate the throat and lungs, making symptoms worse. Using a humidifier can help add moisture to the air and relieve congestion.
- Practicing good hygiene: Washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others can help prevent the spread of infection.
- Getting plenty of rest: Getting enough sleep and taking breaks to rest can help your body recover from illness.
- Avoiding irritants: Avoiding exposure to pollutants, such as smoke or chemicals, can help reduce symptoms and prevent future episodes.
Preventing a Wet Cough with No Fever
Preventing a wet cough with no fever requires a combination of lifestyle changes and preventive measures. Some tips include: * Quitting smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for respiratory conditions, including bronchitis and pneumonia. * Avoiding environmental irritants: Avoiding exposure to pollutants, such as smoke or chemicals, can help reduce the risk of developing a wet cough. * Getting vaccinated: Getting vaccinated against flu and pneumonia can help reduce the risk of developing a wet cough. * Practicing good hygiene: Washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others can help prevent the spread of infection. * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water or tea, can help keep your respiratory system healthy and reduce the risk of developing a wet cough.Complications of a Wet Cough with No Fever

If left untreated, a wet cough with no fever can lead to several complications, including:
- Pneumonia: If the underlying cause of the cough is a bacterial or fungal infection, it can spread to the lungs and cause pneumonia.
- Bronchiectasis: This is a condition where the airways become damaged and widened, leading to chronic coughing and mucus production.
- Respiratory failure: In severe cases, a wet cough can lead to respiratory failure, which requires mechanical ventilation and hospitalization.
- Lung cancer: A chronic wet cough can be a symptom of lung cancer, especially if it's accompanied by other symptoms, such as weight loss or fatigue.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you're experiencing a wet cough with no fever, it's essential to seek medical attention if you notice any of the following symptoms: * Difficulty breathing * Chest pain or tightness * Severe headache or confusion * Fever over 102°F (39°C) * Coughing up blood or yellow or green mucus * Severe fatigue or weaknessConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, a wet cough with no fever can be a symptom of various respiratory conditions, ranging from mild to severe. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms, individuals can seek medical attention if necessary and take steps to manage their symptoms. If you're experiencing a wet cough with no fever, it's essential to stay hydrated, practice good hygiene, and avoid environmental irritants. If your symptoms worsen or you experience any complications, seek medical attention promptly.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with a wet cough with no fever in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one experienced a wet cough with no fever? What steps did you take to manage your symptoms, and what was the outcome? Your input can help others who may be experiencing similar symptoms.
What are the most common causes of a wet cough with no fever?
+A wet cough with no fever can be caused by various factors, including bronchitis, pneumonia, allergies, acid reflux, and environmental irritants.
How can I manage a wet cough with no fever at home?
+To manage a wet cough with no fever at home, stay hydrated, use a humidifier, practice good hygiene, get plenty of rest, and avoid irritants.
When should I seek medical attention for a wet cough with no fever?
+Seek medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, chest pain or tightness, severe headache or confusion, fever over 102°F (39°C), coughing up blood or yellow or green mucus, or severe fatigue or weakness.
