Intro
Understand your sodium blood test results, including normal ranges, high and low sodium levels, and related electrolyte imbalance conditions like hyponatremia and hypernatremia, to manage your health effectively.
The importance of sodium in our bodies cannot be overstated. It is one of the most crucial electrolytes, playing a vital role in maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction. A sodium blood test is a common diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of sodium in the blood. This test is essential in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions, including dehydration, kidney disease, and hormone imbalances. Understanding sodium blood test results is vital for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about patient care.
Sodium levels in the blood are tightly regulated by the body, and any significant deviations from the normal range can indicate an underlying health issue. The normal range for sodium levels in the blood is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). Levels above or below this range can have serious consequences, including seizures, coma, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to understand the significance of sodium blood test results and how they are interpreted.
The interpretation of sodium blood test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence sodium levels in the blood. Healthcare providers consider various factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results, to diagnose and manage underlying conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of sodium blood tests, exploring the importance of sodium, the procedure for conducting the test, and the interpretation of test results. We will also discuss the various factors that can affect sodium levels in the blood and the potential consequences of abnormal sodium levels.
Sodium and Its Importance in the Body
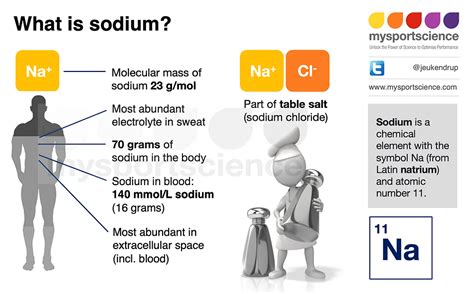
Sodium levels in the blood are influenced by various factors, including diet, hormone levels, and kidney function. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating sodium levels by adjusting the amount of sodium excreted in the urine. Hormones such as aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) also help regulate sodium levels by controlling the amount of sodium reabsorbed in the kidneys. An imbalance of these hormones can lead to abnormal sodium levels, highlighting the importance of proper hormone regulation.
How Sodium Blood Tests Are Conducted

The procedure for conducting a sodium blood test is as follows:
- A healthcare provider will clean the area where the blood sample will be taken with an antiseptic solution.
- A needle will be inserted into a vein in the arm, and a blood sample will be collected in a test tube.
- The needle will be removed, and the area will be covered with a bandage to prevent bleeding.
- The blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Interpreting Sodium Blood Test Results

Here are some possible interpretations of sodium blood test results:
- Hyponatremia: Sodium levels below 135 mEq/L can indicate hyponatremia, a condition characterized by low sodium levels in the blood. Hyponatremia can be caused by various factors, including dehydration, kidney disease, and hormone imbalances.
- Hypernatremia: Sodium levels above 145 mEq/L can indicate hypernatremia, a condition characterized by high sodium levels in the blood. Hypernatremia can be caused by various factors, including dehydration, kidney disease, and hormone imbalances.
- Normal sodium levels: Sodium levels within the normal range can indicate proper sodium regulation in the body. However, it is essential to consider other laboratory test results and medical history to rule out any underlying health issues.
Factors That Can Affect Sodium Levels
Several factors can affect sodium levels in the blood, including: * **Diet**: A diet high in sodium can increase sodium levels in the blood, while a diet low in sodium can decrease sodium levels. * **Hormone levels**: Hormones such as aldosterone and ADH play a crucial role in regulating sodium levels. An imbalance of these hormones can lead to abnormal sodium levels. * **Kidney function**: The kidneys play a vital role in regulating sodium levels by adjusting the amount of sodium excreted in the urine. Kidney disease can lead to abnormal sodium levels. * **Medications**: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can affect sodium levels in the blood.Potential Consequences of Abnormal Sodium Levels

It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of abnormal sodium levels, such as headaches, fatigue, or muscle weakness.
Managing Abnormal Sodium Levels
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of abnormal sodium levels.
Preventing Abnormal Sodium Levels

It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that addresses the underlying cause of abnormal sodium levels.
Conclusion and Next Steps
If you have any concerns about your sodium levels or would like to learn more about sodium blood tests, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others. You can also take a proactive approach to managing your sodium levels by maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying health conditions.
What is the normal range for sodium levels in the blood?
+The normal range for sodium levels in the blood is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What are the potential consequences of abnormal sodium levels?
+Abnormal sodium levels can have serious consequences, including seizures, coma, and death.
How can I prevent abnormal sodium levels?
+Preventing abnormal sodium levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying health conditions.
