The terms sputum and phlegm are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to slightly different substances that are produced by the body. Understanding the difference between sputum and phlegm can be important for diagnosing and treating various respiratory conditions. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, causes, and implications of sputum and phlegm, providing a comprehensive overview of these two related yet distinct concepts.
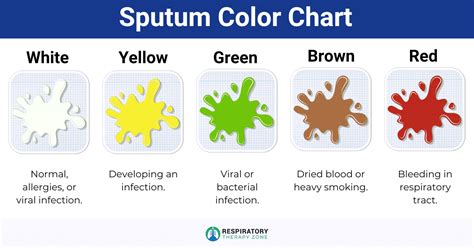
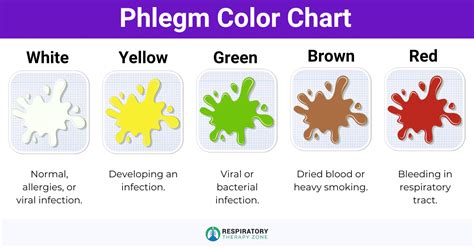
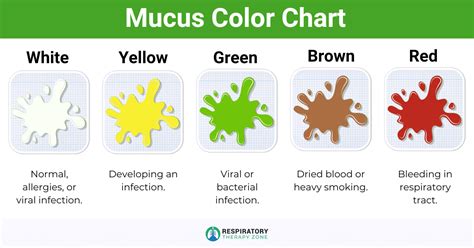
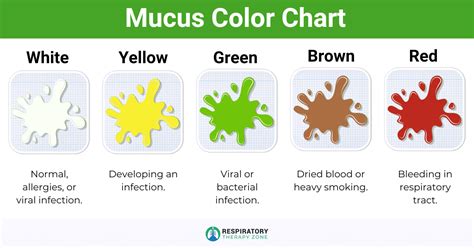
Sputum and phlegm are both types of mucus, which is a thick, protective fluid produced by the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract. However, the key difference lies in their origin, composition, and characteristics. Phlegm is a type of mucus that is produced in the lungs and airways, typically in response to irritation or infection. It is usually clear or white in color and can be coughed up in small amounts. Sputum, on the other hand, is a mixture of mucus, saliva, and other substances that are coughed up from the lungs and airways. It can be colored, ranging from yellow to green to brown, depending on the presence of infection, blood, or other substances.
What is Sputum?
Sputum is a complex mixture of substances that are coughed up from the lungs and airways. It can contain mucus, saliva, bacteria, viruses, and other debris. The color and consistency of sputum can provide important clues about the underlying cause of a respiratory condition. For example, yellow or green sputum may indicate the presence of an infection, while brown or rust-colored sputum can be a sign of bleeding in the lungs. Sputum can be produced in response to a variety of conditions, including pneumonia, bronchitis, tuberculosis, and cystic fibrosis.
Causes of Sputum Production
The production of sputum can be triggered by a range of factors, including:
* Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause the lungs and airways to produce excess mucus, which can lead to sputum production.
* Inflammation: Conditions such as bronchitis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can cause inflammation in the airways, leading to increased mucus production and sputum.
* Irritants: Exposure to pollutants, dust, and other irritants can stimulate the production of mucus and sputum.
* Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause the airways to produce excess mucus, leading to sputum production.
What is Phlegm?
Phlegm is a type of mucus that is produced in the lungs and airways. It is usually clear or white in color and can be coughed up in small amounts. Phlegm is an important part of the body's defense system, helping to trap dust, bacteria, and other foreign particles that enter the airways. However, excessive phlegm production can be a sign of an underlying condition, such as a respiratory infection or allergy.
Causes of Phlegm Production
The production of phlegm can be triggered by a range of factors, including:
* Infections: Respiratory infections such as the common cold, flu, and pneumonia can cause the lungs and airways to produce excess phlegm.
* Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause the airways to produce excess phlegm, leading to congestion and coughing.
* Irritants: Exposure to pollutants, dust, and other irritants can stimulate the production of phlegm.
* Anatomical issues: Conditions such as a deviated septum or nasal polyps can cause phlegm to build up in the airways.
Key Differences Between Sputum and Phlegm
While both sputum and phlegm are types of mucus, there are some key differences between the two:
* Origin: Sputum is a mixture of substances that are coughed up from the lungs and airways, while phlegm is a type of mucus that is produced in the lungs and airways.
* Composition: Sputum can contain a range of substances, including mucus, saliva, bacteria, and other debris, while phlegm is typically composed of mucus and water.
* Color: Sputum can be colored, ranging from yellow to green to brown, while phlegm is usually clear or white.
* Consistency: Sputum can be thick and sticky, while phlegm is typically thin and watery.
Diagnosing and Treating Sputum and Phlegm-Related Conditions
Diagnosing and treating conditions related to sputum and phlegm production typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The following are some common methods used to diagnose and treat sputum and phlegm-related conditions:
* Physical examination: A healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination, including listening to the lungs and airways with a stethoscope.
* Medical history: A healthcare provider will take a medical history, including questions about symptoms, allergies, and exposure to irritants.
* Diagnostic tests: Diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and pulmonary function tests may be used to diagnose underlying conditions.
* Treatment: Treatment for sputum and phlegm-related conditions typically involves a combination of medications, such as antibiotics, bronchodilators, and expectorants, as well as lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and avoiding irritants.
Prevention and Management of Sputum and Phlegm Production
Preventing and managing sputum and phlegm production involves a range of strategies, including:
* Quitting smoking: Smoking is a major cause of respiratory problems, including sputum and phlegm production.
* Avoiding irritants: Avoiding exposure to pollutants, dust, and other irritants can help reduce sputum and phlegm production.
* Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help thin out mucus and make it easier to cough up.
* Using a humidifier: Using a humidifier can help add moisture to the air, making it easier to breathe and reducing sputum and phlegm production.
* Practicing good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, can help reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the difference between sputum and phlegm is important for diagnosing and treating various respiratory conditions. While both sputum and phlegm are types of mucus, they have distinct characteristics and causes. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of sputum and phlegm production, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage these conditions, reducing the risk of respiratory problems and improving overall health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with sputum and phlegm production in the comments section below. Have you ever experienced excessive sputum or phlegm production? What strategies have you found helpful in managing these conditions? Share your story and help others who may be struggling with similar issues.
What is the main difference between sputum and phlegm?
+
The main difference between sputum and phlegm is their origin and composition. Sputum is a mixture of substances that are coughed up from the lungs and airways, while phlegm is a type of mucus that is produced in the lungs and airways.
What causes excessive sputum production?
+
Excessive sputum production can be caused by a range of factors, including infections, inflammation, irritants, and allergies.
How can I prevent and manage sputum and phlegm production?
+
Preventing and managing sputum and phlegm production involves a range of strategies, including quitting smoking, avoiding irritants, staying hydrated, using a humidifier, and practicing good hygiene.