Intro
Discover how stool exams work with 5 key methods, utilizing fecal testing, microbiome analysis, and parasite detection to diagnose gut health issues, digestive problems, and infections, promoting accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The importance of a stool exam cannot be overstated, as it provides crucial insights into the health of an individual's digestive system. By analyzing a stool sample, healthcare professionals can diagnose a range of conditions, from infections and inflammatory diseases to nutritional deficiencies and even certain types of cancer. With the help of a stool exam, patients can receive timely and effective treatment, preventing complications and improving their overall quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of stool exams, exploring the various ways in which they work and the valuable information they can provide.
A stool exam, also known as a stool test or fecal test, is a diagnostic procedure that involves the analysis of a patient's stool sample. The sample is typically collected at home using a special container or kit, and then sent to a laboratory for testing. The laboratory technician will then examine the sample under a microscope, looking for signs of infection, inflammation, or other abnormalities. The results of the stool exam can help healthcare professionals to diagnose a range of conditions, including gastrointestinal infections, inflammatory bowel disease, and even certain types of cancer.
The process of a stool exam is relatively straightforward, and can be performed in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, and even at home. The sample is typically collected using a special container or kit, which is designed to preserve the integrity of the sample and prevent contamination. Once the sample has been collected, it is sent to a laboratory for testing, where it will be examined under a microscope and analyzed for signs of infection, inflammation, or other abnormalities. The results of the stool exam can provide valuable insights into the health of an individual's digestive system, and can help healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a range of conditions.
How Stool Exam Works
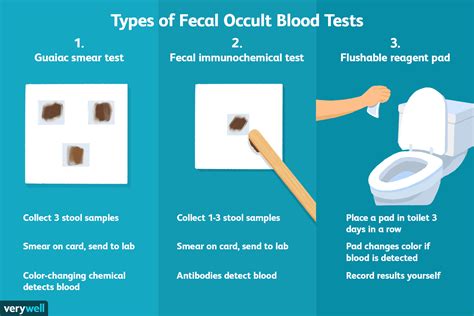
Types of Stool Exams
There are several types of stool exams, each of which is designed to detect specific conditions or abnormalities. Some of the most common types of stool exams include: * Fecal occult blood test (FOBT): This test is used to detect the presence of blood in the stool, which can be a sign of colorectal cancer or other conditions. * Fecal immunochemical test (FIT): This test is used to detect the presence of certain proteins in the stool, which can be a sign of colorectal cancer or other conditions. * Stool culture: This test is used to detect the presence of bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms in the stool, which can be a sign of infection or other conditions. * Ova and parasite exam: This test is used to detect the presence of parasites or eggs in the stool, which can be a sign of infection or other conditions.Benefits of Stool Exam

Preparation for Stool Exam
To prepare for a stool exam, patients should follow these steps: 1. Collect the stool sample in a special container or kit, as instructed by the healthcare professional. 2. Avoid contaminating the sample with urine, water, or other substances. 3. Refrigerate the sample until it is sent to the laboratory for testing. 4. Avoid taking certain medications or supplements that may affect the results of the test. 5. Inform the healthcare professional of any medications or supplements that are being taken.Interpreting Stool Exam Results
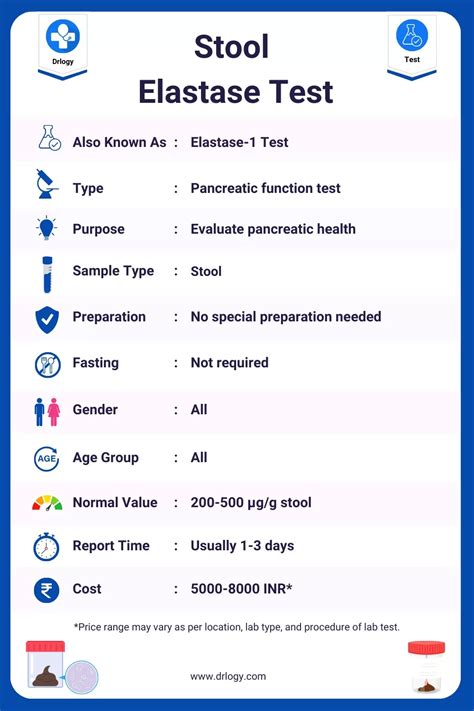
Common Conditions Diagnosed by Stool Exam
Some common conditions that can be diagnosed by a stool exam include: * Gastrointestinal infections, such as gastroenteritis or diverticulitis * Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis * Nutritional deficiencies, such as iron deficiency or vitamin deficiency * Certain types of cancer, such as colorectal cancer * Parasitic infections, such as giardiasis or cryptosporidiosisLimitations of Stool Exam
Future Developments in Stool Exam
Research is ongoing to develop new and improved methods for stool exams, including: * Molecular testing, which can detect specific genetic material or proteins in the stool * Imaging tests, such as colonoscopy or CT scans, which can provide detailed images of the digestive system * Artificial intelligence and machine learning, which can help to interpret the results of stool exams and improve diagnosis and treatmentConclusion and Recommendations

Final Thoughts
A stool exam is an important diagnostic tool that can help to detect and treat a range of conditions affecting the digestive system. By understanding the process of a stool exam, including the types of tests, the benefits, and the limitations, patients can take an active role in their healthcare and work with their healthcare professional to improve their overall health and wellbeing.What is a stool exam?
+A stool exam is a diagnostic test that involves the analysis of a patient's stool sample to detect the presence of blood, bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms.
What are the benefits of a stool exam?
+The benefits of a stool exam include early detection and treatment of gastrointestinal infections and inflammatory diseases, detection of nutritional deficiencies, and monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment.
How do I prepare for a stool exam?
+To prepare for a stool exam, patients should collect the stool sample in a special container or kit, avoid contaminating the sample, and refrigerate it until it is sent to the laboratory for testing.
What are the limitations of a stool exam?
+The limitations of a stool exam include the test may not detect all types of gastrointestinal infections or inflammatory diseases, and the test may require multiple samples or repeat testing to confirm a diagnosis.
What are the future developments in stool exam?
+Research is ongoing to develop new and improved methods for stool exams, including molecular testing, imaging tests, and artificial intelligence and machine learning.
