Tetanus shots are an essential part of maintaining good health, particularly for individuals who work with animals, are involved in outdoor activities, or live in areas where tetanus bacteria are prevalent. Despite their importance, many people are unsure about the specifics of tetanus shots, including when to get them, how they work, and potential side effects. In this article, we will delve into the world of tetanus shots, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and key information that everyone should know.
Tetanus shots are a type of vaccination that protects against tetanus, a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani. This infection can lead to severe muscle stiffness, spasms, and rigidity, making it essential to prevent it through vaccination. The tetanus shot is usually administered in combination with other vaccines, such as diphtheria and pertussis, to provide comprehensive protection against these diseases. Understanding the importance of tetanus shots is crucial for making informed decisions about health and wellbeing.
The tetanus shot has been widely used for decades, and its effectiveness in preventing tetanus infections has been well-documented. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), tetanus shots are approximately 90% effective in preventing tetanus infections. This high level of effectiveness makes tetanus shots a vital tool in the prevention of tetanus. Furthermore, tetanus shots are relatively safe, with most people experiencing only mild side effects, such as redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site.
Tetanus Shot Benefits
The benefits of tetanus shots are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of getting a tetanus shot include:
* Protection against tetanus infections: Tetanus shots provide effective protection against tetanus bacteria, reducing the risk of infection and associated complications.
* Prevention of muscle stiffness and spasms: Tetanus shots can prevent the severe muscle stiffness and spasms that are characteristic of tetanus infections.
* Reduced risk of death: Tetanus infections can be fatal, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Tetanus shots can significantly reduce the risk of death from tetanus.
* Protection for individuals with weakened immune systems: Tetanus shots are especially important for individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or taking immunosuppressive medications.
How Tetanus Shots Work
Tetanus shots work by introducing a small, harmless piece of the tetanus toxin or a weakened form of the tetanus bacteria to the body. This triggers an immune response, causing the body to produce antibodies that can recognize and attack the tetanus bacteria. The antibodies produced in response to the tetanus shot provide long-term protection against tetanus infections. The working mechanism of tetanus shots involves:
* Introduction of the tetanus antigen: The tetanus shot introduces the tetanus antigen to the body, which triggers an immune response.
* Production of antibodies: The immune system produces antibodies in response to the tetanus antigen, which can recognize and attack the tetanus bacteria.
* Long-term protection: The antibodies produced in response to the tetanus shot provide long-term protection against tetanus infections.
Tetanus Shot Side Effects
While tetanus shots are generally safe, some individuals may experience side effects. Common side effects of tetanus shots include:
* Redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site
* Fatigue or tiredness
* Headache or muscle aches
* Nausea or vomiting
* Fever or chills
It is essential to note that severe side effects are rare and usually occur in individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or allergies.
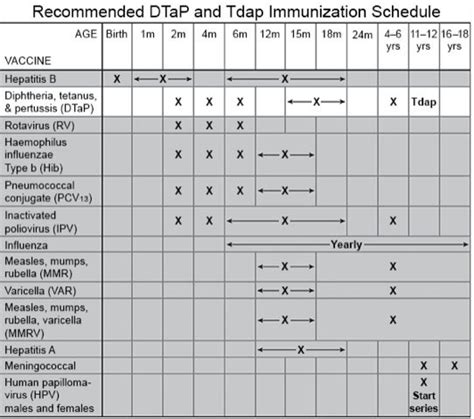
Tetanus Shot Schedule
The tetanus shot schedule varies depending on age, health status, and occupation. Generally, the CDC recommends:
* Infants and children: 3-4 doses of the tetanus shot, usually administered in combination with other vaccines, at 2, 4, 6, and 15-18 months of age.
* Adolescents and adults: A booster shot every 10 years, or as needed, such as after a tetanus-prone injury.
* Individuals with weakened immune systems: More frequent booster shots, usually every 5-10 years, depending on the individual's health status.
Tetanus Shot Precautions
While tetanus shots are generally safe, there are certain precautions to consider:
* Allergies: Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions to tetanus shots or any of their components should not receive the vaccine.
* Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Tetanus shots are safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women, but it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before receiving the vaccine.
* Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or taking immunosuppressive medications, may require more frequent booster shots.
Tetanus Shot Interactions
Tetanus shots can interact with other medications and vaccines, including:
* Antibiotics: Tetanus shots may not be effective in individuals taking antibiotics, as these medications can interfere with the immune response.
* Immunosuppressive medications: Individuals taking immunosuppressive medications may require more frequent booster shots, as these medications can weaken the immune system.
* Other vaccines: Tetanus shots can be administered in combination with other vaccines, but it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best vaccination schedule.
Tetanus Shot Effectiveness
The effectiveness of tetanus shots has been well-documented, with studies showing that the vaccine is approximately 90% effective in preventing tetanus infections. The effectiveness of tetanus shots can be influenced by various factors, including:
* Age: Tetanus shots are most effective in individuals who receive the vaccine at a young age.
* Health status: Individuals with weakened immune systems may not respond as well to the tetanus shot.
* Booster shots: Regular booster shots can help maintain immunity and prevent tetanus infections.
Tetanus Shot Risks
While tetanus shots are generally safe, there are some risks to consider:
* Severe allergic reactions: Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions to tetanus shots or any of their components should not receive the vaccine.
* Neurological problems: There is a small risk of neurological problems, such as seizures or Guillain-Barré syndrome, associated with tetanus shots.
* Infection: As with any injection, there is a small risk of infection at the injection site.
In conclusion, tetanus shots are a crucial part of maintaining good health, particularly for individuals who work with animals, are involved in outdoor activities, or live in areas where tetanus bacteria are prevalent. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects of tetanus shots, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and wellbeing. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with tetanus shots, and to take the necessary steps to protect themselves against tetanus infections.
What is the recommended schedule for tetanus shots?
+
The recommended schedule for tetanus shots varies depending on age, health status, and occupation. Generally, the CDC recommends 3-4 doses of the tetanus shot, usually administered in combination with other vaccines, at 2, 4, 6, and 15-18 months of age, and a booster shot every 10 years, or as needed.
What are the potential side effects of tetanus shots?
+
Common side effects of tetanus shots include redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site, fatigue or tiredness, headache or muscle aches, nausea or vomiting, and fever or chills. Severe side effects are rare and usually occur in individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or allergies.
Can I get a tetanus shot if I have a weakened immune system?
+
Yes, individuals with weakened immune systems can receive tetanus shots, but they may require more frequent booster shots. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best vaccination schedule and to discuss any potential risks or interactions with other medications.
How effective are tetanus shots in preventing tetanus infections?
+
Tetanus shots are approximately 90% effective in preventing tetanus infections. The effectiveness of tetanus shots can be influenced by various factors, including age, health status, and booster shots.
Can I get a tetanus shot if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
+
Yes, tetanus shots are safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before receiving the vaccine to discuss any potential risks or interactions with other medications.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of tetanus shots, and we encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments below. By working together, we can promote health and wellbeing, and reduce the risk of tetanus infections.