Intro
Stroke is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either due to a blockage or a rupture of the blood vessels. This interruption can cause damage to the brain cells, leading to a range of symptoms, including weakness, numbness, and difficulty with speech and vision. Understanding the medical term "stroke" is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as it can help facilitate early diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
The importance of understanding stroke cannot be overstated. Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, accounting for over 6 million deaths each year. In addition, stroke can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, causing long-term disability and cognitive impairment. Furthermore, stroke can have a significant economic burden, with estimated annual costs exceeding $100 billion in the United States alone. Therefore, it is essential to understand the medical term "stroke" and its underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Stroke is a complex medical condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Healthcare professionals use a range of diagnostic tests, including imaging studies and laboratory tests, to determine the underlying cause of stroke. Treatment options may include medications, surgery, and rehabilitation therapy, depending on the severity and location of the stroke. In addition, lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, healthy diet, and stress management, can help reduce the risk of stroke. By understanding the medical term "stroke" and its underlying causes, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health.
Types of Stroke
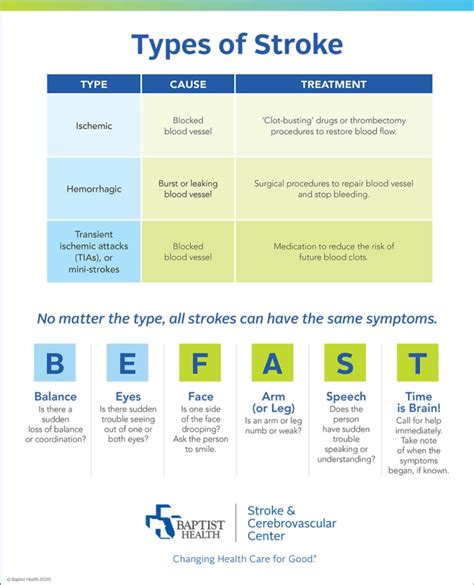
Ischemic Stroke
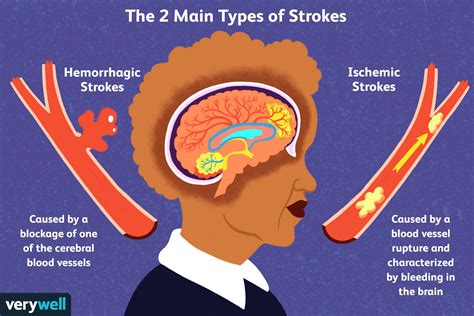
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, accounting for approximately 87% of all stroke cases. It occurs when a blood clot forms in a blood vessel in the brain, either due to atherosclerosis or a blood clot that has traveled from another part of the body. The symptoms of ischemic stroke can vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage, but may include weakness, numbness, and difficulty with speech and vision.Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding in the surrounding tissue. This type of stroke can be caused by a range of factors, including high blood pressure, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). The symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke can be severe and may include sudden headache, vomiting, and loss of consciousness.Symptoms of Stroke
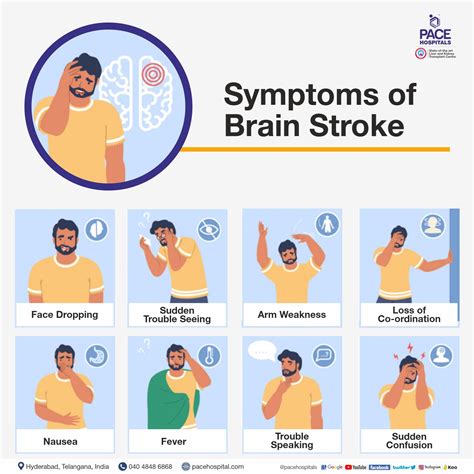
- Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty with speech or understanding
- Vision changes, such as double vision or loss of vision
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden headache or vomiting
Acting F.A.S.T.
The American Stroke Association recommends using the F.A.S.T. acronym to identify the symptoms of stroke:- F: Face - Ask the person to smile. Does one side of their face droop?
- A: Arm - Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- S: Speech - Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Is their speech slurred or difficult to understand?
- T: Time - Time is of the essence. If the person shows any of these symptoms, call for emergency medical services immediately.
Causes and Risk Factors of Stroke
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of stroke
- Age - stroke risk increases with age
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of stroke. These include:- Regular exercise - at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day
- Healthy diet - a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Stress management - techniques such as meditation and deep breathing
- Quitting smoking - smoking cessation programs can help
- Limiting alcohol consumption - no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men
Treatment Options for Stroke
- Medications - such as thrombolytics to dissolve blood clots
- Surgery - to remove blood clots or repair damaged blood vessels
- Rehabilitation therapy - to help individuals regain strength and mobility
- Lifestyle modifications - to reduce the risk of future stroke
Rehabilitation Therapy
Rehabilitation therapy can help individuals regain strength and mobility after a stroke. This may include:- Physical therapy - to improve mobility and balance
- Occupational therapy - to improve daily living skills
- Speech therapy - to improve communication skills
- Cognitive therapy - to improve memory and problem-solving skills
Prevention of Stroke

- Maintaining a healthy blood pressure
- Controlling cholesterol levels
- Managing diabetes
- Quitting smoking
- Engaging in regular exercise
- Eating a healthy diet
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups can help identify risk factors for stroke and provide opportunities for early intervention. Individuals should:- Get regular blood pressure checks
- Have their cholesterol levels checked regularly
- Manage their diabetes
- Discuss their risk factors with their healthcare provider
Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the symptoms of stroke?
+The symptoms of stroke can vary depending on the location and severity of the damage, but may include weakness, numbness, and difficulty with speech and vision.
How can I reduce my risk of stroke?
+Individuals can reduce their risk of stroke by maintaining a healthy blood pressure, controlling cholesterol levels, managing diabetes, quitting smoking, engaging in regular exercise, and eating a healthy diet.
What are the treatment options for stroke?
+The treatment options for stroke depend on the type and severity of the stroke, but may include medications, surgery, rehabilitation therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
