Intro
The medical field is filled with abbreviations, and understanding them is crucial for effective communication among healthcare professionals. One such abbreviation is "SUD," which stands for Substance Use Disorder. Substance Use Disorder is a medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant distress and impairment in daily life. In this article, we will delve into the world of SUD, exploring its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more.
The importance of understanding SUD cannot be overstated. As a medical condition, it requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and therapists, must be aware of the complexities of SUD to provide effective care. Moreover, individuals struggling with SUD and their loved ones need to understand the condition to navigate the healthcare system and access appropriate resources. By shedding light on SUD, we hope to reduce stigma and promote a culture of compassion and support.
Substance Use Disorder is a complex condition characterized by the problematic use of substances, such as alcohol, illicit drugs, or prescription medications. The use of these substances can lead to physical dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms, making it challenging for individuals to control their consumption. SUD can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic background, and its consequences can be devastating, impacting not only the individual but also their family, friends, and community.
Definition and Diagnosis of SUD

Causes and Risk Factors of SUD
The causes and risk factors of SUD are complex and multifaceted. Research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors contribute to the development of SUD. Genetic predisposition, family history, and mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety, can increase an individual's risk of developing SUD. Additionally, environmental factors, such as exposure to substance use at a young age, peer pressure, and socioeconomic disadvantage, can also play a role in the development of SUD. Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.Symptoms and Signs of SUD

Treatment Options for SUD
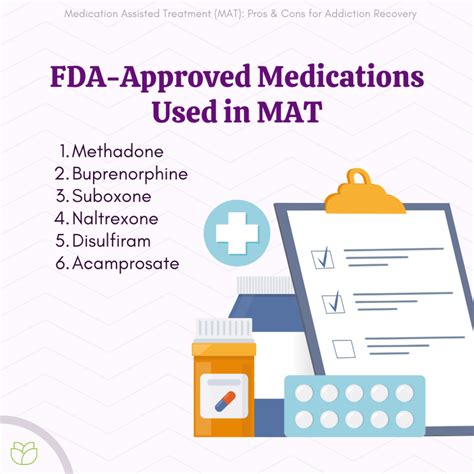
Treatment for SUD typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and support groups. Medications, such as methadone or buprenorphine, can help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or contingency management, can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with substance use. Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), provide a sense of community and connection, helping individuals stay motivated and engaged in their recovery.Medications for SUD
Therapy and Counseling for SUD
Therapy and counseling are essential components of SUD treatment. Individual and group therapy can help individuals: * Identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors * Develop coping skills and strategies to manage cravings and triggers * Improve relationships and communication skills * Address underlying mental health conditions, such as depression or anxietySupport Groups for SUD
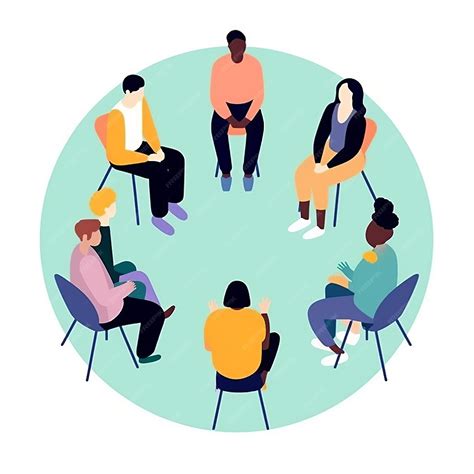

Prevention and Education
Prevention and education are critical in reducing the risk of SUD. Educating individuals, particularly young people, about the risks and consequences of substance use can help prevent the development of SUD. Prevention programs, such as school-based programs or community-based initiatives, can provide individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to make informed decisions about substance use.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with SUD in the comments below. Your stories and insights can help others understand the complexities of this condition and promote a culture of empathy and support. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be struggling with SUD or who are interested in learning more about this condition.
What is Substance Use Disorder?
+Substance Use Disorder is a medical condition characterized by the problematic use of substances, such as alcohol, illicit drugs, or prescription medications.
What are the symptoms of SUD?
+The symptoms of SUD can vary depending on the type of substance used, but common symptoms include tolerance, withdrawal, loss of control, neglect of responsibilities, and continued use despite negative consequences.
How is SUD treated?
+Treatment for SUD typically involves a combination of medication, therapy, and support groups. Medications can help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, while therapy and support groups can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Can SUD be prevented?
+Yes, SUD can be prevented through education and prevention programs. Educating individuals, particularly young people, about the risks and consequences of substance use can help prevent the development of SUD.
Where can I find support for SUD?
+Support for SUD can be found through support groups, such as NA or AA, as well as through healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, and therapists. Additionally, online resources and hotlines can provide individuals with information and support.
