Intro
Understand the 5 sugar level ranges, including normal, prediabetic, and diabetic ranges, to manage blood glucose levels, prevent hyperglycemia, and maintain healthy insulin levels, optimizing your overall well-being.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight management, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors, including diet, physical activity, and stress. Understanding the different sugar level ranges and their implications on health is essential for making informed lifestyle choices. In this article, we will delve into the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels, the factors that influence them, and the steps to maintain healthy sugar levels.
The human body relies on glucose, a type of sugar, as its primary source of energy. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, thereby regulating blood sugar levels. However, when the body's ability to produce or respond to insulin is impaired, blood sugar levels can become elevated, leading to a range of health problems.
Effective management of blood sugar levels is critical for preventing and managing diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and vision loss, if left uncontrolled. By understanding the different sugar level ranges and taking proactive steps to maintain healthy levels, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications.
Normal Sugar Level Range

Factors Influencing Normal Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence normal sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, and certain medications. Consuming a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also improve insulin sensitivity, allowing glucose to enter cells more efficiently. Additionally, getting adequate sleep and managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can help maintain healthy sugar levels.Elevated Sugar Level Range
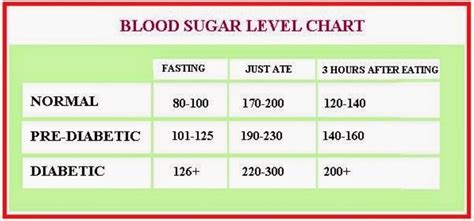
Managing Elevated Sugar Levels
Managing elevated sugar levels requires a multi-faceted approach that includes dietary changes, increased physical activity, and stress management. Incorporating more fiber-rich foods, such as legumes, nuts, and seeds, can help slow down the digestion and absorption of glucose, reducing the risk of elevated sugar levels. Engaging in regular aerobic exercise, such as cycling or swimming, can also improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in the muscles. Furthermore, practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as deep breathing or tai chi, can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on blood sugar levels.Diabetic Sugar Level Range
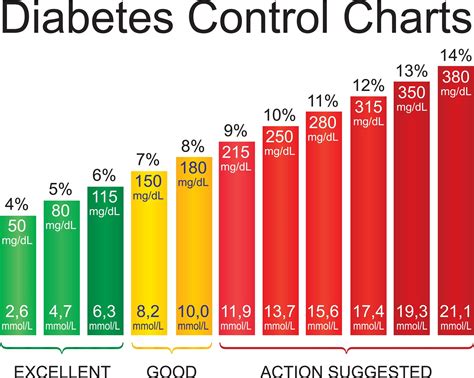
Diabetes Management Strategies
Effective diabetes management involves a range of strategies, including medication adherence, healthy eating, regular physical activity, and stress management. Individuals with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account their unique needs and health status. This plan may include medications, such as metformin or insulin, to help regulate blood sugar levels, as well as lifestyle modifications, such as following a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise.Pre-Diabetic Sugar Level Range
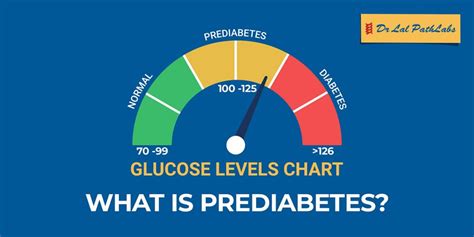
Preventing Progression to Diabetes
Preventing the progression from pre-diabetes to diabetes requires prompt intervention and lifestyle modifications. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) has shown that individuals with pre-diabetes can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58% through a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss. This can be achieved by incorporating more whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, into the diet, and engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week.Hypoglycemic Sugar Level Range
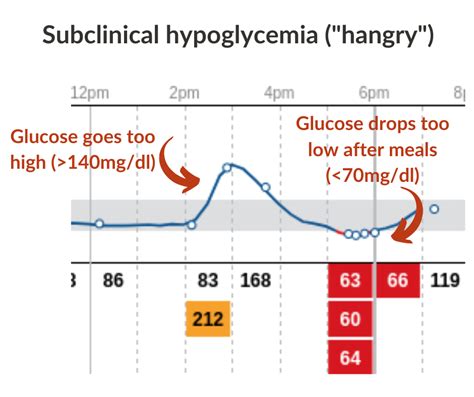
Managing Hypoglycemia
Managing hypoglycemia requires prompt recognition and treatment of low blood sugar levels. Individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a plan for managing hypoglycemia, which may include adjusting medication doses, eating smaller, more frequent meals, and carrying glucose-rich snacks. It is also essential to educate family members and friends on how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia, in case of an emergency.In conclusion, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the different sugar level ranges and taking proactive steps to manage blood sugar levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications. Whether you have diabetes, pre-diabetes, or are simply looking to maintain healthy sugar levels, making informed lifestyle choices and working closely with your healthcare provider can help you achieve your goals.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on managing blood sugar levels in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, if you have any questions or topics related to sugar level ranges that you would like us to address in future articles, please let us know.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar levels include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I lower my blood sugar levels naturally?
+Natural ways to lower blood sugar levels include drinking plenty of water, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods and low in processed and sugary foods.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
+Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, resulting in a complete deficiency of insulin production. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance, in which the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, and impaired insulin secretion.
Can I reverse pre-diabetes through lifestyle changes?
+Yes, pre-diabetes can often be reversed through lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, increasing physical activity, and eating a healthy, balanced diet. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) has shown that individuals with pre-diabetes can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58% through a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the individual's health status and treatment plan. Generally, individuals with diabetes should check their blood sugar levels at least four times a day, including before meals, after meals, and before bedtime. However, the exact frequency may vary depending on the type of diabetes, medication regimen, and other factors, and should be determined in consultation with a healthcare provider.
