Intro
Discover 5 essential uses of Sulfamethoxazole, a potent antibiotic, including treating urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and travelers diarrhea, with benefits of sulfonamide therapy and antimicrobial properties.
The importance of antibiotics in modern medicine cannot be overstated. Among the numerous antibiotics available, Sulfamethoxazole stands out due to its broad spectrum of activity and its effectiveness against a wide range of bacterial infections. Sulfamethoxazole, often used in combination with trimethoprim, is a sulfonamide antibiotic that works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. This article delves into the various uses of Sulfamethoxazole, exploring its applications, benefits, and the science behind its mechanism of action.
Sulfamethoxazole's versatility is a significant factor in its widespread use. It is prescribed for various infections, including those of the urinary tract, respiratory system, and skin. The drug's ability to target a broad range of bacteria makes it a valuable asset in the fight against bacterial infections. Moreover, its combination with trimethoprim enhances its efficacy, allowing it to tackle more complex infections. Understanding the uses of Sulfamethoxazole is crucial for both medical professionals and patients, as it can significantly impact treatment outcomes and patient recovery.
The mechanism of action of Sulfamethoxazole is based on its ability to interfere with the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which is essential for bacterial growth and replication. When used in conjunction with trimethoprim, the combination is particularly potent, as trimethoprim further inhibits the dihydrofolate reductase enzyme, crucial for the conversion of folic acid into its active form. This synergistic effect makes the Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim combination highly effective against a wide range of bacterial infections.
Urinary Tract Infections
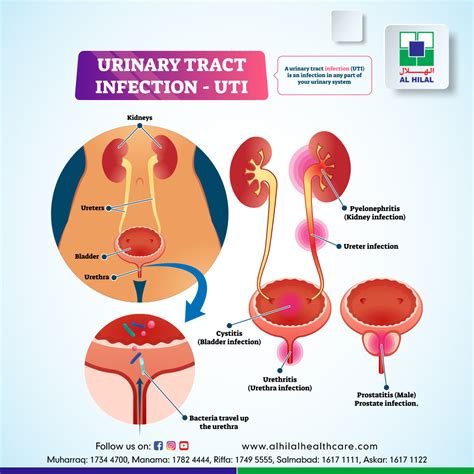
Benefits and Considerations
The use of Sulfamethoxazole for UTIs offers several benefits, including a high success rate in clearing the infection and preventing recurrence. However, it's crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure the infection is fully cleared. Additionally, patients should be aware of potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal upset or allergic reactions, although these are relatively rare.Respiratory Tract Infections
Working Mechanism
The working mechanism of Sulfamethoxazole in respiratory infections involves the inhibition of folic acid synthesis in bacteria, as mentioned earlier. This action is critical for preventing the multiplication of bacteria and ultimately leading to their death. The combination with trimethoprim further enhances this effect, making the Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim combination a potent tool against bacterial respiratory infections.Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
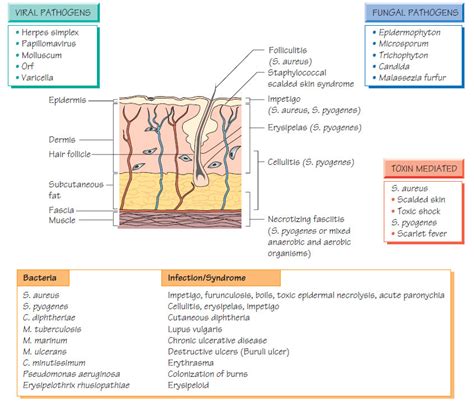
Practical Examples
Practical examples of Sulfamethoxazole's use in skin infections include its application in treating MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) infections, where it is often used off-label due to its efficacy against this resistant bacterium. However, it's essential to note that the use of Sulfamethoxazole for MRSA should be guided by susceptibility testing to ensure the bacteria are sensitive to the drug.Prevention of Opportunistic Infections

Steps for Prevention
Steps for the prevention of opportunistic infections with Sulfamethoxazole include: - Identifying individuals at high risk of opportunistic infections due to immunocompromised states. - Initiating prophylactic treatment with Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim based on clinical guidelines and the patient's risk factors. - Monitoring patients for signs of infection and adjusting the prophylactic regimen as necessary. - Ensuring adherence to the prescribed prophylactic regimen to maximize efficacy.Traveler's Diarrhea

Statistical Data
Statistical data indicate that the use of Sulfamethoxazole in preventing traveler's diarrhea can reduce the incidence of the disease by up to 80% in high-risk areas. However, it's crucial to weigh this benefit against the potential risks and to consider alternative preventive measures, such as strict adherence to safe food and water practices.Conclusion and Future Directions

As we move forward, it's essential to continue monitoring the effectiveness of Sulfamethoxazole and to adapt its use based on emerging resistance patterns and new clinical evidence. By doing so, we can maximize the benefits of this valuable antibiotic while minimizing its contribution to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Sulfamethoxazole, either as a patient or a healthcare provider. Your insights can help inform others and contribute to a broader understanding of the role of antibiotics in modern healthcare. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who might find it informative.
What is Sulfamethoxazole used for?
+Sulfamethoxazole is used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and to prevent opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals.
How does Sulfamethoxazole work?
+Sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which is essential for bacterial growth and replication. When combined with trimethoprim, it further inhibits the dihydrofolate reductase enzyme, enhancing its bactericidal effect.
What are the common side effects of Sulfamethoxazole?
+Common side effects of Sulfamethoxazole include gastrointestinal upset, such as nausea and vomiting, allergic reactions, and in rare cases, severe reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
