Intro
Discover Mash Liver Disease causes, symptoms, and treatment options, understanding liver health, liver function, and fatty liver disease to manage this metabolic disorder effectively.
Liver disease is a significant health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the lesser-known but equally important conditions is Mash Liver Disease, also known as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). This condition is characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver cells, which can lead to inflammation, scarring, and eventually liver failure. In this article, we will delve into the world of Mash Liver Disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
The liver plays a vital role in our overall health, responsible for filtering toxins, producing bile, and regulating metabolism. However, when the liver becomes overwhelmed with excess fat, it can lead to a range of problems. Mash Liver Disease is often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, which are all interconnected factors that contribute to the development of this condition. As the prevalence of obesity and related disorders continues to rise, it is essential to understand the risks and consequences of Mash Liver Disease.
The importance of addressing Mash Liver Disease cannot be overstated. If left untreated, this condition can progress to more severe forms of liver disease, such as Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Furthermore, Mash Liver Disease is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making it challenging to diagnose and treat. Therefore, it is crucial to raise awareness about this condition, its risk factors, and the available treatment options. By doing so, we can empower individuals to take control of their liver health and reduce the burden of Mash Liver Disease on the healthcare system.
Causes and Risk Factors of Mash Liver Disease
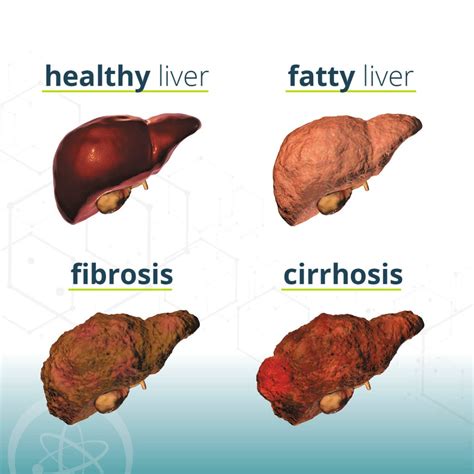
Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for preventing and managing Mash Liver Disease. By addressing these underlying factors, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this condition and improve their overall liver health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Mash Liver Disease
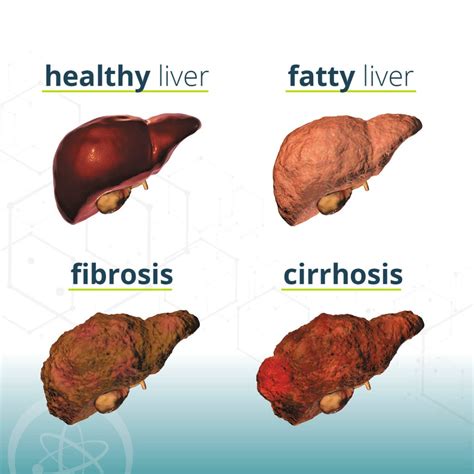
Diagnosing Mash Liver Disease typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and laboratory tests. Some common diagnostic tools include:
- Liver function tests (LFTs)
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, or MRI)
- Liver biopsy
Early diagnosis is critical for effective management and treatment of Mash Liver Disease. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above or have a family history of liver disease, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Mash Liver Disease
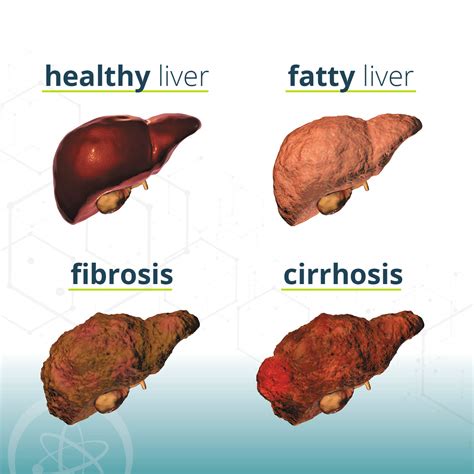
It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and health status. By making lifestyle changes and adhering to treatment recommendations, individuals can effectively manage Mash Liver Disease and reduce the risk of progression to more severe liver conditions.
Prevention Strategies for Mash Liver Disease
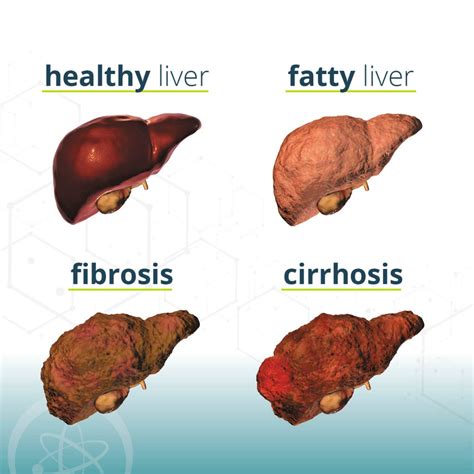
By adopting these prevention strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing Mash Liver Disease and promote overall liver health.
Complications and Prognosis of Mash Liver Disease
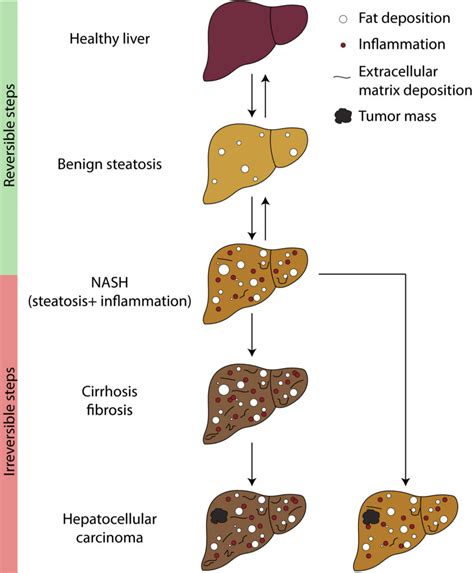
The prognosis for Mash Liver Disease varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. With early diagnosis and proper management, individuals can significantly improve their liver health and reduce the risk of complications.
Current Research and Future Directions
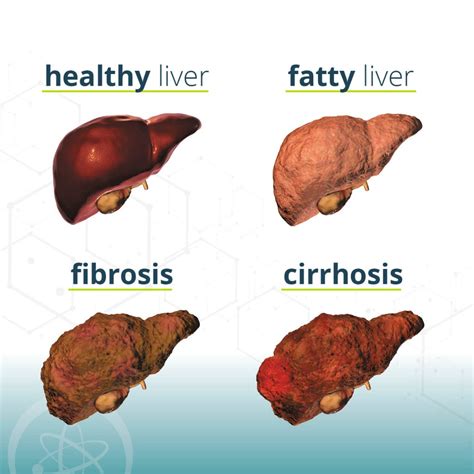
As our understanding of Mash Liver Disease continues to evolve, we can expect to see the development of more effective treatments and prevention strategies. By staying informed about the latest research and advancements, individuals can make informed decisions about their liver health and stay ahead of this complex condition.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
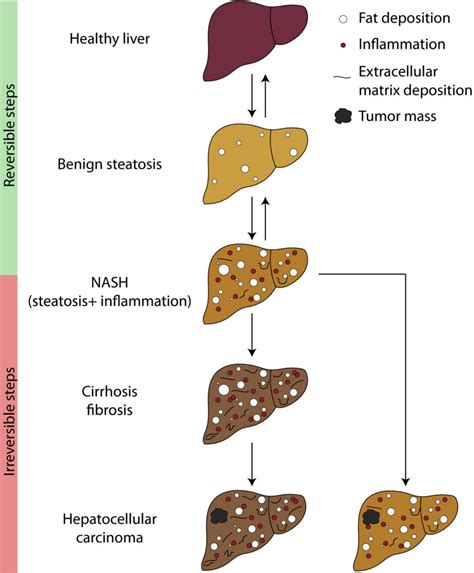
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about Mash Liver Disease in the comments section below. Your input can help raise awareness and facilitate a better understanding of this complex condition. Additionally, please consider sharing this article with friends, family, and social networks to help spread the word about the importance of liver health.
What are the early signs of Mash Liver Disease?
+The early signs of Mash Liver Disease may include fatigue, weight loss, and abdominal swelling. However, it is essential to note that this condition can be asymptomatic in its early stages, making regular health check-ups crucial for early diagnosis.
Can Mash Liver Disease be reversed?
+Yes, Mash Liver Disease can be reversed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. Losing weight, adopting a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce liver fat accumulation and improve liver health.
Is Mash Liver Disease contagious?
+No, Mash Liver Disease is not contagious. It is a non-infectious condition that develops due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
