Intro
Discover effective surgery options for nephrolithiasis treatment, including lithotripsy and ureteroscopy, to relieve kidney stone symptoms and prevent complications, promoting urinary tract health and wellness.
Nephrolithiasis, commonly known as kidney stones, is a condition where small, hard mineral deposits form inside the kidneys. These deposits can cause severe pain, nausea, and vomiting, and if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications such as kidney damage or infection. While some kidney stones can be treated with medication and lifestyle changes, others may require surgical intervention. In this article, we will explore the importance of surgery for nephrolithiasis treatment and the various options available.
The prevalence of kidney stones has been increasing over the years, affecting millions of people worldwide. The condition can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, including diet, hydration, and certain medical conditions. While some kidney stones can pass on their own, others may require medical attention to prevent complications. Surgery is often necessary to remove large or stubborn stones that cannot be treated with other methods.
Kidney stones can be categorized into different types, including calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones. Each type of stone has its own unique characteristics and treatment options. For example, calcium oxalate stones are the most common type and can often be treated with medication and lifestyle changes. However, larger stones or those that are causing severe symptoms may require surgical removal. Understanding the type of stone and its location is crucial in determining the best course of treatment.
Introduction to Surgical Options

Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
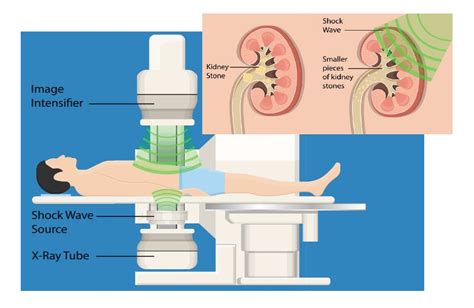
Benefits and Risks of ESWL
The benefits of ESWL include minimal invasion, faster recovery times, and reduced risk of complications compared to other surgical options. However, ESWL may not be effective for larger stones or those that are located in the lower ureter. Additionally, ESWL can cause side effects such as bruising, bleeding, and infection. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of ESWL with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the best option for treatment.Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
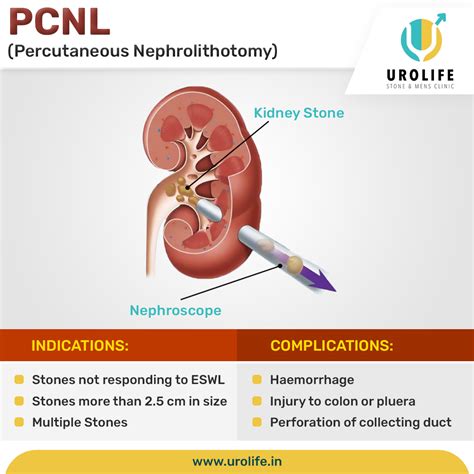
Benefits and Risks of PCNL
The benefits of PCNL include high success rates for removing large stones and reduced risk of complications compared to open surgery. However, PCNL can cause side effects such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, PCNL may require a longer recovery time compared to ESWL. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of PCNL with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the best option for treatment.Ureteroscopy
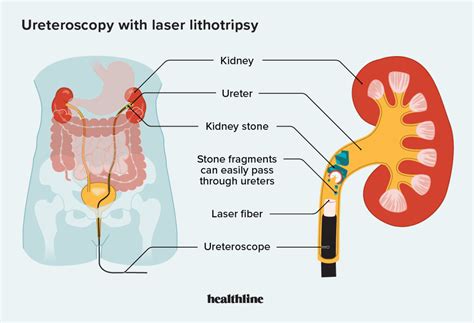
Benefits and Risks of Ureteroscopy
The benefits of ureteroscopy include high success rates for removing stones and reduced risk of complications compared to other surgical options. However, ureteroscopy can cause side effects such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, ureteroscopy may require a longer recovery time compared to ESWL. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of ureteroscopy with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the best option for treatment.Open Surgery

Benefits and Risks of Open Surgery
The benefits of open surgery include high success rates for removing complex stones and reduced risk of complications compared to other surgical options. However, open surgery can cause side effects such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, open surgery may require a longer recovery time compared to other surgical options. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of open surgery with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the best option for treatment.Laparoscopic Surgery
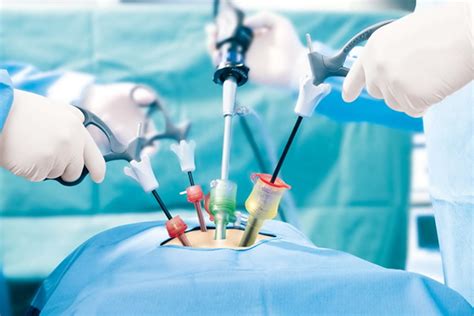
Benefits and Risks of Laparoscopic Surgery
The benefits of laparoscopic surgery include high success rates for removing complex stones and reduced risk of complications compared to open surgery. However, laparoscopic surgery can cause side effects such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, laparoscopic surgery may require a longer recovery time compared to other surgical options. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of laparoscopic surgery with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the best option for treatment.Robotic Surgery
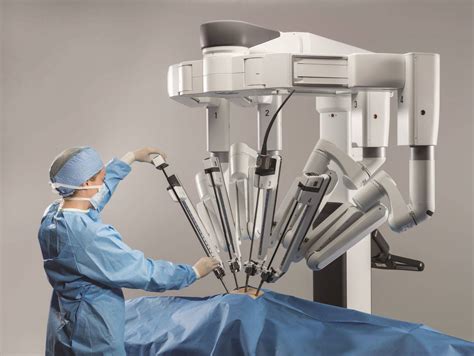
Benefits and Risks of Robotic Surgery
The benefits of robotic surgery include high success rates for removing complex stones and reduced risk of complications compared to open surgery. However, robotic surgery can cause side effects such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, robotic surgery may require a longer recovery time compared to other surgical options. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of robotic surgery with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the best option for treatment.Preparation and Recovery

Tips for a Smooth Recovery
Here are some tips for a smooth recovery after surgical treatment for nephrolithiasis: * Follow your healthcare provider's instructions * Take pain medication as directed * Rest and avoid heavy lifting * Drink plenty of water to help pass the stone * Avoid strenuous activities for several weeks * Attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare providerWhat are the symptoms of kidney stones?
+The symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and frequent urination. In some cases, kidney stones may not cause any symptoms until they move into the ureter and block the flow of urine.
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
+Kidney stones are diagnosed using imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds. Blood and urine tests may also be used to check for signs of infection or other complications.
What are the treatment options for kidney stones?
+The treatment options for kidney stones include medication, lifestyle changes, and surgery. The best treatment option depends on the size, location, and type of stone, as well as the patient's overall health.
Can kidney stones be prevented?
+Yes, kidney stones can be prevented by drinking plenty of water, limiting sodium and animal protein, and avoiding foods that are high in oxalate. Maintaining a healthy weight and managing underlying medical conditions can also help prevent kidney stones.
What are the complications of kidney stones?
+The complications of kidney stones include infection, kidney damage, and ureteral obstruction. In severe cases, kidney stones can cause sepsis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
In conclusion, surgery is a crucial aspect of nephrolithiasis treatment, offering a range of options to remove kidney stones and prevent future occurrences. By understanding the different surgical options available, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be affected by kidney stones, and to explore other resources and support groups for more information and guidance.
