Intro
Learn about diverticulitis symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understand abdominal pain, bloating, and bowel changes associated with diverticulitis disease, and discover management strategies for digestive health.
Diverticulitis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing a range of uncomfortable and potentially serious symptoms. The condition occurs when small, bulging pouches called diverticula develop in the digestive tract, typically in the colon. If these diverticula become inflamed or infected, it can lead to diverticulitis. Understanding the symptoms of diverticulitis is crucial for seeking medical attention and receiving proper treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of diverticulitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
The importance of recognizing diverticulitis symptoms cannot be overstated. If left untreated, diverticulitis can lead to serious complications, such as abscesses, perforations, and peritonitis. Moreover, diverticulitis can significantly impact a person's quality of life, causing persistent pain, discomfort, and changes in bowel habits. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall well-being.
Diverticulitis is often associated with a range of factors, including age, diet, and lifestyle. As people get older, the risk of developing diverticulitis increases, with most cases occurring in individuals over the age of 40. A low-fiber diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity can also contribute to the development of diverticulitis. Furthermore, certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease, can increase the risk of diverticulitis.
What are the Symptoms of Diverticulitis?
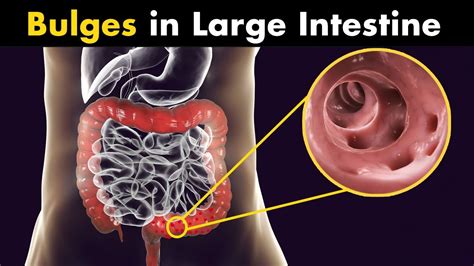
Types of Diverticulitis Symptoms
The symptoms of diverticulitis can be categorized into several types, including: * Acute symptoms: These are sudden and severe, often requiring immediate medical attention. * Chronic symptoms: These are ongoing and persistent, often causing significant discomfort and changes in bowel habits. * Complicated symptoms: These are serious and potentially life-threatening, often requiring hospitalization and surgical intervention.Causes and Risk Factors of Diverticulitis
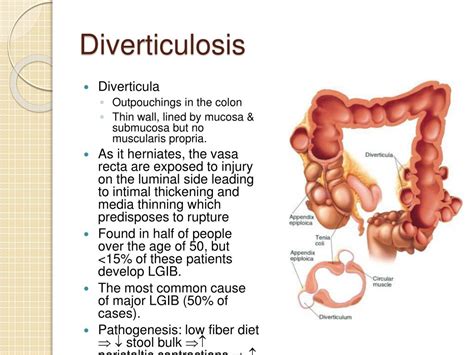
How to Reduce the Risk of Diverticulitis
While it is not possible to completely prevent diverticulitis, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. These include: * Eating a high-fiber diet: Foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help to reduce the risk of diverticulitis. * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help to prevent constipation and reduce the risk of diverticulitis. * Exercising regularly: Regular physical activity can help to improve bowel function and reduce the risk of diverticulitis. * Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity can increase the risk of diverticulitis, so maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise is essential.Diagnosis and Treatment of Diverticulitis
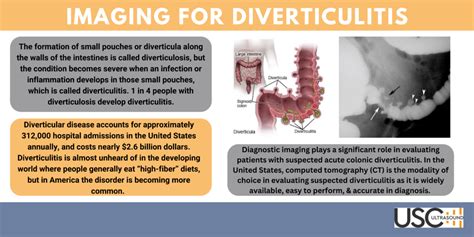
Treatment for diverticulitis typically depends on the severity of the condition and may include:
- Antibiotics: These medications can help to treat bacterial infections and reduce inflammation.
- Pain relief medications: These medications can help to manage pain and discomfort.
- Bowel rest: This involves avoiding solid foods and drinking plenty of fluids to give the bowel a chance to rest and recover.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the colon or to treat complications such as abscesses or perforations.
Complications of Diverticulitis
If left untreated, diverticulitis can lead to several complications, including: * Abscesses: These are pockets of pus that can form in the wall of the colon. * Perforations: These are holes that can develop in the wall of the colon, allowing bacteria to leak into the abdominal cavity. * Peritonitis: This is inflammation of the lining of the abdominal cavity, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. * Fistulas: These are abnormal connections that can form between the colon and other organs, such as the bladder or skin.Prevention Strategies for Diverticulitis

Lifestyle Changes for Diverticulitis Prevention
In addition to dietary changes, there are several lifestyle changes that can help to reduce the risk of diverticulitis. These include: * Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of diverticulitis, so quitting is essential for reducing the risk. * Reducing stress: Stress can exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms, so finding ways to manage stress, such as through meditation or yoga, can be helpful. * Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health and can help to reduce the risk of diverticulitis.Conclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diverticulitis in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with diverticulitis? What steps have you taken to manage symptoms and prevent complications? By sharing your story, you can help to raise awareness and support others who may be going through a similar experience.
What are the symptoms of diverticulitis?
+The symptoms of diverticulitis can include abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, fever, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, diverticulitis can cause rectal bleeding, which can be a sign of a more serious complication.
How is diverticulitis diagnosed?
+Diagnosing diverticulitis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, and ultrasound.
What are the treatment options for diverticulitis?
+Treatment for diverticulitis typically depends on the severity of the condition and may include antibiotics, pain relief medications, bowel rest, and surgery. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to treat complications such as abscesses or perforations.
