Intro
Discover Tourettes symptoms, including tics, involuntary movements, and vocal outbursts, to understand this neurodevelopmental disorder, its causes, and effects on daily life, and explore treatment options for managing symptoms.
Tourette's syndrome is a complex and multifaceted neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by repetitive and involuntary movements or vocalizations, known as tics, Tourette's can have a significant impact on an individual's daily life, social interactions, and overall well-being. Despite its prevalence, Tourette's remains shrouded in mystery, with many misconceptions and stigmas surrounding the condition. As we delve into the world of Tourette's, it is essential to understand the symptoms, causes, and effects of this disorder, as well as the latest research and treatment options available.
The symptoms of Tourette's syndrome can vary widely from person to person, and may include a range of physical and vocal tics. Physical tics, also known as motor tics, can manifest as simple movements, such as eye blinking or facial grimacing, or as more complex actions, like arm flailing or leg twitching. Vocal tics, on the other hand, can range from simple sounds, like grunting or barking, to more complex vocalizations, such as coprolalia, which is the involuntary use of obscene language. In addition to these physical and vocal tics, individuals with Tourette's may also experience other symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
As we explore the complexities of Tourette's syndrome, it is crucial to recognize the significant impact that this condition can have on an individual's daily life. From social stigma and bullying to difficulties in school and the workplace, the effects of Tourette's can be far-reaching and debilitating. Furthermore, the unpredictability of tics can make everyday activities, like eating or sleeping, a challenge. Despite these challenges, many individuals with Tourette's lead fulfilling and productive lives, and with the right support, treatment, and accommodations, it is possible to manage the symptoms of this condition and thrive.
Tourette's Symptoms and Characteristics
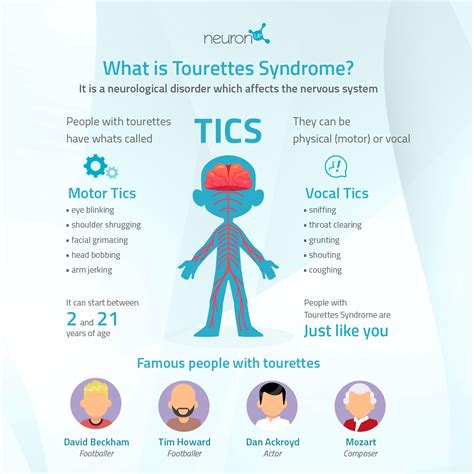
Some common examples of Tourette's symptoms include:
- Eye blinking or facial grimacing
- Arm flailing or leg twitching
- Grunting or barking
- Coprolalia, or the involuntary use of obscene language
- Echolalia, or the repetition of words or phrases
- Palilalia, or the repetition of words or phrases
Motor Tics
Motor tics are a hallmark symptom of Tourette's syndrome, and can range from simple movements, like eye blinking or facial grimacing, to more complex actions, like arm flailing or leg twitching. Simple motor tics are typically brief and repetitive, and may be triggered by stress, anxiety, or other emotional states. Complex motor tics, on the other hand, are longer and more intricate, and may involve multiple muscle groups.Some common examples of motor tics include:
- Eye blinking or facial grimacing
- Arm flailing or leg twitching
- Shoulder shrugging or head jerking
- Touching or tapping objects
- Smelling or tasting objects
Vocal Tics
Vocal tics are another common symptom of Tourette's syndrome, and can range from simple sounds, like grunting or barking, to more complex vocalizations, like coprolalia or echolalia. Simple vocal tics are typically brief and repetitive, and may be triggered by stress, anxiety, or other emotional states. Complex vocal tics, on the other hand, are longer and more intricate, and may involve multiple syllables or words.Some common examples of vocal tics include:
- Grunting or barking
- Coprolalia, or the involuntary use of obscene language
- Echolalia, or the repetition of words or phrases
- Palilalia, or the repetition of words or phrases
- Whistling or making other sounds
Tourette's Causes and Risk Factors

Some common risk factors for Tourette's include:
- Family history of Tourette's or other tic disorders
- Genetics, particularly mutations in the DRD4 and DRD5 genes
- Brain abnormalities, particularly in the basal ganglia and cortex
- Prenatal and perinatal complications, such as low birth weight or maternal smoking
- Infections, such as strep throat or Lyme disease
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of Tourette's syndrome, with studies suggesting that individuals with a family history of Tourette's are more likely to develop the condition. Research has identified several genes that may contribute to the development of Tourette's, including the DRD4 and DRD5 genes, which code for dopamine receptors in the brain.Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as prenatal and perinatal complications, infections, and stress, may also contribute to the development of Tourette's syndrome. Research has shown that individuals who experience stress, anxiety, or other emotional states are more likely to exhibit tics, suggesting a link between environmental factors and tic severity.Tourette's Diagnosis and Treatment

Treatment for Tourette's syndrome typically involves a combination of behavioral therapies, medications, and lifestyle changes. Behavioral therapies, such as habit reversal training and exposure and response prevention, can help individuals with Tourette's manage their tics and reduce their severity. Medications, such as neuroleptics and alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, can also be effective in reducing tic severity, although they may have side effects.
Some common treatment options for Tourette's include:
- Behavioral therapies, such as habit reversal training and exposure and response prevention
- Medications, such as neuroleptics and alpha-2 adrenergic agonists
- Lifestyle changes, such as stress management and sleep hygiene
- Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and mindfulness meditation
Behavioral Therapies
Behavioral therapies, such as habit reversal training and exposure and response prevention, can be effective in helping individuals with Tourette's manage their tics and reduce their severity. These therapies typically involve a combination of education, skills training, and practice, and can be tailored to meet the individual needs of each patient.Medications
Medications, such as neuroleptics and alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, can also be effective in reducing tic severity, although they may have side effects. Neuroleptics, such as haloperidol and risperidone, can help reduce tic severity by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain. Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, such as clonidine and guanfacine, can help reduce tic severity by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain.Tourette's and Quality of Life

However, with the right treatment and support, individuals with Tourette's can lead fulfilling and productive lives. Many people with Tourette's have successful careers, relationships, and hobbies, and are able to manage their symptoms and reduce their impact on daily life.
Some common strategies for improving quality of life with Tourette's include:
- Seeking social support from family, friends, and support groups
- Practicing stress management and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation
- Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity
- Getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy diet
- Seeking professional help and treatment when needed
Social Support
Social support from family, friends, and support groups can be essential for individuals with Tourette's, particularly during times of stress or crisis. Support groups, such as the Tourette Association of America, can provide a sense of community and connection, as well as access to resources and information.Stress Management
Stress management and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help reduce tic severity and improve overall well-being. Regular exercise and physical activity can also help reduce stress and improve mood, while getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy diet can help reduce tic severity and improve overall health.What is Tourette's syndrome?
+Tourette's syndrome is a neurological disorder characterized by repetitive and involuntary movements or vocalizations, known as tics.
What are the symptoms of Tourette's syndrome?
+The symptoms of Tourette's syndrome can include motor tics, such as eye blinking or arm flailing, and vocal tics, such as grunting or coprolalia.
How is Tourette's syndrome diagnosed?
+Tourette's syndrome is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, including a physical exam, medical history, and psychological assessment.
What are the treatment options for Tourette's syndrome?
+Treatment options for Tourette's syndrome can include behavioral therapies, medications, and lifestyle changes, such as stress management and sleep hygiene.
Can individuals with Tourette's syndrome lead normal lives?
+Yes, with the right treatment and support, individuals with Tourette's syndrome can lead fulfilling and productive lives, despite the challenges posed by their condition.
As we conclude our exploration of Tourette's syndrome, it is essential to recognize the complexity and multifaceted nature of this condition. From the symptoms and characteristics of Tourette's to its causes, diagnosis, and treatment, there is much to learn and understand about this disorder. By promoting awareness, education, and support, we can work towards a future where individuals with Tourette's can thrive and reach their full potential. If you or someone you know is affected by Tourette's, we encourage you to seek out resources and support, and to share your experiences and stories with others. Together, we can build a community of understanding and acceptance, and work towards a brighter future for all individuals with Tourette's syndrome.
