Intro
Discover how atherosclerosis impacts the aorta, causing plaque buildup, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular disease, leading to aneurysms, dissections, and heart attacks, affecting blood flow and overall heart health.
Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to their hardening and narrowing. This condition can affect any artery in the body, but when it affects the aorta, the largest artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body, it can have severe consequences. The aorta is a critical blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the entire body, and any damage to it can lead to life-threatening complications. In this article, we will explore the ways in which atherosclerosis affects the aorta and the potential risks and consequences of this condition.
Atherosclerosis is a slow and progressive disease that can start as early as childhood, but it often goes unnoticed until later in life. The buildup of plaque in the arteries is a result of a combination of factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes. As the plaque builds up, it can cause the arteries to narrow and harden, leading to a reduction in blood flow to the affected areas. When atherosclerosis affects the aorta, it can lead to a range of complications, including aneurysms, dissections, and rupture.
The aorta is a complex and dynamic blood vessel that plays a critical role in maintaining blood pressure and flow. It is divided into several sections, including the ascending aorta, the arch of the aorta, and the descending aorta. Each section of the aorta has its unique characteristics and functions, and atherosclerosis can affect each section in different ways. Understanding how atherosclerosis affects the aorta is essential for developing effective treatment strategies and preventing potential complications.
Atherosclerosis and Aortic Stenosis
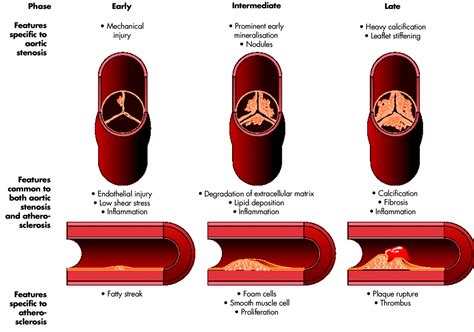
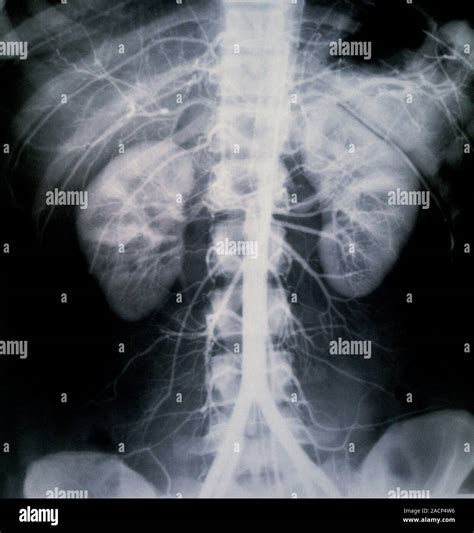
Atherosclerosis and Aortic Aneurysms
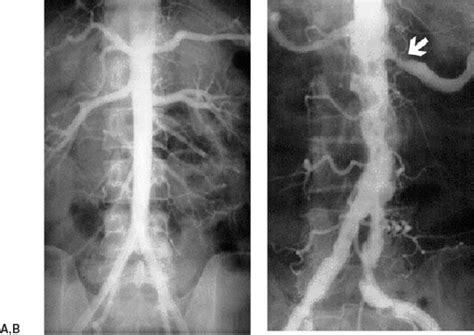
Atherosclerosis and Aortic Dissection
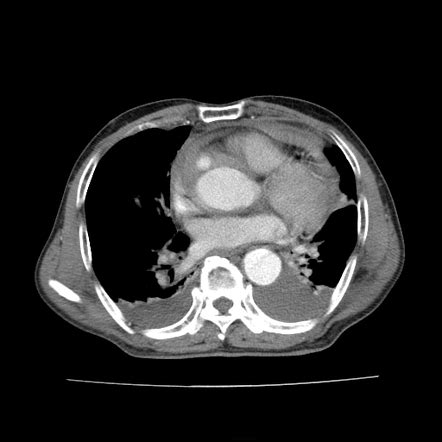
Atherosclerosis and Aortic Rupture
Managing Atherosclerosis and Aortic Disease
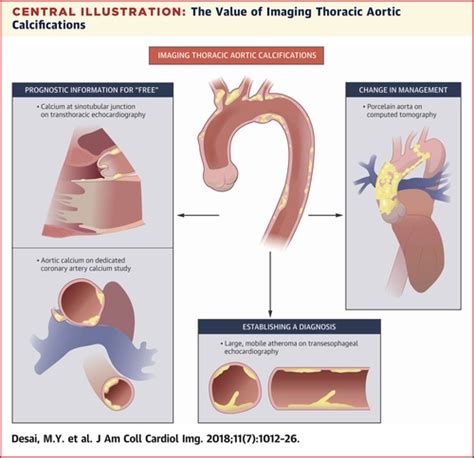
Prevention Strategies
Preventing atherosclerosis and aortic disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and early detection. Lifestyle modifications can include: * Quitting smoking * Exercising regularly * Eating a healthy diet * Maintaining a healthy weight * Managing stress Early detection can include regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, blood pressure monitoring, and cholesterol screening. Managing atherosclerosis and aortic disease requires a proactive approach that includes prevention strategies and prompt treatment.Treatment Options
Treating atherosclerosis and aortic disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes medications, surgical interventions, and lifestyle modifications. Medications can include: * Statins * Beta blockers * Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Surgical interventions can include: * Aortic valve replacement * Aortic aneurysm repair * Aortic dissection repair Lifestyle modifications can include: * Quitting smoking * Exercising regularly * Eating a healthy diet * Maintaining a healthy weight * Managing stressWhat is atherosclerosis and how does it affect the aorta?
+Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to their hardening and narrowing. When atherosclerosis affects the aorta, it can lead to a range of complications, including aneurysms, dissections, and rupture.
What are the symptoms of aortic stenosis?
+The symptoms of aortic stenosis can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting. If left untreated, aortic stenosis can lead to heart failure and even death.
How is atherosclerosis managed and prevented?
+Managing atherosclerosis requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgical interventions. Preventing atherosclerosis requires a proactive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and early detection.
In summary, atherosclerosis can have severe consequences when it affects the aorta, leading to complications such as aortic stenosis, aneurysms, dissections, and rupture. Managing atherosclerosis and aortic disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgical interventions. Preventing atherosclerosis requires a proactive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and early detection. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with atherosclerosis and aortic disease, and to take action to manage and prevent this condition. By working together, we can reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and aortic disease, and improve overall health and well-being.
