Intro
Learn about bladder tumor symptoms, including bloody urine, frequent urination, and pelvic pain, to detect bladder cancer early, improving treatment outcomes for urinary tract issues.
Bladder tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the bladder, which is a critical organ responsible for storing urine. These tumors can be either benign, meaning non-cancerous, or malignant, meaning cancerous. The symptoms associated with bladder tumors can vary depending on the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the individual's overall health. Recognizing the symptoms of bladder tumors is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding bladder tumor symptoms, their impact on daily life, and the various treatment options available.
The bladder plays a vital role in the urinary system, and any abnormalities in this organ can significantly affect an individual's quality of life. Bladder tumors, in particular, can cause a range of symptoms that may be mild or severe, depending on the stage of the disease. Some people may experience symptoms that are similar to those of other urinary tract infections or conditions, making it essential to seek medical attention if any unusual symptoms persist. The importance of recognizing bladder tumor symptoms cannot be overstated, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes and overall prognosis.
Bladder tumor symptoms can vary from person to person, but some common signs include blood in the urine, painful urination, frequent urination, and urinary urgency. In some cases, individuals may experience pelvic pain, back pain, or weight loss, although these symptoms are less common. It is essential to note that some people may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages of the disease. This highlights the importance of regular check-ups and screenings, particularly for individuals who are at high risk of developing bladder tumors.
Understanding Bladder Tumors
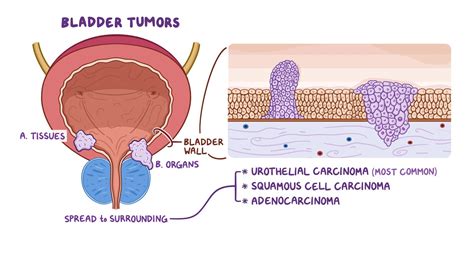
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of bladder tumors are not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified. These include smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, radiation therapy, and a family history of bladder cancer. Some people may also be at higher risk due to their occupation, such as those who work with dyes, rubber, or leather. Understanding the causes and risk factors of bladder tumors is essential for developing effective prevention strategies and reducing the risk of developing the disease.Bladder Tumor Symptoms in Detail
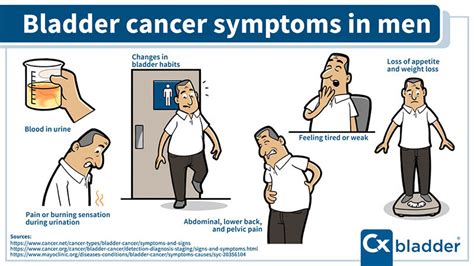
In some cases, individuals may experience more severe symptoms, such as:
- Pelvic pain: This can be a dull ache or a sharp pain in the pelvic area.
- Back pain: This can be a dull ache or a sharp pain in the lower back.
- Weight loss: This can be caused by the tumor affecting the body's ability to absorb nutrients.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If bladder tumor symptoms are suspected, a doctor will typically perform a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include: * Urine tests: To check for blood or other abnormalities in the urine. * Imaging tests: Such as CT scans or MRI scans to visualize the bladder and surrounding tissues. * Cystoscopy: A procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end into the bladder to visualize the inside of the bladder.Treatment for bladder tumors depends on the type and stage of the disease. Some common treatment options include:
- Surgery: To remove the tumor or the entire bladder.
- Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells using medication.
- Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells using high-energy rays.
- Immunotherapy: To stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Living with Bladder Tumors
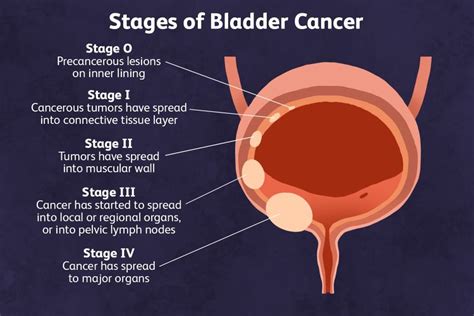
Nutrition and Bladder Tumors
A healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing bladder tumor symptoms and reducing the risk of complications. Some foods that may be beneficial for bladder health include: * Cranberry juice: Which may help prevent urinary tract infections. * Leafy green vegetables: Which are rich in antioxidants and may help reduce the risk of cancer. * Fatty fish: Which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and may help reduce inflammation. * Whole grains: Which are rich in fiber and may help regulate bowel movements.On the other hand, some foods may exacerbate bladder tumor symptoms, such as:
- Spicy foods: Which can irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms.
- Caffeine: Which can increase urine production and worsen frequency and urgency.
- Carbonated drinks: Which can irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms.
Prevention and Screening
Screening for bladder tumors typically involves a series of tests, including:
- Urine tests: To check for blood or other abnormalities in the urine.
- Imaging tests: Such as CT scans or MRI scans to visualize the bladder and surrounding tissues.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end into the bladder to visualize the inside of the bladder.
Current Research and Developments
Researchers are continually working to improve our understanding of bladder tumors and develop new treatments. Some current areas of research include: * Immunotherapy: Which involves stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells. * Targeted therapy: Which involves using medication to target specific genes or proteins involved in cancer growth. * Stem cell therapy: Which involves using stem cells to repair damaged bladder tissue.What are the most common symptoms of bladder tumors?
+The most common symptoms of bladder tumors include blood in the urine, painful urination, frequent urination, and urinary urgency.
How are bladder tumors diagnosed?
+Bladder tumors are typically diagnosed using a combination of urine tests, imaging tests, and cystoscopy.
What are the treatment options for bladder tumors?
+Treatment options for bladder tumors depend on the type and stage of the disease, but may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy.
Can bladder tumors be prevented?
+While bladder tumors cannot always be prevented, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk, including quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to certain chemicals, and staying hydrated.
What is the prognosis for individuals with bladder tumors?
+The prognosis for individuals with bladder tumors depends on the type and stage of the disease, as well as the effectiveness of treatment. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
In conclusion, bladder tumors are a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors associated with bladder tumors, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of bladder tumors, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. We encourage you to share this article with others, comment below with your thoughts and experiences, and take the necessary steps to prioritize your bladder health. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
