Intro
Unlock T protein blood test results, understanding troponin levels, and cardiac biomarkers to diagnose heart conditions, myocardial infarction, and cardiac risk factors.
The importance of understanding blood test results cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to proteins in the blood. Proteins are essential components of the body, playing critical roles in various bodily functions, including enzyme activity, hormone regulation, and immune response. One such protein is troponin, often referred to in the context of a "T protein blood test." This test is crucial for diagnosing and managing heart conditions, particularly myocardial infarction (heart attack). The troponin test has become a cornerstone in cardiology due to its high sensitivity and specificity for cardiac muscle damage.
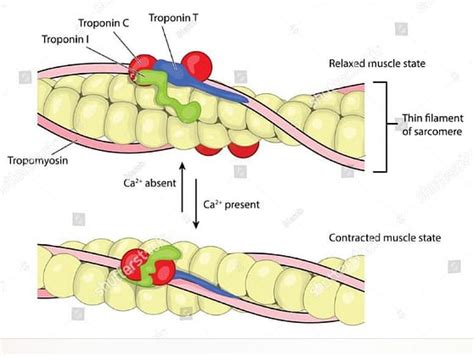
The T protein blood test, or troponin test, measures the levels of troponin in the blood. Troponin is a protein found in cardiac muscle fibers and is released into the bloodstream when the heart is damaged, such as during a heart attack. The test is highly specific for heart muscle damage, making it an invaluable tool for emergency departments and cardiac units worldwide. Understanding the results of this test is critical for both healthcare providers and patients, as it guides treatment decisions and prognosis. The troponin levels can indicate not only the presence of heart damage but also the severity of the damage.
The mechanism behind the troponin test is based on the principle that cardiac muscle cells contain troponin. When these cells are damaged, as in the case of a heart attack, troponin is released into the bloodstream. The test can detect even slight elevations in troponin levels, allowing for early diagnosis and intervention. This early detection is crucial because timely treatment of heart attacks can significantly improve outcomes, reducing the risk of complications and death. Furthermore, the troponin test can also be used to monitor patients with known heart disease, helping to assess the effectiveness of treatments and detect any new cardiac events.
Troponin Test Results Interpretation
Interpreting the results of a troponin test requires an understanding of the normal and abnormal ranges of troponin levels in the blood. Generally, troponin levels are considered normal when they are below a certain threshold, which can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific test used. Elevated troponin levels indicate cardiac muscle damage. The higher the troponin level, the more extensive the heart damage is likely to be. However, it's also important to consider the clinical context, including symptoms and other diagnostic findings, as elevated troponin can also be seen in conditions other than heart attack, such as heart failure, myocarditis, and severe pulmonary embolism.
Understanding Troponin Levels
The interpretation of troponin levels must be done with caution and in the context of the patient's overall clinical picture. Here are some general guidelines on troponin levels: - **Normal Levels**: Below the threshold set by the laboratory (typically <0.04 ng/mL, but this can vary). - **Elevated Levels**: Above the normal threshold, indicating cardiac damage. The degree of elevation can correlate with the severity of the damage. - **Serial Measurements**: In many cases, especially when the initial troponin level is not conclusively elevated, serial measurements over time can help confirm the diagnosis of a heart attack by showing a rising or falling pattern of troponin levels.Clinical Applications of the Troponin Test
The troponin test has several clinical applications, making it a versatile diagnostic tool in cardiology. Some of its key applications include:
- Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction: The primary use of the troponin test is to diagnose heart attacks. Elevated troponin levels in the context of chest pain or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac ischemia can confirm the diagnosis.
- Risk Stratification: Troponin levels can help in risk stratifying patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome, guiding the intensity of treatment and the need for urgent coronary angiography.
- Monitoring of Cardiac Conditions: For patients with known heart disease, serial troponin measurements can monitor disease progression and the effectiveness of treatments.
Limitations and Considerations
While the troponin test is highly specific for cardiac muscle damage, there are limitations and considerations to be aware of: - **False Positives**: Conditions other than heart attacks can cause elevated troponin levels, such as severe pulmonary embolism, heart failure, and myocarditis. - **Timing of Sample Collection**: Troponin levels may not be elevated immediately after a heart attack; thus, serial measurements are often necessary. - **Interference with Other Conditions**: Certain conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, can affect troponin levels, and these need to be considered when interpreting results.Practical Considerations for Patients

For patients undergoing a troponin test, understanding the process and what to expect can reduce anxiety and improve compliance with treatment plans. Here are some practical considerations:
- Pre-test Preparation: Generally, no specific preparation is required for a troponin test, but following the instructions of healthcare providers is essential.
- Understanding Results: Patients should ask their healthcare providers to explain the results in a way that is easy to understand, including what the results mean for their care and treatment.
- Follow-up Care: Depending on the results, follow-up appointments or additional tests may be necessary to monitor cardiac health and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Role of Troponin in Emergency Medicine
In emergency medicine, the troponin test plays a critical role in the rapid diagnosis of heart attacks. Emergency departments use protocols that include troponin testing as part of the initial evaluation of patients with chest pain or suspected acute coronary syndrome. The ability to quickly and accurately diagnose heart attacks allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve patient outcomes.Future Directions and Advances

Research and development in the field of cardiac biomarkers, including troponin, are ongoing. Future directions and advances may include:
- High-Sensitivity Troponin Assays: Newer, more sensitive assays can detect even lower levels of troponin, potentially allowing for earlier diagnosis of cardiac events.
- Point-of-Care Testing: Advances in point-of-care testing technology may enable quicker and more accessible troponin testing in various settings, not limited to hospitals.
- Combination Biomarker Strategies: Using troponin in combination with other biomarkers may enhance diagnostic accuracy and provide more comprehensive information about cardiac health.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the T protein blood test, or troponin test, is a critical diagnostic tool in cardiology, offering high sensitivity and specificity for cardiac muscle damage. Understanding the results of this test is essential for both healthcare providers and patients, as it guides treatment decisions and prognosis. As research and technology continue to evolve, the role of troponin testing in diagnosing and managing cardiac conditions is likely to expand, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes.What is the normal range for troponin levels in the blood?
+The normal range for troponin levels can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific test used, but generally, levels below a certain threshold (often <0.04 ng/mL) are considered normal.
Can troponin levels be elevated due to conditions other than heart attacks?
+How soon after a heart attack do troponin levels become elevated?
+Troponin levels may not be immediately elevated after a heart attack. They typically start to rise within 2-3 hours after the onset of cardiac damage and can remain elevated for up to 14 days.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about the troponin test and its implications for cardiac health. Your feedback and queries can help us better understand the needs of our audience and provide more targeted information in the future. Whether you are a healthcare professional seeking to deepen your understanding of cardiac biomarkers or a patient looking for clear and concise information about your test results, we hope this article has been informative and helpful. Please feel free to comment or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
