Intro
Discover common side effects of TB tests, including skin reactions, fever, and fatigue. Learn about latent TB test side effects, TB blood test symptoms, and more, to understand the risks and benefits of tuberculosis testing and diagnosis.
The TB test, also known as the tuberculin skin test, is a widely used method for detecting tuberculosis (TB) infection. While the test is generally safe, there are some common side effects that individuals should be aware of. Understanding these side effects can help alleviate concerns and ensure that individuals are prepared for any potential reactions.
The TB test is a crucial tool in the diagnosis and prevention of TB, a bacterial infection that can be serious if left untreated. The test involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin, usually on the forearm. The injection site is then observed for any reactions, such as redness, swelling, or induration (hardening of the skin). The presence and severity of these reactions can indicate whether an individual has been infected with TB.
It is essential to note that the TB test is not a vaccination, and it does not provide immunity against TB. Instead, it is a diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of TB infection. The test is commonly used in high-risk populations, such as healthcare workers, individuals with compromised immune systems, and those who have been in close contact with someone with TB.
Introduction to TB Test Side Effects
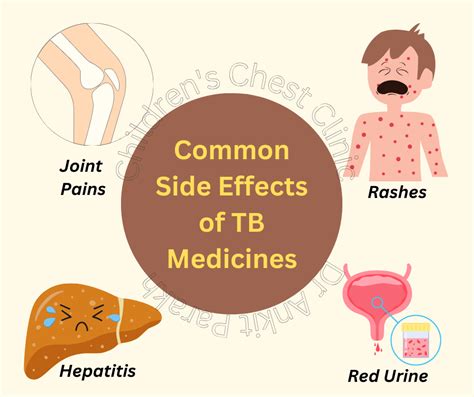
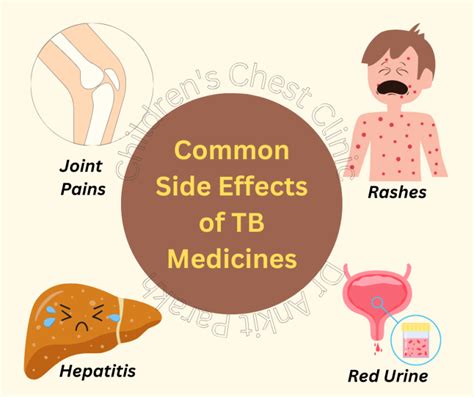
The TB test can cause some side effects, which are usually mild and temporary. These side effects can vary in severity and may include redness, swelling, itching, and pain at the injection site. In some cases, the reaction may be more severe, leading to blistering, ulceration, or scarring. It is crucial to report any unusual or severe reactions to a healthcare professional, as they may indicate an underlying condition or an adverse reaction to the test.
Common Side Effects of the TB Test
The most common side effects of the TB test include: * Redness and swelling at the injection site * Itching or burning sensation * Pain or tenderness * Induration (hardening of the skin) * Blistering or ulceration (in rare cases)These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days. However, if the reaction is severe or persists, it is essential to seek medical attention.
Understanding the TB Test Reaction
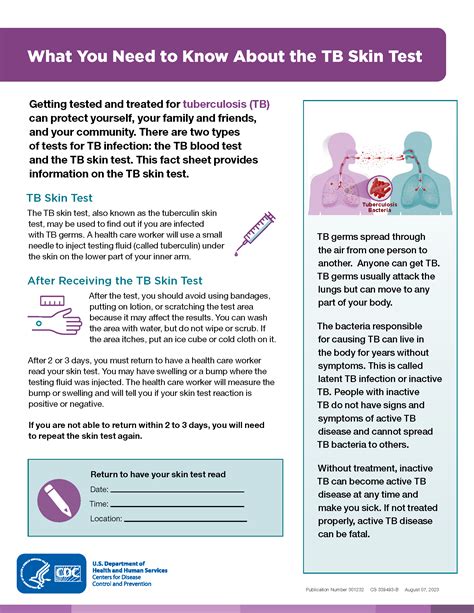
The TB test reaction is measured in millimeters, and the results are interpreted based on the size of the induration. A positive reaction typically indicates that an individual has been infected with TB, while a negative reaction suggests that they have not been infected. However, it is essential to note that a negative reaction does not necessarily rule out TB infection, as some individuals may not react to the test.
The TB test reaction can be influenced by various factors, including the individual's immune status, the presence of other medical conditions, and the use of certain medications. For example, individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, may not react to the test, even if they are infected with TB.
Factors that Influence the TB Test Reaction
The following factors can influence the TB test reaction: * Immune status * Presence of other medical conditions * Use of certain medications * Age and nutritional status * Presence of other infectionsUnderstanding these factors can help healthcare professionals interpret the results of the TB test and make informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.
Managing TB Test Side Effects
While the TB test side effects are usually mild and temporary, there are steps that individuals can take to manage them. These include:
- Applying a cold compress to the injection site to reduce swelling and itching
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to manage pain and discomfort
- Avoiding scratching or rubbing the injection site, as this can lead to further irritation and scarring
- Keeping the injection site clean and dry to prevent infection
It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional and to report any unusual or severe reactions to the test.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience any of the following: * Severe pain or swelling at the injection site * Blistering or ulceration * Scarring or permanent damage to the skin * Fever or chills * Difficulty breathing or swallowingPrompt medical attention can help prevent complications and ensure that any adverse reactions are managed effectively.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The TB test is a crucial tool in the diagnosis and prevention of TB. While the test can cause some side effects, these are usually mild and temporary. By understanding the common side effects of the TB test and taking steps to manage them, individuals can ensure that they are prepared for any potential reactions.
If you have any concerns about the TB test or have experienced any unusual or severe reactions, it is essential to discuss these with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance and support to help you navigate the testing process and ensure that you receive the necessary care and treatment.
Final Thoughts
The TB test is an essential tool in the fight against TB. By understanding the test and its potential side effects, individuals can take an active role in their health and well-being. Remember to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional and to report any unusual or severe reactions to the test.What is the TB test used for?
+The TB test is used to detect tuberculosis (TB) infection. It is a diagnostic tool that involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin and observing the reaction.
What are the common side effects of the TB test?
+The common side effects of the TB test include redness, swelling, itching, and pain at the injection site. In some cases, the reaction may be more severe, leading to blistering, ulceration, or scarring.
How is the TB test reaction measured?
+The TB test reaction is measured in millimeters, and the results are interpreted based on the size of the induration. A positive reaction typically indicates that an individual has been infected with TB, while a negative reaction suggests that they have not been infected.
What factors can influence the TB test reaction?
+Factors that can influence the TB test reaction include immune status, presence of other medical conditions, use of certain medications, age, and nutritional status. Understanding these factors can help healthcare professionals interpret the results of the TB test and make informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.
When should I seek medical attention after a TB test?
+Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience any unusual or severe reactions to the TB test, such as severe pain or swelling, blistering or ulceration, scarring or permanent damage to the skin, fever or chills, or difficulty breathing or swallowing.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the TB test and its potential side effects. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Share this article with others to help raise awareness about the importance of TB testing and diagnosis.
