Intro
Unlock thyroid health with 5 crucial blood tests, including TSH, Free T4, and Thyroid Antibodies, to diagnose hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and Hashimotos, and understand thyroid function, hormone levels, and autoimmune disorders.
Thyroid blood tests are a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing the health of the thyroid gland, which plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. The thyroid gland produces hormones that influence almost every organ in the body, and any abnormalities in thyroid function can have significant consequences on overall health. Therefore, understanding the different types of thyroid blood tests and their significance is essential for individuals who suspect they may have thyroid-related issues or for those who have been diagnosed with thyroid disorders.
The importance of thyroid blood tests lies in their ability to detect thyroid dysfunction, which can manifest in various forms, including hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), and thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland). These conditions can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can impact the quality of life significantly. By conducting thyroid blood tests, healthcare providers can determine the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood, identify potential issues, and develop appropriate treatment plans to manage thyroid-related conditions effectively.
Thyroid blood tests are also crucial for monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for thyroid disorders. For individuals with hypothyroidism, for example, regular blood tests can help healthcare providers adjust the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement medication to ensure that the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood remain within a healthy range. Similarly, for those with hyperthyroidism, blood tests can help monitor the levels of thyroid hormones and adjust treatment plans accordingly. In addition to diagnostic and monitoring purposes, thyroid blood tests can also help identify potential complications associated with thyroid disorders, such as thyroid storm or myxedema coma, which require immediate medical attention.
Types of Thyroid Blood Tests

There are several types of thyroid blood tests, each measuring different aspects of thyroid function. The most common thyroid blood tests include:
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) test: Measures the level of TSH in the blood, which helps regulate the production of thyroid hormones.
- Free T4 (FT4) test: Measures the level of FT4 in the blood, which is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
- Free T3 (FT3) test: Measures the level of FT3 in the blood, which is another hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid Antibody Tests: Measures the level of antibodies in the blood that are associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves' disease.
- Reverse T3 (RT3) test: Measures the level of RT3 in the blood, which is an inactive form of T3 that can help diagnose certain thyroid conditions.
Understanding TSH Test Results
The TSH test is one of the most commonly used thyroid blood tests, and it measures the level of TSH in the blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. The normal range for TSH levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but generally, a TSH level between 0.4 and 4.5 mU/L is considered normal. A high TSH level may indicate hypothyroidism, while a low TSH level may indicate hyperthyroidism.Interpreting Thyroid Blood Test Results
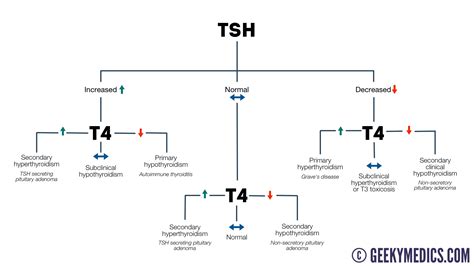
Interpreting thyroid blood test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the different tests and their significance. Healthcare providers consider the results of multiple tests to diagnose and manage thyroid-related conditions. For example, a high TSH level may indicate hypothyroidism, but a low FT4 level can confirm the diagnosis. On the other hand, a low TSH level may indicate hyperthyroidism, but a high FT3 level can confirm the diagnosis.
In addition to considering the results of individual tests, healthcare providers also consider the patient's symptoms, medical history, and physical examination findings. This comprehensive approach helps healthcare providers develop accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans for thyroid-related conditions.
Thyroid Blood Tests for Hypothyroidism
For individuals with hypothyroidism, thyroid blood tests are crucial for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. The goal of treatment is to restore normal levels of thyroid hormones in the blood, and regular blood tests can help healthcare providers adjust the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement medication accordingly. The most common thyroid blood tests for hypothyroidism include: * TSH test: Measures the level of TSH in the blood to determine if the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement medication needs to be adjusted. * FT4 test: Measures the level of FT4 in the blood to determine if the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement medication needs to be adjusted. * FT3 test: Measures the level of FT3 in the blood to determine if the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement medication needs to be adjusted.Thyroid Blood Tests for Hyperthyroidism

For individuals with hyperthyroidism, thyroid blood tests are crucial for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. The goal of treatment is to reduce the production of thyroid hormones, and regular blood tests can help healthcare providers adjust the treatment plan accordingly. The most common thyroid blood tests for hyperthyroidism include:
- TSH test: Measures the level of TSH in the blood to determine if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted.
- FT4 test: Measures the level of FT4 in the blood to determine if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted.
- FT3 test: Measures the level of FT3 in the blood to determine if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted.
- Thyroid antibody tests: Measures the level of antibodies in the blood that are associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Graves' disease.
Thyroid Blood Tests for Thyroiditis
For individuals with thyroiditis, thyroid blood tests are crucial for monitoring the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The goal of treatment is to reduce the inflammation and restore normal thyroid function, and regular blood tests can help healthcare providers adjust the treatment plan accordingly. The most common thyroid blood tests for thyroiditis include: * TSH test: Measures the level of TSH in the blood to determine if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted. * FT4 test: Measures the level of FT4 in the blood to determine if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted. * FT3 test: Measures the level of FT3 in the blood to determine if the treatment plan needs to be adjusted. * Thyroid antibody tests: Measures the level of antibodies in the blood that are associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis.Preparation for Thyroid Blood Tests
To prepare for thyroid blood tests, individuals should follow these steps:
- Avoid eating or drinking anything that may interfere with the test results, such as foods or supplements that contain iodine.
- Inform the healthcare provider about any medications or supplements being taken, as they may interfere with the test results.
- Avoid taking any medications or supplements that may interfere with the test results, such as biotin or vitamin B12 supplements.
- Get plenty of rest and avoid strenuous activities before the test, as they may affect the test results.
Risks and Side Effects of Thyroid Blood Tests
Thyroid blood tests are generally safe and do not have any significant risks or side effects. However, some individuals may experience: * Pain or bruising at the injection site * Dizziness or lightheadedness * Nausea or vomiting * Allergic reactions to the needle or other materials used in the testConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, thyroid blood tests are a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing the health of the thyroid gland. By understanding the different types of thyroid blood tests and their significance, individuals can take an active role in managing their thyroid health. If you suspect you may have a thyroid-related condition or have been diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best course of action. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can manage their thyroid health effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with thyroid blood tests in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
What are the different types of thyroid blood tests?
+The different types of thyroid blood tests include TSH test, FT4 test, FT3 test, thyroid antibody tests, and reverse T3 test.
What is the normal range for TSH levels?
+The normal range for TSH levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, but generally, a TSH level between 0.4 and 4.5 mU/L is considered normal.
How often should I get thyroid blood tests?
+The frequency of thyroid blood tests depends on the individual's condition and the healthcare provider's recommendations. Generally, individuals with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism may need to get blood tests every 3-6 months to monitor their condition.
