Intro
Tizanidine is used for muscle relaxation, treating muscle spasms, and relieving tension. Its a muscle relaxant, also known as Zanaflex, helping with spasticity and stiffness, often prescribed for conditions like multiple sclerosis and spinal injuries, providing relief and comfort.
Muscle relaxation is a crucial aspect of managing various medical conditions, including muscle spasms, anxiety, and sleep disorders. One medication that has gained popularity for its muscle relaxation properties is tizanidine. Tizanidine is a centrally acting muscle relaxant that is used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and stroke. In this article, we will delve into the world of tizanidine, exploring its uses, benefits, and potential side effects.
The importance of muscle relaxation cannot be overstated. When muscles are relaxed, they are less prone to spasms, cramps, and strains. This can lead to improved mobility, reduced pain, and enhanced overall well-being. Tizanidine works by blocking the nerve impulses that cause muscles to contract, resulting in a state of relaxation. This makes it an effective treatment for conditions that involve muscle spasms, such as multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injuries.
Tizanidine has also been used to treat other conditions, including anxiety and insomnia. Its muscle relaxation properties can help reduce anxiety and promote a good night's sleep. Additionally, tizanidine has been used to treat conditions such as fibromyalgia and temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). The medication's ability to relax muscles and reduce pain makes it a popular choice for managing these conditions.
Tizanidine Mechanism of Action
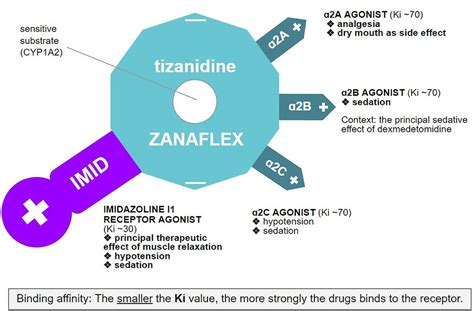
Tizanidine Benefits

Some of the other benefits of tizanidine include:
- Reduced muscle pain and stiffness
- Improved range of motion and mobility
- Enhanced overall well-being and quality of life
- Ability to manage conditions such as fibromyalgia and TMJ
- Can be used in combination with other medications to enhance its effects
Tizanidine Side Effects

In rare cases, tizanidine can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Hallucinations and psychosis
- Seizures and convulsions
- Abnormal heart rhythms and cardiac arrest
- Liver damage and hepatitis
Tizanidine Dosage and Administration

It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure the medication's effectiveness. Tizanidine can be taken with or without food, but it is recommended to take it with food to reduce the risk of nausea and vomiting.
Tizanidine Interactions
It is crucial to inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, to minimize the risk of interactions and ensure safe treatment.
Tizanidine Precautions and Warnings

Additionally, tizanidine can cause liver damage and hepatitis, especially in individuals with pre-existing liver conditions. Regular liver function tests are recommended to monitor for any potential liver damage.
Tizanidine is also not recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions, including:
- Hypotension and orthostatic hypotension
- Renal impairment and kidney disease
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Tizanidine and Pregnancy
Tizanidine is classified as a category C medication, which means that it may harm the fetus if taken during pregnancy. It is essential to inform your doctor if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant while taking tizanidine.Tizanidine and Breastfeeding
Tizanidine can pass into breast milk, and it is not recommended for breastfeeding mothers. The medication can cause drowsiness and other side effects in infants, and it is essential to consult your doctor before taking tizanidine while breastfeeding.What is tizanidine used for?
+Tizanidine is a centrally acting muscle relaxant used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and stroke.
How does tizanidine work?
+Tizanidine works by binding to alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking the release of excitatory neurotransmitters that stimulate muscle contractions.
What are the common side effects of tizanidine?
+Common side effects of tizanidine include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache, and dry mouth.
Can tizanidine be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Tizanidine is not recommended for individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding, as it can harm the fetus or cause side effects in infants.
How should tizanidine be taken?
+Tizanidine should be taken orally, 2-3 times a day, with or without food, as directed by your doctor.
In conclusion, tizanidine is a valuable medication for managing muscle spasms and relaxation. Its benefits, including reduced muscle pain and stiffness, improved mobility, and enhanced overall well-being, make it a popular choice for individuals with conditions such as multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injuries. However, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects, interactions, and precautions associated with tizanidine to ensure safe and effective treatment. If you have any questions or concerns about tizanidine, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
