Intro
Discover Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) explained, a life-saving intravenous nutrition therapy for patients with gut failure, malabsorption, or high metabolic needs, covering TPN benefits, risks, and management, including central lines, nutritional support, and parenteral nutrition solutions.
Total Parenteral Nutrition, commonly referred to as TPN, is a method of providing essential nutrients to the body through intravenous (IV) administration. This approach is utilized when an individual's digestive system is unable to adequately absorb nutrients from food, often due to various medical conditions or surgical interventions. The importance of TPN lies in its ability to support the body's nutritional needs, ensuring proper functioning, recovery, and overall health.
In certain situations, the digestive system may not be functioning correctly, making it challenging for the body to obtain the necessary nutrients for optimal health. This can occur due to a range of factors, including severe gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, and its treatment, or following significant surgeries that affect the digestive tract. In such cases, TPN serves as a vital lifeline, providing the body with the necessary building blocks for energy, growth, and repair.
The application of TPN is not limited to specific patient groups; it can be used in various clinical settings, including intensive care units, hospitals, and even at home for patients requiring long-term nutritional support. The versatility and effectiveness of TPN have made it an indispensable tool in modern healthcare, allowing medical professionals to tailor nutritional support to the unique needs of each patient. This personalized approach to nutrition is crucial for promoting healing, preventing malnutrition, and improving patient outcomes.
Introduction to Total Parenteral Nutrition

Total Parenteral Nutrition involves the delivery of a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals directly into the bloodstream through a large vein. This method bypasses the digestive system entirely, ensuring that the body receives the nutrients it needs without relying on the normal process of eating and digestion. The composition of TPN is carefully formulated to meet the individual's nutritional requirements, taking into account factors such as age, weight, medical condition, and activity level.
Components of TPN
The formulation of TPN typically includes: - Carbohydrates: Provided as dextrose, which serves as a primary source of energy. - Proteins: Supplied as amino acids, essential for building and repairing tissues. - Fats: Administered as lipid emulsions, crucial for energy and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. - Vitamins and Minerals: Added to ensure the patient receives all necessary micronutrients. - Electrolytes: Included to maintain proper fluid balance and support various bodily functions.Benefits of TPN
The benefits of Total Parenteral Nutrition are multifaceted, addressing both the immediate and long-term nutritional needs of patients. Some of the key advantages include:
- Nutritional Support: Ensures patients receive adequate nutrition, even when they cannot eat or digest food normally.
- Customization: Can be tailored to meet the specific nutritional requirements of each patient.
- Rapid Delivery: Nutrients are delivered directly into the bloodstream, allowing for rapid utilization by the body.
- Supports Healing: Provides the necessary building blocks for recovery from illness, surgery, or injury.
- Improves Outcomes: By preventing malnutrition, TPN can lead to better patient outcomes, including faster recovery times and reduced complications.
Indications for TPN
Total Parenteral Nutrition is indicated in a variety of clinical scenarios, including: - Severe gastrointestinal disorders that prevent normal feeding, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. - Cancer and its treatment, which can lead to malnutrition due to poor appetite, nausea, or impaired nutrient absorption. - Post-surgical patients who have undergone significant gastrointestinal surgery and cannot eat normally for an extended period. - Critically ill patients in intensive care units who require nutritional support to aid in recovery.Administration and Monitoring of TPN

The administration of TPN requires careful consideration and monitoring to ensure patient safety and effectiveness. This includes:
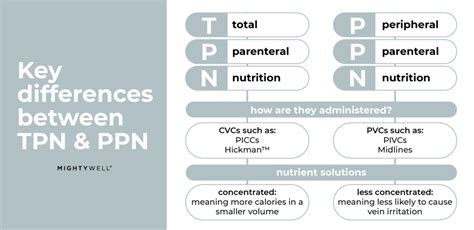
- Insertion of a Central Venous Catheter: A large vein, typically in the neck or chest, is used for TPN administration due to the high concentration of the solution.
- Formulation and Preparation: The TPN solution is customized based on the patient's nutritional needs and is prepared in a sterile environment to minimize the risk of infection.
- Infusion Rate: The rate at which TPN is administered is carefully controlled to prevent complications such as hyperglycemia or electrolyte imbalances.
- Regular Monitoring: Patients on TPN are closely monitored for signs of complications, including infection, metabolic disturbances, and catheter-related issues.
Potential Complications of TPN
While TPN is a lifesaving intervention for many patients, it is not without potential complications. These can include: - **Infections**: Related to the central venous catheter or the TPN solution itself. - **Metabolic Complications**: Such as hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, or electrolyte imbalances. - **Liver Dysfunction**: Prolonged use of TPN can lead to changes in liver function tests and, in some cases, more severe liver damage. - **Catheter-Related Complications**: Including thrombosis, catheter occlusion, or malposition.Home TPN and Long-Term Nutritional Support

For patients requiring long-term nutritional support, home TPN offers a viable option. This allows individuals to receive the necessary nutrients in the comfort of their own homes, improving quality of life and reducing the need for prolonged hospital stays. Home TPN requires comprehensive training for patients and their caregivers, focusing on the safe administration of TPN, monitoring for complications, and maintaining catheter integrity.
Quality of Life on TPN
Despite the complexities and potential complications associated with TPN, many patients adapt well to this form of nutritional support. With proper management and support, individuals on TPN can lead active lives, engage in their favorite activities, and maintain a positive outlook on their health and well-being.Future Directions in TPN

Research and advancements in the field of nutrition and gastroenterology continue to shape the practice of TPN. Future directions may include the development of new, more efficient formulations, improved methods for minimizing complications, and enhanced patient-centered care approaches. The integration of technology, such as smart infusion pumps and telehealth services, may also play a significant role in optimizing TPN therapy and patient outcomes.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Total Parenteral Nutrition is a powerful tool in the management of patients with complex nutritional needs. By understanding the principles, benefits, and potential complications of TPN, healthcare providers can offer personalized care that addresses the unique requirements of each individual. As medical science continues to evolve, the role of TPN in supporting patient health and recovery is likely to remain pivotal, underscoring the importance of ongoing research, education, and innovation in this field.What is Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)?
+Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) is a method of providing nutrients to the body through intravenous (IV) administration, bypassing the digestive system.
Who is a candidate for TPN?
+Candidates for TPN include individuals whose digestive system is not functioning properly due to illness, surgery, or other conditions, preventing them from absorbing nutrients from food.
What are the benefits of TPN?
+The benefits of TPN include providing essential nutrients when the digestive system cannot, supporting healing and recovery, and improving patient outcomes by preventing malnutrition.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions regarding Total Parenteral Nutrition in the comments below. Your engagement contributes to a richer understanding of this critical aspect of healthcare and can help others navigating similar challenges.
