Intro
Treat Mycoplasma Genitalium infection with effective antibiotics and therapies, addressing symptoms and complications like urethritis and cervicitis, to prevent STD transmission and promote sexual health.
Mycoplasma genitalium (MG) is a type of bacteria that can cause infections in the genital area. It is a relatively new discovery, first identified in the 1980s, and has since become a significant concern in the field of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). MG infections can affect both men and women, and if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of MG infections, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
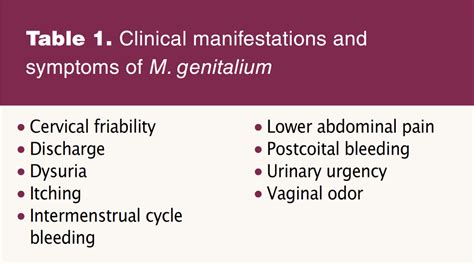
MG infections are often referred to as "silent" infections, as they can be asymptomatic, meaning that individuals may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can be similar to those of other STIs, making it challenging to diagnose MG infections based on symptoms alone. In men, MG infections can cause urethritis, which is an inflammation of the urethra, leading to symptoms such as burning during urination, discharge, and pain in the genital area. In women, MG infections can cause cervicitis, which is an inflammation of the cervix, leading to symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge, bleeding, and pain during intercourse.
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Causes
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Symptoms
- Abnormal vaginal discharge or bleeding
- Pain during urination or intercourse
- Burning or itching in the genital area
- Swollen or tender lymph nodes in the groin area
- Fever or chills
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Diagnosis
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests
- Culture tests
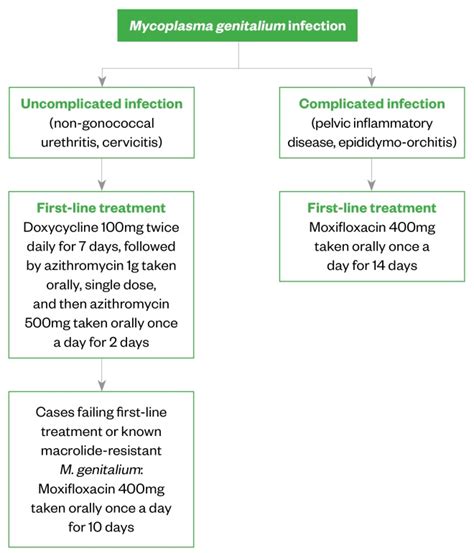
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Treatment
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Chronic pain
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Prevention
Preventing MG infections is crucial, as it can help reduce the risk of transmission and complications. Some ways to prevent MG infections include:- Practicing safe sex, such as using condoms or dental dams
- Getting tested regularly for STIs
- Avoiding sharing sex toys or other objects that come into contact with the genital area
- Avoiding sexual contact with someone who has an MG infection
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Complications
- PID
- Infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Chronic pain
- Increased risk of HIV transmission
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection in Men

- Urethritis
- Epididymitis
- Prostatitis
- Orchitis
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection in Women
- Cervicitis
- PID
- Infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Chronic pain
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Statistics
Some statistics on MG infections include:- MG infections affect approximately 1-2% of the general population
- MG infections are more common in young adults, with a peak age range of 20-30 years
- MG infections are more common in individuals with a history of STIs
- MG infections can increase the risk of HIV transmission by up to 20%
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Treatment Options
- Azithromycin
- Moxifloxacin
- Doxycycline
- Metronidazole
Mycoplasma Genitalium Infection Home Remedies
- Practicing good hygiene
- Using warm compresses to reduce pain and discomfort
- Taking over-the-counter pain medication
- Avoiding sexual contact until treatment is complete
What is Mycoplasma genitalium?
+Mycoplasma genitalium is a type of bacteria that can cause infections in the genital area.
How is Mycoplasma genitalium transmitted?
+Mycoplasma genitalium is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
What are the symptoms of Mycoplasma genitalium infection?
+Symptoms of Mycoplasma genitalium infection can include abnormal vaginal discharge or bleeding, pain during urination or intercourse, and burning or itching in the genital area.
How is Mycoplasma genitalium infection diagnosed?
+Mycoplasma genitalium infection is diagnosed through laboratory tests, such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests.
How is Mycoplasma genitalium infection treated?
+Mycoplasma genitalium infection is treated with antibiotics, such as azithromycin or moxifloxacin.
In conclusion, Mycoplasma genitalium infections are a significant concern in the field of sexually transmitted infections. It is essential to practice safe sex, get tested regularly, and seek medical attention if symptoms occur. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of MG infections, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their partners from this potentially serious infection. We encourage readers to share this article with others, comment below with any questions or concerns, and take action to prioritize their sexual health.
