Intro
Discover what a hematoma is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment. Learn about bruising, blood clots, and swelling related to hematomas, including subdural and epidural types, and understand the differences between hematomas and other bleeding disorders.
A hematoma is a collection of blood that has leaked out of blood vessels and accumulated in the surrounding tissue. This can occur as a result of injury, trauma, or certain medical conditions. Hematomas can be found in various parts of the body, including the skin, muscles, and organs. They can range in size from small and barely noticeable to large and severely debilitating.
The formation of a hematoma typically involves the rupture of blood vessels, which can be caused by a variety of factors such as accidents, falls, sports injuries, or surgical procedures. When blood vessels are damaged, they can leak blood into the surrounding tissue, leading to the accumulation of blood and the formation of a hematoma. In some cases, hematomas can also be caused by underlying medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or blood vessel diseases.
Hematomas can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility. In severe cases, they can lead to more serious complications, such as infection, nerve damage, or even organ failure. It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have a hematoma, as prompt treatment can help to prevent further complications and promote healing.
Types of Hematomas
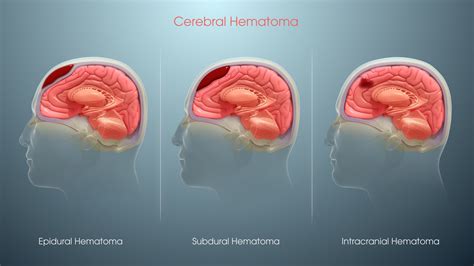
There are several types of hematomas, each with its own unique characteristics and causes. Some of the most common types of hematomas include:
- Subcutaneous hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs just beneath the skin and is often caused by minor injuries or trauma.
- Intramuscular hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs within the muscles and can be caused by more severe injuries or trauma.
- Epidural hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs in the space between the skull and the brain and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Subdural hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs in the space between the brain and the skull and can also be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Causes of Hematomas
Hematomas can be caused by a variety of factors, including:- Trauma or injury: This is one of the most common causes of hematomas, and can include accidents, falls, sports injuries, or surgical procedures.
- Bleeding disorders: Certain medical conditions, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease, can increase the risk of developing a hematoma.
- Blood vessel diseases: Conditions such as atherosclerosis or vasculitis can weaken blood vessels and increase the risk of hematoma formation.
- Infection: In some cases, hematomas can be caused by infection, such as abscesses or sepsis.
Symptoms of Hematomas

The symptoms of a hematoma can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain: Hematomas can cause significant pain, especially if they are large or located in a sensitive area.
- Swelling: Hematomas can cause swelling and bruising, which can be visible on the skin or hidden beneath the surface.
- Limited mobility: Hematomas can cause stiffness and limited mobility, especially if they are located in a joint or muscle.
- Numbness or tingling: In some cases, hematomas can cause numbness or tingling sensations, especially if they are located near nerves.
Diagnosis of Hematomas
Diagnosing a hematoma typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. Some common diagnostic tests include:- X-rays: These can help to identify any underlying bone fractures or injuries.
- CT scans: These can help to identify any internal injuries or bleeding.
- MRI scans: These can help to identify any soft tissue injuries or bleeding.
- Ultrasound: This can help to identify any bleeding or fluid accumulation in the body.
Treatment of Hematomas
The treatment of a hematoma depends on the location, size, and severity of the condition. Some common treatment options include:
- Rest and ice: Applying ice to the affected area and resting the injured limb can help to reduce pain and swelling.
- Compression: Applying compression bandages or wraps can help to reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Elevation: Elevating the affected limb above the level of the heart can help to reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Medication: Pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to drain the hematoma or repair any underlying damage.
Complications of Hematomas
If left untreated, hematomas can lead to a range of complications, including:- Infection: Hematomas can become infected, leading to abscesses or sepsis.
- Nerve damage: Hematomas can cause nerve damage, leading to numbness, tingling, or paralysis.
- Organ failure: In severe cases, hematomas can cause organ failure, especially if they are located in critical areas such as the brain or liver.
- Chronic pain: Hematomas can cause chronic pain, especially if they are large or located in sensitive areas.
Prevention of Hematomas

While it is not always possible to prevent hematomas, there are some steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing one. These include:
- Wearing protective gear: Wearing protective gear, such as helmets or pads, can help to reduce the risk of injury and hematoma formation.
- Avoiding trauma: Avoiding situations that could lead to trauma or injury, such as contact sports or high-risk activities, can help to reduce the risk of hematoma formation.
- Managing bleeding disorders: If you have a bleeding disorder, managing the condition through medication and lifestyle changes can help to reduce the risk of hematoma formation.
- Avoiding certain medications: Certain medications, such as anticoagulants, can increase the risk of hematoma formation. Avoiding these medications or using them with caution can help to reduce the risk.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, hematomas are a serious medical condition that can cause significant pain, swelling, and limited mobility. If you suspect that you have a hematoma, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further complications and promote healing. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hematomas, you can take the necessary steps to manage the condition and reduce the risk of future complications.What is a hematoma?
+A hematoma is a collection of blood that has leaked out of blood vessels and accumulated in the surrounding tissue.
What are the symptoms of a hematoma?
+The symptoms of a hematoma can include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility.
How are hematomas treated?
+The treatment of a hematoma depends on the location, size, and severity of the condition, and can include rest, ice, compression, elevation, medication, and surgery.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of hematomas, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may be interested. By working together, we can promote awareness and understanding of this important medical condition and help to reduce the risk of complications and improve treatment outcomes.
